What is Isomerism?
Isomerism is the phenomenon where compounds with the same chemical formula have different chemical structures. These compounds, called isomers, exhibit different properties and arrangements of atoms despite having the same formula.
Types of Isomerism
Isomerism is primarily divided into two types: Structural Isomerism and Stereoisomerism. These types have further subcategories.
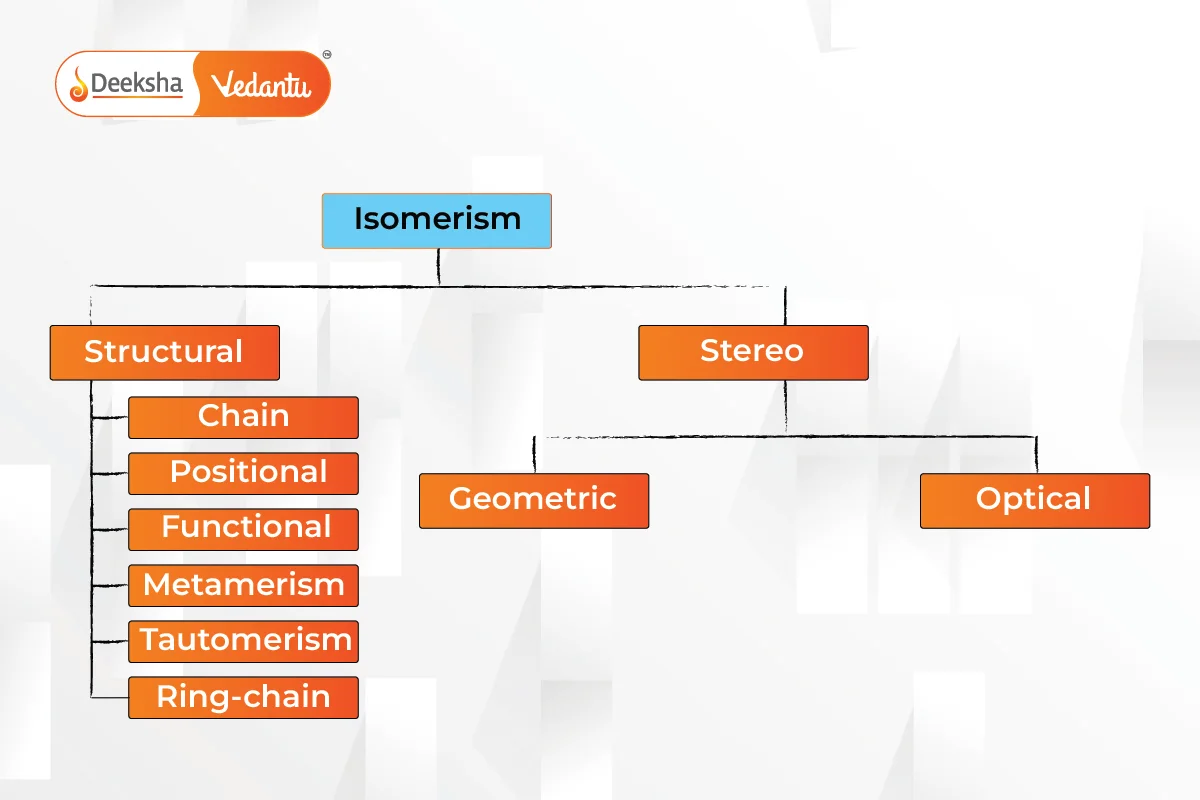
Structural Isomerism
Also known as constitutional isomerism, it occurs when atoms and functional groups are connected in different ways.
