Introduction
Acids and bases exhibit several characteristic chemical properties that distinguish them from one another. These properties are key in understanding how they behave in different chemical reactions. In this section, we will explore how acids and bases react with various substances and why these reactions are important.
Reaction of Acids and Bases with Indicators
Indicators are special substances that change color when they come in contact with an acid or a base. They help us determine whether a solution is acidic or basic without tasting it. Common indicators include litmus paper, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, and natural indicators like turmeric.
- Litmus Paper:
- Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
- Bases turn red litmus paper blue.

- Phenolphthalein:
- Acids: Remains colorless.
- Bases: Turns pink.

- Methyl Orange:
- Acids: Turns red.
- Bases: Turns yellow
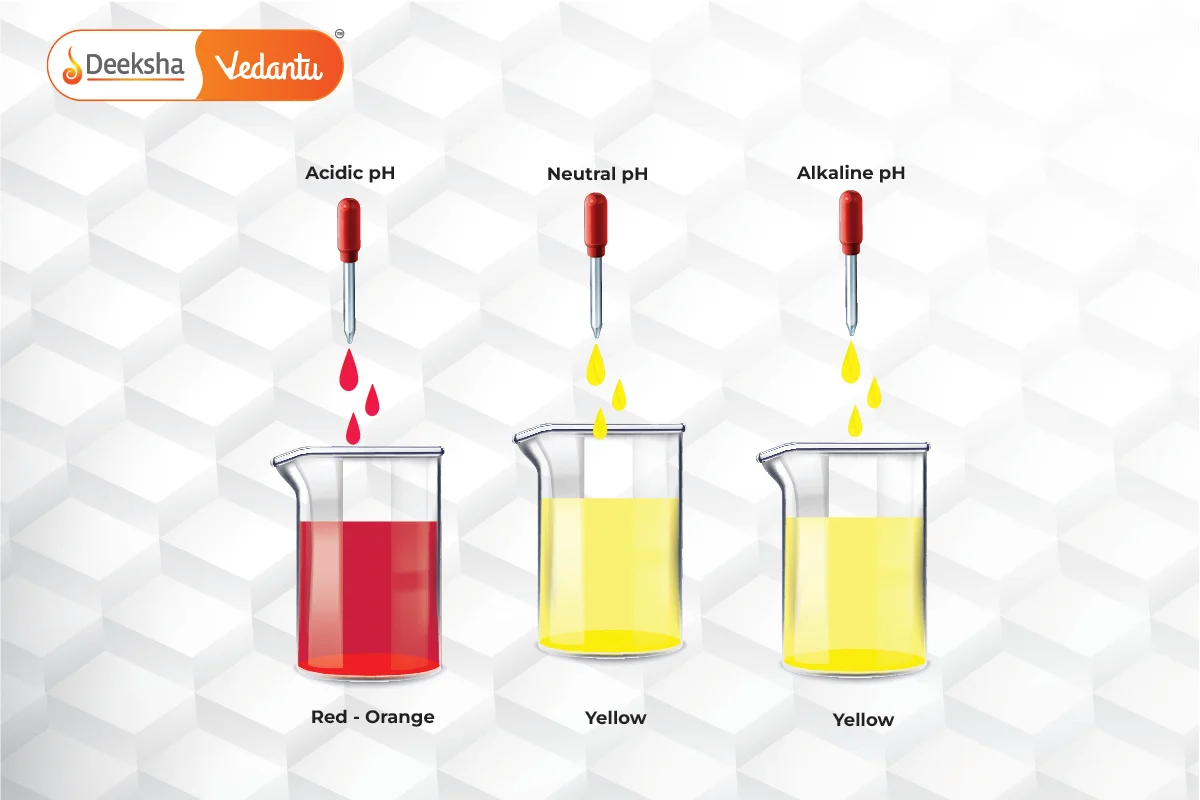

- Example: If you dip red litmus paper into vinegar (acetic acid), it stays red, confirming that vinegar is acidic. If you dip blue litmus paper into a soap solution (sodium hydroxide), it turns blue, indicating that the solution is basic.
