What is Chemical Formula?
A chemical formula is a symbolic representation of the composition of a chemical compound. It shows the types and numbers of atoms involved in a compound and provides essential information about the elements that make up the substance. In simpler terms, a chemical formula tells us which elements are present in a compound and in what proportion they combine.
Types of Chemical Formulas
There are several types of chemical formulas, each conveying different information:
- Empirical Formula:
- The empirical formula gives the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
- It does not provide information about the actual number of atoms, but it tells us the proportion of each type of atom.
- Example: The empirical formula of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is HO, indicating that hydrogen and oxygen are present in a 1:1 ratio.
- Molecular Formula:
- The molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
- It provides more detailed information than the empirical formula because it represents the true composition of the compound.
- Example: The molecular formula of water is H₂O, meaning each molecule contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Structural Formula:
- The structural formula shows the arrangement of atoms within a molecule and how they are bonded together.
- This formula is especially useful for understanding the geometry and connectivity of molecules.
- Example: The structural formula of methane (CH₄) shows that the carbon atom is at the center, bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
- Condensed Structural Formula:
- This is a simplified form of the structural formula that omits some details about bonds but still shows the relationships between atoms.
- Example: The condensed formula of ethanol is CH₃CH₂OH.
- Ionic Formula:
- The ionic formula represents ionic compounds, showing the ratio of positive and negative ions in the compound.
- Example: The formula of sodium chloride (NaCl) indicates that it is made up of sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻).
How to Write a Chemical Formula
Writing a chemical formula requires understanding the elements involved, their valency (combining capacity), and the way atoms combine to form compounds. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a chemical formula, along with examples to illustrate each step.
Step-by-Step Process for Writing a Chemical Formula
1. Identify the Elements Involved
The first step is to recognize which elements are present in the compound. Every element has a unique chemical symbol, which is usually derived from its Latin or English name.
- Example: In water (H₂O), the elements are hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O).
2. Determine the Valency of Each Element
Valency is the ability of an element to combine with other elements, determined by the number of electrons an atom can lose, gain, or share to complete its outer shell.
- Monovalent elements: Elements like hydrogen (H), sodium (Na), and chlorine (Cl) have a valency of 1.
- Divalent elements: Elements like oxygen (O), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg) have a valency of 2.
- Trivalent elements: Elements like aluminum (Al) and nitrogen (N) have a valency of 3.
The valency helps determine how atoms bond with each other to form compounds.
- Example: Hydrogen has a valency of 1, and oxygen has a valency of 2. Thus, two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom to form water (H₂O).
3. Balance the Valency to Ensure the Compound is Neutral
For compounds to be neutral, the total positive charge from the metal or cation must balance the total negative charge from the non-metal or anion. Use the cross-multiplication method to balance the valencies of the elements.
- Example 1 (Ionic Compound): For sodium chloride (NaCl):
- Sodium (Na) has a valency of 1, and chlorine (Cl) has a valency of 1. Since the valencies are equal, the formula is written as NaCl.
- Example 2 (Ionic Compound): For magnesium chloride (MgCl₂):
- Magnesium (Mg) has a valency of 2, and chlorine (Cl) has a valency of 1. To balance, we need two chlorine atoms for every magnesium atom, so the formula is MgCl₂.
- Example 3 (Covalent Compound): For methane (CH₄):
- Carbon (C) has a valency of 4, and hydrogen (H) has a valency of 1. To balance the formula, one carbon atom bonds with four hydrogen atoms, giving us CH₄.
4. Write the Chemical Symbols
Write the chemical symbols for the elements involved. For ionic compounds, write the cation (positive ion) first and then the anion (negative ion).
- Example: For sodium chloride, the chemical symbols are Na (for sodium) and Cl (for chlorine), giving the formula NaCl.
5. Use Subscripts to Indicate the Number of Atoms
The number of atoms of each element is written as a subscript after the symbol. If only one atom of an element is present, no subscript is needed.
- Example: In carbon dioxide (CO₂), the subscript “2” indicates that there are two oxygen atoms bonded to one carbon atom. No subscript is written for carbon because there is only one carbon atom in the molecule.
6. Write Parentheses for Polyatomic Ions (if needed)
When dealing with polyatomic ions (groups of atoms that carry a charge and act as a unit), use parentheses to group the ion when there is more than one in the formula.