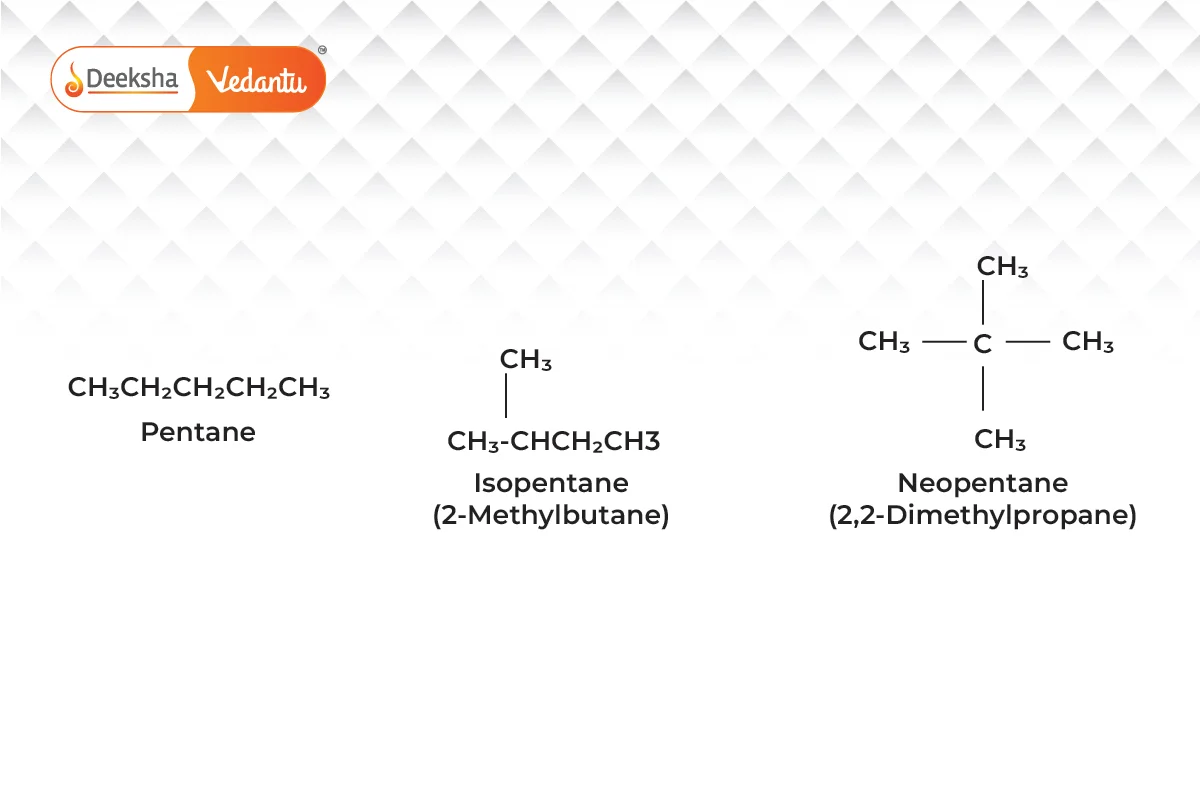
- Chain Isomerism
- Different branching of carbon chains.
- Example:
(pentane and its isomers).
- Position Isomerism
- Different positions of functional groups or substituents on the carbon chain.
- Example:
(1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane).

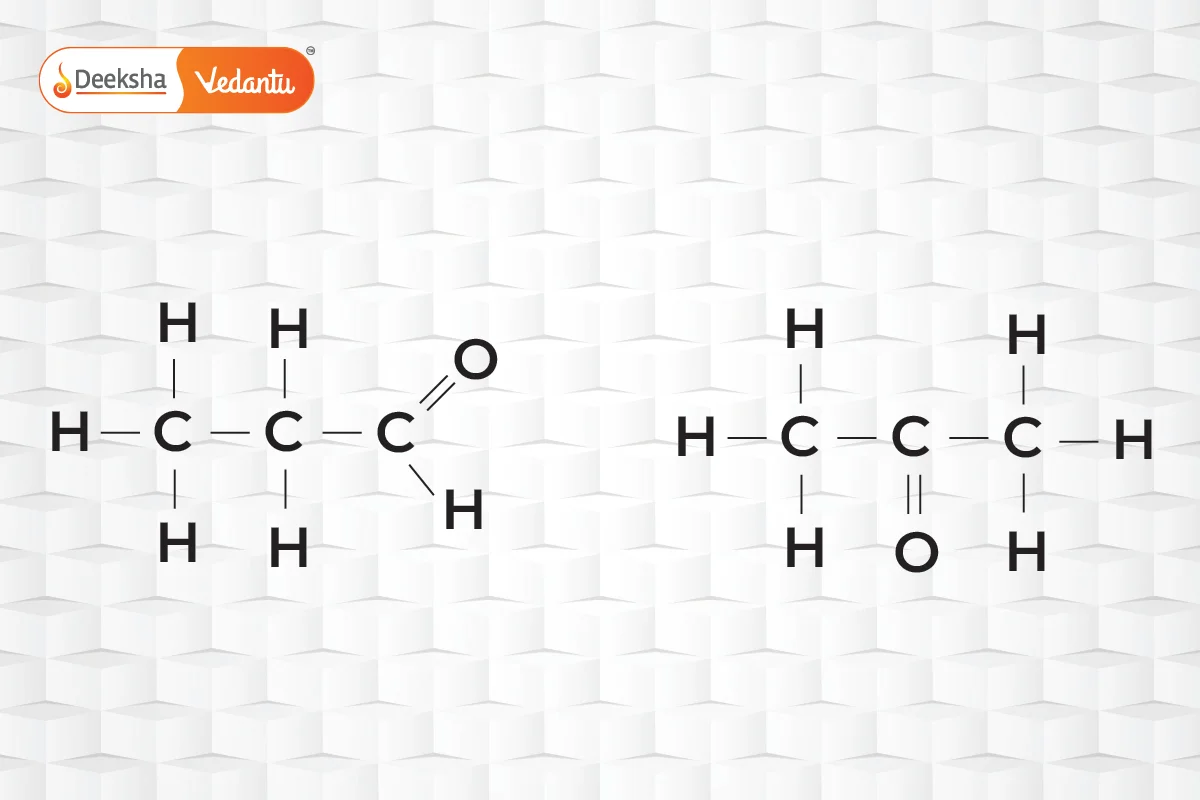
- Functional Isomerism
- Same chemical formula but different functional groups.
- Example:
(propanal and acetone).