Reaction of Acids and Bases with Metals
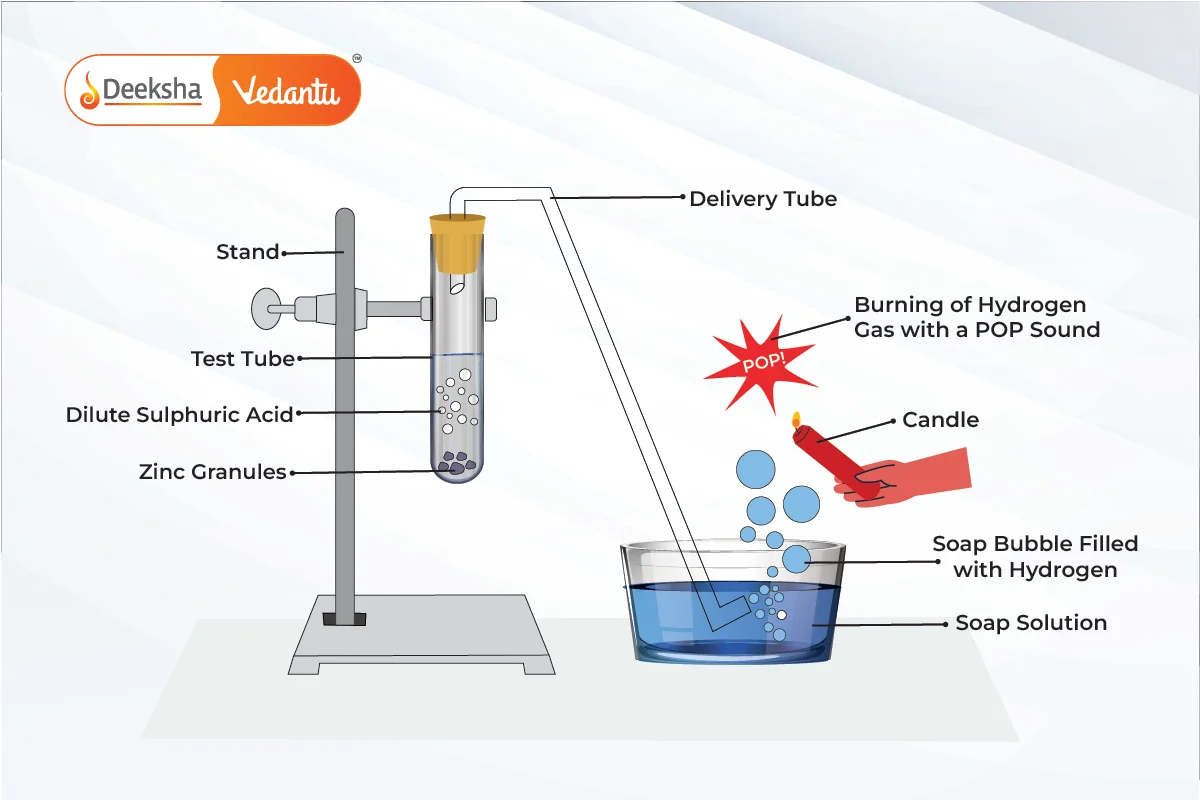
- Acids react with active metals such as zinc
, magnesium
, and iron
to produce salt and hydrogen gas. The general equation for this reaction is:
- Example: Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
- Test for Hydrogen Gas: When hydrogen gas is released, it can be tested by bringing a burning splint near it. If it burns with a ‘pop’ sound, it confirms the presence of hydrogen.