- Example: In calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂), the hydroxide ion (OH⁻) is a polyatomic ion. Since there are two hydroxide ions for every calcium ion, parentheses are used around OH, followed by the subscript “2”.
Examples of Writing Chemical Formulas
1. Water (H₂O)
- Elements: Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O).
- Valency: Hydrogen has a valency of 1, and oxygen has a valency of 2.
- Formula: H₂O, because two hydrogen atoms bond with one oxygen atom to form water.
2. Ammonium Sulfate ((NH₄)₂SO₄)
- Elements: Nitrogen (N), Hydrogen (H), Sulfur (S), and Oxygen (O).
- Valency:
- Ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) has a valency of 1.
- Sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻) has a valency of 2.
- Formula: Since two ammonium ions are needed to balance one sulfate ion, the formula is written as (NH₄)₂SO₄.
3. Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃)
- Elements: Calcium (Ca), Carbon (C), and Oxygen (O).
- Valency:
- Calcium has a valency of 2.
- The carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻) has a valency of 2.
- Formula: CaCO₃, because the valencies are equal and no subscripts are needed.
4. Aluminum Sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃)
- Elements: Aluminum (Al), Sulfur (S), and Oxygen (O).
- Valency:
- Aluminum has a valency of 3.
- Sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻) has a valency of 2.
- Formula: To balance, two aluminum ions combine with three sulfate ions, giving the formula Al₂(SO₄)₃.
Tips for Writing Chemical Formulas
- Use the Criss-Cross Method for Ionic Compounds:
- Cross-multiply the valencies of the cation and anion to balance the charges.
- Example: For aluminum chloride (Al³⁺ and Cl⁻), cross-multiply the valencies to get AlCl₃.
- Check the Overall Charge:
- Ensure that the total positive and negative charges balance out to make the compound neutral.
- Polyatomic Ions:
- Memorize common polyatomic ions like hydroxide (OH⁻), sulfate (SO₄²⁻), nitrate (NO₃⁻), etc., and use parentheses if more than one polyatomic ion is needed.
- Naming Conventions:
- For covalent compounds, prefixes like mono-, di-, tri- may be used to indicate the number of atoms. For example, CO₂ is called carbon dioxide because it has two oxygen atoms.
Importance of Chemical Formulas
Chemical formulas are crucial for understanding the composition and properties of compounds. They provide the following key information:
- Composition: Chemical formulas tell us the exact composition of a compound in terms of the elements involved and the ratio of atoms or ions.
- Molecular Structure: For covalent compounds, chemical formulas (especially structural formulas) help us visualize the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
- Chemical Reactions: Chemical formulas are used in chemical equations to represent reactants and products in a reaction.
- Stoichiometry: Formulas are essential in calculating the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction, as they provide the mole ratios needed for stoichiometric calculations.
- Properties of Compounds: Knowing the formula of a compound helps predict its physical and chemical properties, such as solubility, reactivity, and bonding.
Examples of Chemical Formulas
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
- Elements involved: Carbon (C) and Oxygen (O).
- Formula: CO₂.
- Interpretation: One carbon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆):
- Elements involved: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O).
- Formula: C₆H₁₂O₆.
- Interpretation: Six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms form one molecule of glucose.
- Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄):
- Elements involved: Hydrogen (H), Sulfur (S), and Oxygen (O).
- Formula: H₂SO₄.
- Interpretation: Two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms form one molecule of sulfuric acid.
- Ammonia (NH₃):
- Elements involved: Nitrogen (N) and Hydrogen (H).
- Formula: NH₃.
- Interpretation: One nitrogen atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
Chemical Formulas and the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a crucial tool for writing chemical formulas. The position of an element in the periodic table provides information about its valency, or the number of electrons it can lose, gain, or share in chemical bonding. For example:
- Group 1 elements (like sodium, Na) form +1 ions.
- Group 17 elements (like chlorine, Cl) form -1 ions.
- Group 2 elements (like calcium, Ca) form +2 ions.
Using the periodic table helps ensure that the chemical formulas are written correctly by balancing the charges in ionic compounds and understanding the bonding behavior of elements in covalent compounds.