- Metamerism
- Different alkyl chains on either side of a functional group, usually involving divalent atoms like oxygen or sulfur.
- Example:
(ethoxyethane and methoxypropane).
- Tautomerism
- Isomers that differ in the position of protons and electrons, existing in equilibrium.
- Example: Keto-enol tautomerism.
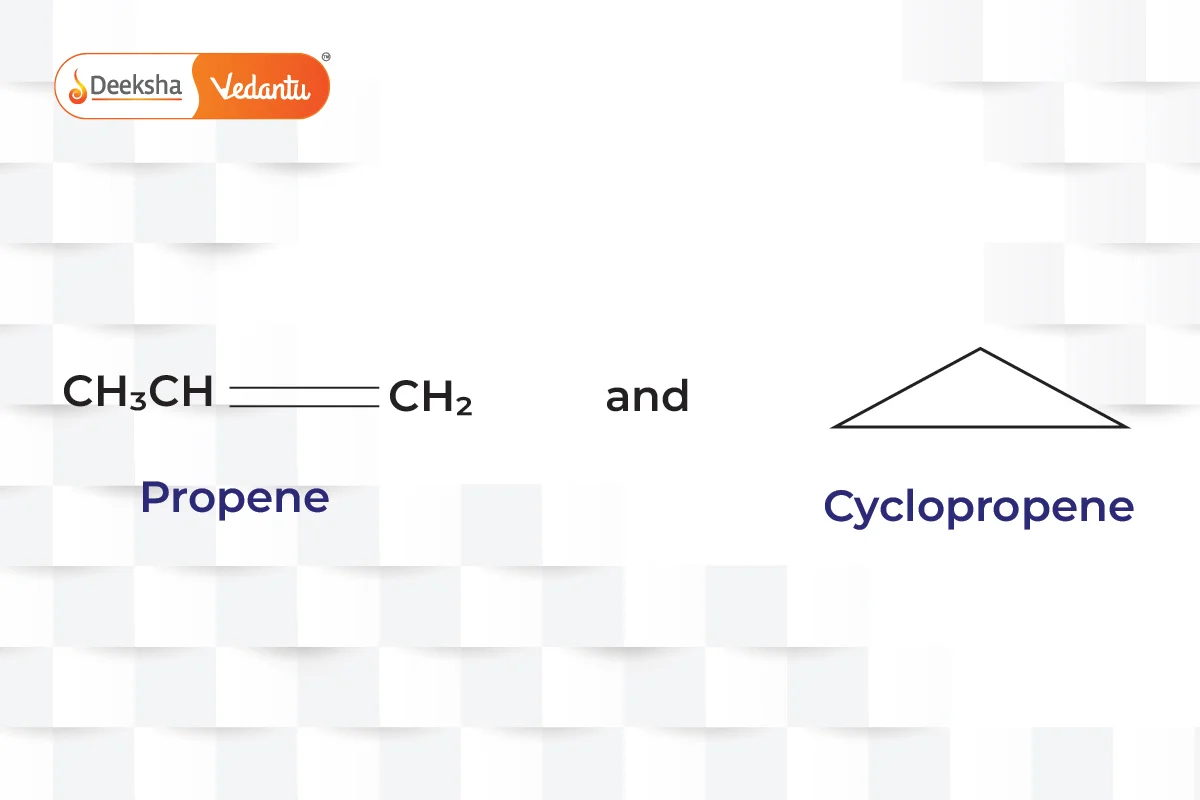
- Ring-Chain Isomerism
- One isomer has an open-chain structure, while the other has a ring structure.
