Cell Definition
“A cell is the smallest, basic unit of life responsible for all life processes.”
What is a Cell?
A cell is the building block of all living beings. It can independently replicate and carry out life functions. Each cell contains a fluid called cytoplasm, enclosed by a membrane, and various cell structures known as organelles.
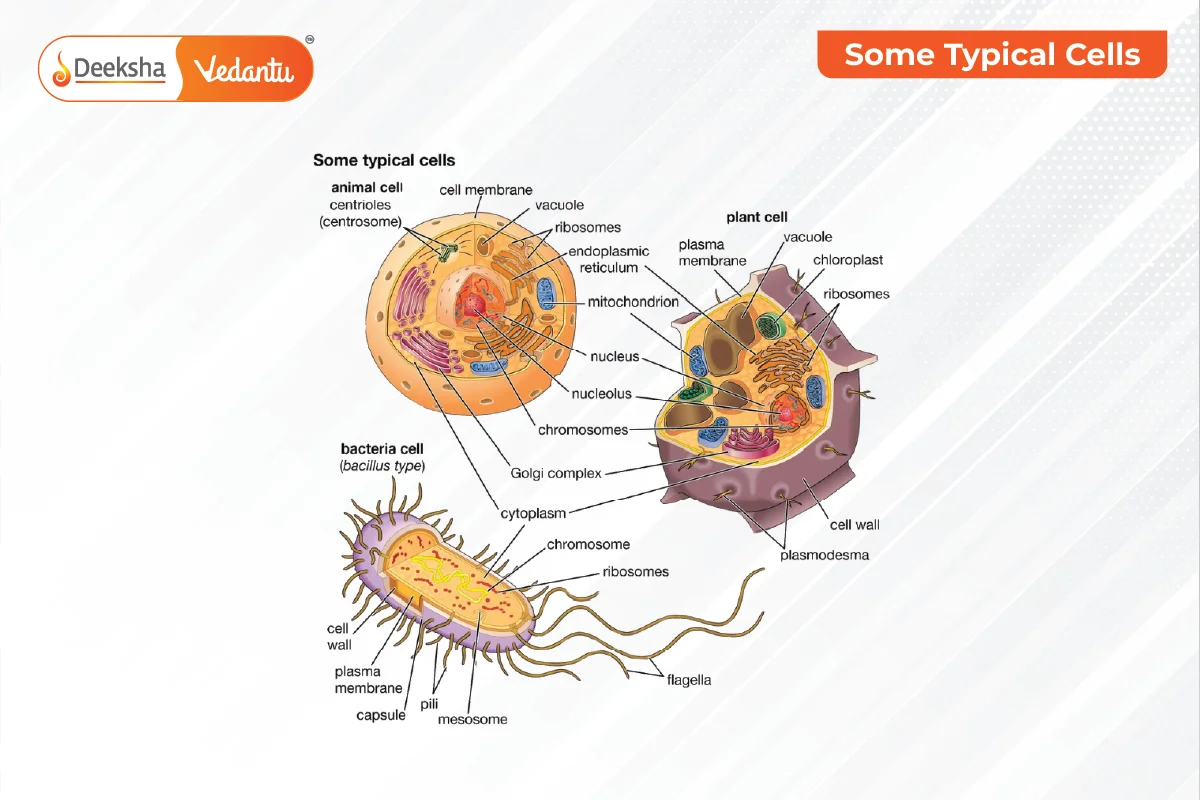
Characteristics of Cells
- Provide structure and support.
- Organized interior with membrane-bound organelles.
- Nucleus holds genetic information.
- Mitochondria produce energy.
- Lysosomes digest unwanted materials.
- Endoplasmic reticulum helps in organizing and processing molecules.
Types of Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells: No nucleus, single-celled (e.g., bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells: Have a nucleus, can be single-celled or multi-celled (e.g., plants, animals).