List of Common Chemical Compound Formulas
Here’s a list of some commonly known chemical compounds and their formulas:
| Sl no. | Name of the Chemical Compound | Formula |
| 1 | Acetate formula | CH3COO- |
| 2 | Acetic acid formula | CH3COOH |
| 3 | Acetone formula | C3H6O |
| 4 | Aluminium acetate formula | C6H9AlO6 |
| 5 | Aluminium bromide formula | AlBr3 |
| 6 | Aluminium carbonate formula | Al2(CO3)3 |
| 7 | Aluminium chloride formula | AlCl3 |
| 8 | Aluminium fluoride formula | AlF3 |
| 9 | Aluminium formula | Al |
| 10 | Aluminium hydroxide formula | Al(OH)3 |
| 11 | Aluminium iodide formula | AlI3 |
| 12 | Aluminium oxide formula | Al2O3 |
| 13 | Aluminium phosphate formula | AlPO4 |
| 14 | Aluminium sulfide formula | Al2S3 |
| 15 | Aluminum bromide formula | AlBr3 |
| 16 | Aluminum sulfide formula | Al2S3 |
| 17 | Amino acid formula | H2NCHRCOOH |
| 18 | Ammonia formula | NH3 |
| 19 | Ammonium acetate formula | C2H3O2NH4 |
| 20 | Ammonium bicarbonate formula | NH4HCO3 |
| 21 | Ammonium bromide formula | NH4Br |
| 22 | Ammonium carbonate formula | (NH4)2CO3 |
| 23 | Ammonium carbonate formula | (NH4)2CO3 |
| 24 | Ammonium chloride formula | NH4Cl |
| 25 | Ammonium dichromate formula | Cr2H8N2O7 |
| 26 | Ammonium hydroxide formula | NH4OH |
| 27 | Ammonium iodide formula | NH4I |
| 28 | Ammonium nitrate formula | NH4NO3 |
| 29 | Ammonium nitrate formula | (NH4)(NO3) |
| 30 | Ammonium nitrite formula | NH4NO2 |
| 31 | Ammonium oxide formula | (NH4)2O |
| 32 | Ammonium phosphate formula | (NH4)3PO4 |
| 33 | Ammonium phosphate formula | (NH4)3PO4 |
| 34 | Ammonium sulfate formula | (NH4)2SO4 |
| 35 | Ammonium sulfide formula | (NH4)2S |
| 36 | Argon gas formula | Ar |
| 37 | Ascorbic acid formula | C6H8O6 |
| 38 | Barium acetate formula | Ba(C2H3O2)2 |
| 39 | Barium bromide formula | BaBr2 |
| 40 | Barium chloride formula | BaCl2 |
| 41 | Barium chloride formula | BaCl2 |
| 42 | Barium fluoride formula | BaF2 |
| 43 | Barium hydroxide formula | Ba(OH)2 |
| 44 | Barium iodide formula | BaI2 |
| 45 | Barium nitrate formula | Ba(NO3)2 |
| 46 | Barium oxide formula | BaO |
| 47 | Barium phosphate formula | Ba3O8P2 |
| 48 | Barium sulfate formula | BaSO4 |
| 49 | Barium sulfate formula | BaSO4 |
| 50 | Benzene formula | C6H6 |
| 51 | Benzoic acid formula | C7H6O2 |
| 52 | Bicarbonate formula | CHO3– |
| 53 | Bleach formula | NaClO |
| 54 | Boric acid formula | H3BO3 |
| 55 | Bromic acid formula | HBrO3 |
| 56 | Bromine formula | Br |
| 57 | Butane formula | C4H10 |
| 58 | Butanoic acid formula | C4H8O2 |
| 59 | Calcium acetate formula | C₄H₆CaO₄ |
| 60 | Calcium bromide formula | CaBr2 |
| 61 | Calcium carbonate formula | CaCO3 |
| 62 | Calcium hydride formula | CaH2 |
| 63 | Calcium hydroxide formula | Ca(OH)2 |
| 64 | Calcium iodide formula | CaI2 |
| 65 | Calcium nitrate formula | Ca(NO3)2 |
| 66 | Calcium nitrate formula | Ca(NO3)2 |
| 67 | Calcium oxide formula | CaO |
| 68 | Calcium phosphate formula | Ca3(PO4)2 |
| 69 | Carbon monoxide formula | CO |
| 70 | Carbon monoxide formula | CO |
| 71 | Carbon tetrachloride formula | CCl4 |
| 72 | Carbon tetrachloride formula | CCl4 |
| 73 | Carbonic acid formula | H2CO3 |
| 74 | Carbonic acid formula | H2CO3 |
| 75 | Carbonic acid formula | H2CO3 |
| 76 | Chlorate formula | ClO–3 |