- Example:
(propene and cyclopropane).
Stereoisomerism
Isomers have the same chemical formula but different spatial orientations of atoms.
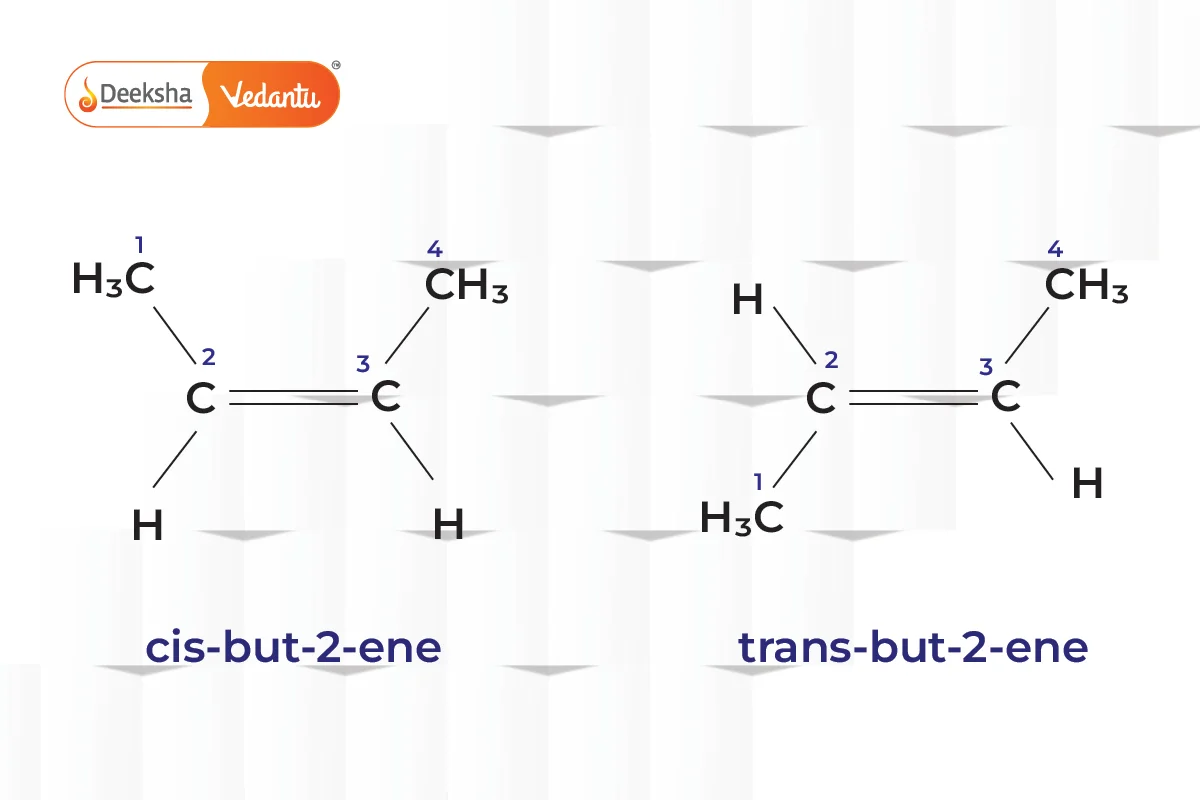
- Geometric Isomerism (Cis-Trans Isomerism)
- Different spatial arrangements of atoms.