Cell Structure
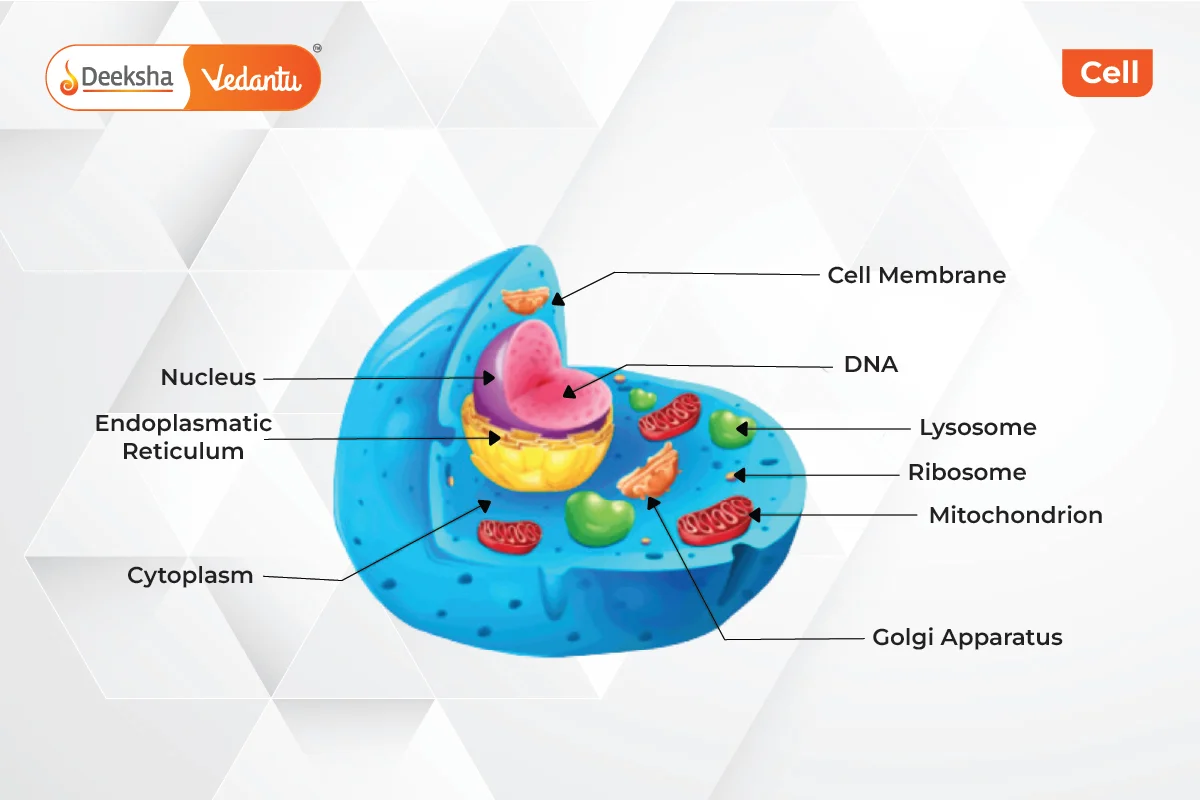
- Cell Membrane: Controls movement in and out of the cell, protects the cell.
- Cell Wall: Found in plant cells, provides structure and protection.
- Cytoplasm: Jelly-like substance inside the cell where organelles are suspended.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA, controls cell activities.
- Cell Organelles: Include structures like the nucleolus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, mitochondria, lysosomes, chloroplasts (in plants), and vacuoles.
Cell Theory
Proposed by Schwann, Schleiden, and Virchow:
- All living things are made of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Functions of a Cell
- Support and Structure: Cells form the body’s structure (e.g., skin, plant xylem).
- Growth (Mitosis): Cells divide to form new cells.
- Transport: Nutrients and waste move in and out of cells.
- Energy Production: Cells produce energy through photosynthesis (in plants) and respiration (in animals).
- Reproduction: Cells reproduce through mitosis (asexual) and meiosis (sexual).
FAQs
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they produce energy.
The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities.
Cells reproduce through mitosis (asexual reproduction) and meiosis (sexual reproduction).
Cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Cell organelles are specialized structures within a cell, each performing specific functions (e.g., mitochondria produce energy, lysosomes digest waste).
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell and provides protection.
There are two main types: Prokaryotic cells (without a nucleus) and Eukaryotic cells (with a nucleus).
A cell is the smallest unit of life, capable of performing all life processes independently.
Related Topics
- Greenhouse Effect
- Nutrition
- Modes Of Reproduction Used By Single Organisms
- Enzymes
- Ozone Layer and its Depletion
- Neurons
- Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction
- Heredity Traits
- Human Digestive System
- Ecosystem
- Global Warming
- Hormones In Animals
- Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
- Plant Cell
- Animals – Nervous System








Get Social