| 77 | Chlorine formula | Cl |
| 78 | Chlorine gas formula | Cl2 |
| 79 | Chlorous acid formula | HClO2 |
| 80 | Chromate formula | CrO42- |
| 81 | Chromic acid formula | H2CrO4 |
| 82 | Citric acid formula | C6H8O7 |
| 83 | Citric acid formula | C6H8O7 |
| 84 | Copper ii carbonate formula | CuCO3 |
| 85 | Copper ii nitrate formula | Cu(NO3)2 |
| 86 | Cyanide formula | CN– |
| 87 | Dichromate formula | K2Cr2O7 |
| 88 | Dihydrogen monoxide formula | H2O |
| 89 | Dinitrogen monoxide formula | N2O |
| 90 | Dinitrogen pentoxide formula | N2O5 |
| 91 | Dinitrogen trioxide formula | N2O3 |
| 92 | Ethanol formula | C2H5OH |
| 93 | Ethylene glycol formula | C2H6O2 |
| 94 | Fluorine gas formula | F2 |
| 95 | Fructose chemical formula | C6H12O6 |
| 96 | Glycerol formula | C3H8O3 |
| 97 | Helium gas formula | He |
| 98 | Hexane formula | C6H14 |
| 99 | Hydrobromic acid formula | HBr |
| 100 | Hydrochloric acid formula | HCl |
| 101 | Hydrocyanic acid formula | HCN |
| 102 | Hydrofluoric acid formula | HF |
| 103 | Hydrofluoric acid formula | HF |
| 104 | Hydrogen carbonate formula | CHO3– |
| 105 | Hydrogen gas formula | H2 |
| 106 | Hydrogen peroxide formula | H2O2 |
| 107 | Hydrogen phosphate formula | H3PO4 |
| 108 | Hydrogen sulfate formula | HSO4– |
| 109 | Hydroiodic acid formula | HI |
| 110 | Hydroiodic acid formula | HI |
| 111 | Hydrosulfuric acid formula | H2SO4 |
| 112 | Hydroxide ion formula | OH– |
| 113 | Hypobromous acid formula | HBrO |
| 114 | Hypochlorite formula | NaClO |
| 115 | Hypochlorous acid formula | HClO |
| 116 | Hypochlorous acid formula | HClO |
| 117 | Hypoiodous acid formula | HIO |
| 118 | Iodic acid formula | HIO3 |
| 119 | Iodide ion formula | I– |
| 120 | Iodine formula | I2 |
| 121 | Iron (ii) oxide formula | FeO |
| 122 | Iron (iii) carbonate formula | Fe2(CO3)3 |
| 123 | Iron (iii) chloride formula | FeCl3 |
| 124 | Iron (iii) hydroxide formula | Fe(OH)3 |
| 125 | Iron (iii) nitrate formula | Fe(NO3)3 |
| 126 | Iron (iii) oxide formula | Fe2O3 |
| 127 | Iron oxide formula | Fe2O3 |
| 128 | Lactic acid formula | C3H6O3 |
| 129 | Lead (ii) acetate formula | Pb(C2H3O2)2 |
| 130 | Lead (iv) oxide formula | PbO2 |
| 131 | Lead acetate formula | Pb(C2H3O2)2 |
| 132 | Lead iodide formula | PbI2 |
| 133 | Lead nitrate formula | Pb(NO3)2 |
| 134 | Lithium bromide formula | LiBr |
| 135 | Lithium chloride formula | LiCl |
| 136 | Lithium hydroxide formula | LiOH |
| 137 | Lithium iodide formula | LiI |
| 138 | Lithium oxide formula | Li2O |
| 139 | Lithium phosphate formula | Li3PO4 |
| 140 | Lithium phosphate formula | Li3PO4 |
| 141 | Magnesium acetate formula | Mg(CH3COO)2 |
| 142 | Magnesium bicarbonate formula | C2H2MgO6 |
| 143 | Magnesium bromide formula | MgBr2 |
| 144 | Magnesium carbonate formula | MgCO3 |
| 145 | Magnesium carbonate formula | MgCO3 |
| 146 | Magnesium chloride formula | MgCl2 |
| 147 | Magnesium hydroxide formula | Mg(OH)2 |
| 148 | Magnesium iodide formula | MgI2 |
| 149 | Magnesium nitrate formula | MgNO3 |
| 150 | Magnesium nitrate formula | Mg(NO3)2 |
FAQs
Look for consistent results, expert faculty, academic support, and mentoring. Deeksha Vedantu’s proven track record and personalized approach make Tathastu one of the best choices for NEET aspirants.