- Example: But-2-ene (cis-but-2-ene and trans-but-2-ene).
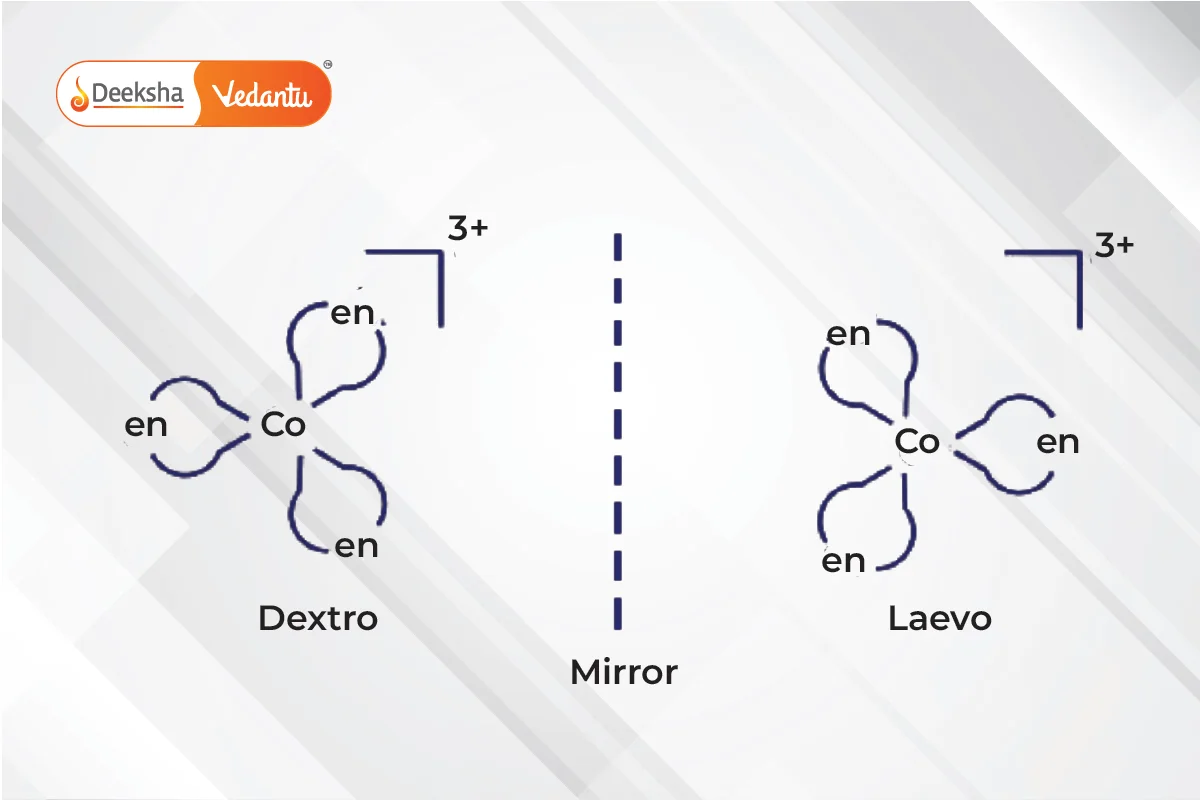
- Optical Isomerism
- Non-superimposable mirror images called enantiomers.
- Enantiomers differ in their optical activity:
- Dextro (right-rotating) enantiomers.
- Laevo (left-rotating) enantiomers.
- Ionization Isomerism
- Compounds give different ions in solution but have the same composition.
- Example:
and
Summary
Isomerism is a crucial concept in chemistry, explaining how compounds with the same formula can have different properties due to variations in their structure or spatial arrangement. Structural isomerism includes chain, position, functional, metamerism, tautomerism, and ring-chain isomerism, while stereoisomerism includes geometric, optical, and ionization isomerism.
FAQs
Ionization isomerism occurs when compounds give different ions in solution despite having the same composition.
Enantiomers are optical isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images, differing in their optical activity.
Stereoisomerism occurs when compounds have the same formula but different spatial arrangements of atoms.
Structural isomerism occurs when atoms and functional groups are connected differently.
The main types are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Isomerism is when compounds with the same chemical formula have different structures or arrangements of atoms.











Get Social