- Example: Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
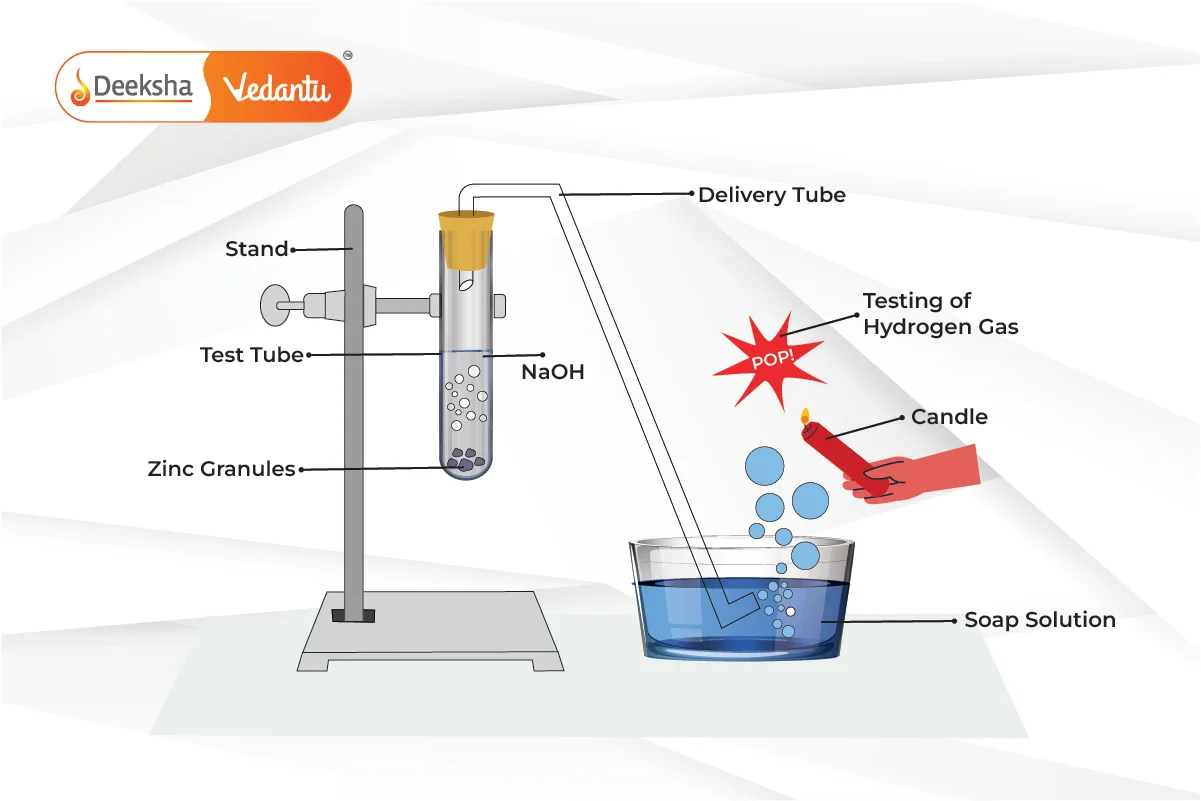
- Bases generally do not react with metals, except with amphoteric metals like zinc and aluminum. When bases react with these metals, they produce salt and hydrogen gas.
- Example: Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide
to form sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
.
- Example: Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide
Reaction of Acids with Metal Carbonates and Bicarbonates
Acids react with metal carbonates and bicarbonates to form salt, carbon dioxide , and water
. This is an important reaction in many natural and industrial processes, such as in baking and the formation of cave formations.
- General Equation:
- Example 1: When hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate
, it produces calcium chloride
, carbon dioxide
, and water.
- Example 2: Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) reacts with vinegar (acetic acid) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and sodium acetate.
- Test for Carbon Dioxide: When carbon dioxide is passed through limewater (a solution of calcium hydroxide), it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
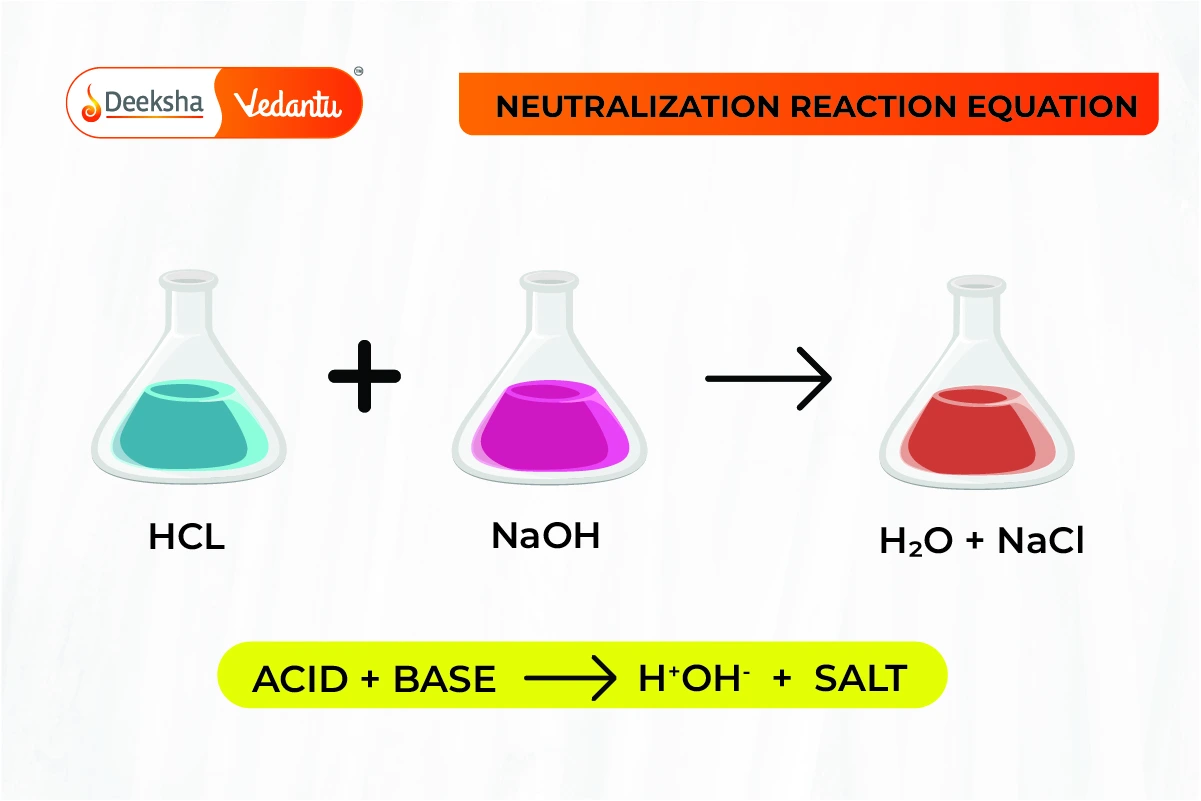
Neutralization Reaction (Reaction Between Acids and Bases)
A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water. In this reaction, the acidic properties of the acid and the basic properties of the base cancel each other out, resulting in a neutral solution.
- General Equation:
- Example: Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride (table salt) and water.
- Real-life Application:
- Antacids: When you suffer from indigestion, an antacid (a mild base like magnesium hydroxide) is used to neutralize the excess stomach acid
, relieving discomfort.
- Antacids: When you suffer from indigestion, an antacid (a mild base like magnesium hydroxide) is used to neutralize the excess stomach acid
Reaction of Metallic Oxides with Acids
Metallic oxides react with acids to form salt and water. Metallic oxides are basic in nature, which is why they react with acids in a neutralization reaction.
- General Equation:
- Example: Copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form copper chloride and water.

- Application: This reaction is commonly used in the extraction and purification of metals from their ores.
Reaction of Non-metallic Oxides with Bases
Non-metallic oxides react with bases to form salt and water. Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature, which is why they react with bases.
- General Equation:
- Example: Carbon dioxide
reacts with calcium hydroxide
to form calcium carbonate
and water.
Real-life Applications of Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
- Household Cleaners: Many cleaning products are basic in nature (like sodium hydroxide in drain cleaners) and are used to neutralize acidic substances.
- Agriculture: Farmers use lime (calcium hydroxide) to neutralize acidic soils, ensuring the soil is suitable for crop growth.
- Baking: The reaction between baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) releases carbon dioxide, which helps dough rise in baking.
Practice Questions with Answers
Q1. What happens when hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc? Write the balanced chemical equation.
- Answer: When hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are produced.
- Equation :
- Equation :
Q2. How can you distinguish between an acidic and basic solution using phenolphthalein?
- Answer: Phenolphthalein remains colorless in acidic solutions but turns pink in basic solutions.
Q3. What is the product when calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid?
- Answer: Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Equation :
- Equation :
Q4. What happens when copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid?
- Answer: Copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form copper chloride and water.
- Equation :
- Equation :
FAQs
Carbon dioxide turns limewater milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
Indicators change color in the presence of an acid or a base, helping to identify whether a solution is acidic or basic.
Acids donate hydrogen ions () in water. When they react with metals, the hydrogen ions are reduced to hydrogen gas.
A neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
Example:












Get Social