Yes, Deeksha Vedantu offers safe and comfortable hostel facilities with academic supervision, healthy meals, and a study-conducive environment for NEET aspirants.
Currently, the program is designed as an offline classroom experience across Deeksha Vedantu campuses in Bengaluru to ensure focused learning, peer interaction, and regular in-person mentoring.
NCERT textbooks are the foundation. Tathastu also provides curated study material, practice sheets, and test series aligned with NEET standards. Reference books like H.C. Verma, Trueman’s Biology, and MTG series are also recommended.
Cut-offs vary by category, college, and year. For government medical colleges in Bengaluru, the general category cut-off is typically above 630+ marks. Our mentors help students set realistic targets based on previous trends.
The syllabus covers Physics, Chemistry, and Biology curriculum from NCERT Class 11 & 12, aligned with NEET UG guidelines. The course includes concept building, doubt clearing, and regular practice tests and Mock Tests.
Students who are currently in or have completed Class 12 are eligible to apply. Concessions are granted based on NEET performance, with top performers qualifying for up to 90% reduction in the total program cost.
The counselling process is conducted by MCC (for All India Quota) and State counselling is conducted by respective state counselling authorities. It includes registration, choice filling, seat allotment, and document verification. Our academic team will guide students throughout the process
The total cost depends on merit-based concessions. Deserving students may receive up to 90% reduction in the overall program charges based on their NEET performance. Please connect with Deeksha Vedantu for detailed information regarding the applicable amount.
Yes, with a structured plan, personalized mentoring, and consistent effort, 9 months is sufficient to secure a top rank in NEET 2025, especially through a program like Tathastu which focuses on concept clarity and test readiness.
The Tathastu NEET Long Term Program is a 9-month intensive coaching program designed to help students thoroughly prepare for NEET 2025 through in-depth concept mastery, regular assessments, and expert mentorship.
The NEET Long Term Cost Reduction is awarded purely on merit, and every student who has appeared for NEET is eligible to apply.
The cost reduction is calculated as:
NEET Score × ₹100
For example, a student scoring 600 in NEET will receive a cost reduction worth ₹60,000 on the course fees.
Please note: The final cost reduction amount is subject to our terms and conditions, including document verification and course selection.
The syllabus covers Physics, Chemistry, and Biology from Class 11 & 12 NCERT textbooks, with a focus on important topics and previous years’ questions.
- NCERT Biology, Physics & Chemistry
- Objective NEET Guidebooks
- 30-Day NEET Revision Books
Yes, many NEET coaching centers in Bangalore provide hostel facilities with study-friendly environments.
Look for factors like faculty experience, success rate, study materials, test series, and student reviews before choosing a coaching center.
Yes, many coaching institutes offer online crash courses with live classes, recorded lectures, and doubt-solving sessions.
The expected cut-off varies based on category and college but is generally between 450-650+ for government colleges and 200-500+ for private colleges.
The counselling process involves registration, document verification, choice filling, seat allotment, and reporting to the allotted college.
The fees vary depending on the institute and duration, typically ranging from ₹20,000 to ₹1,50,000.
A 1-month crash course is useful for revision but may not be sufficient for beginners. A 3–6 month crash course is recommended for thorough preparation.
A NEET crash course is an intensive short-term program designed to help students revise and practice important concepts before the exam.
For board exams, minimum passing marks are 35% in each subject. However, for students aiming for competitive exams like JEE, NEET, or KCET, scoring higher is recommended to strengthen their foundation.
For Deeksha, dSAT is the entrance test, covering Mathematics, Science, and Logical Reasoning based on 10th-grade concepts. No additional entrance syllabus is required beyond this assessment.
The last date for PU entrance varies by college. At Deeksha, students should register for dSAT 2025 as early as possible to secure a seat. Visit dSAT registration for deadlines and updates.
At Deeksha, admission is not based on marks but on dSAT performance. Qualifying for dSAT ensures admission without additional entrance criteria. Students are encouraged to take dSAT to secure their admission.
The PU entrance exam difficulty depends on the college. At Deeksha, students qualify through dSAT, which assesses their aptitude and places them in the best-fit academic stream.
Most PU colleges require a minimum of 60% – 70% in 10th grade, but top colleges like Deeksha may have specific criteria based on dSAT performance.
Yes, students can transfer to another PU college after 1st PUC, but they need to follow specific guidelines, such as obtaining a transfer certificate (TC) and meeting the new college’s admission criteria.
Most PU colleges, including Deeksha, have strict policies on phone usage during academic hours to ensure a distraction-free learning environment. However, some colleges allow limited use under supervision.
Yes, many PU colleges in Bengaluru offer direct admissions based on 10th board exam results. However, at Deeksha, students qualify for admission through the dSAT (Deeksha Scholastic Aptitude Test), which helps assess their potential and place them in the right academic program. Register for dSAT 2025 here to secure your place.
Deeksha is an excellent choice for 1st PUC students, offering a structured curriculum, experienced faculty, and integrated coaching programs that help students excel in academics and entrance exams simultaneously.
The fee for 1st PUC depends on the stream and additional programs opted for. At Deeksha, we offer flexible fee structures based on the course, coaching modules, and facilities provided. Get in touch with our admissions team to know more about the latest fee structure.
For students aspiring to pursue Science in 11th and 12th, Deeksha is one of the best PU colleges in Bengaluru. With focused coaching in Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, and Biology, along with a well-structured learning methodology, students are well-prepared for competitive exams.
Choosing the right PU college is crucial for your academic and career goals. Here’s what you should consider:
- Quality of Education: Look for a college with a strong track record of academic excellence.
- Faculty & Infrastructure: Ensure the college has experienced teachers and modern facilities.
- Integrated Coaching: Choose a college like Deeksha that provides coaching for JEE, NEET, and KCET along with PUC curriculum.
- Student Support: Check for mentoring, counseling, and extracurricular opportunities.
The fees for PU colleges in Bengaluru vary depending on the institution, the stream chosen (Science, Commerce, or Arts), and additional coaching programs. On average, PU college fees can range from ₹50,000 to ₹2,00,000 per year. At Deeksha, we offer value-packed education with integrated coaching options that ensure students excel in both board exams and competitive entrance tests.
Bengaluru is home to some of the best PU colleges in Karnataka. Deeksha stands out as a top choice for students due to its integrated coaching for competitive exams like JEE, NEET, and KCET, along with a strong academic foundation. With experienced faculty, structured study plans, and excellent results, Deeksha has consistently ranked among the best PU colleges in Bengaluru.
To prove similarity, use the AA, SSS, or SAS criterion:
-
.
.
.
Similar triangles are used in:
-
- Indirect measurement techniques (e.g., finding heights of buildings).
- Map scaling and architectural designs.
In a right-angled triangle, one angle measures , and the Pythagoras Theorem holds:
.
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always .
The sum is derived by pairing terms of the sequence in reverse order, resulting in a simplified formula.
It helps in solving problems involving large sequences without manually adding all terms.
The nth term formula is derived from the general property of AP, where each term is the sum of the first term and a multiple of the common difference.
The nth term formula helps to calculate specific terms in a sequence without listing all preceding terms.
It is the formula used to find any term in the sequence: .
The common difference () is the fixed value obtained by subtracting any term from the next term.
An AP is a sequence of numbers where the difference between consecutive terms is constant.
Complex roots are non-real roots that exist in pairs and are conjugates of each other (e.g., and
)
Calculate the discriminant and use its value to identify the root type.
: Two distinct real roots.
: One repeated real root.
: Two complex roots.
The discriminant () determines the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation.
Use other methods like the quadratic formula or completing the square.
Factorisation works best when the quadratic equation can be split into integer factors easily.
Factorisation rewrites a quadratic equation as a product of two linear factors to find the variable’s value
Quadratic equations are used in physics, geometry, economics, engineering, and optimization problems.
The discriminant () determines if roots are real, repeated, or complex.
Factorization, completing the square, quadratic formula, and graphical method.
A polynomial equation of degree two, expressed as , where
.
If the equations represent parallel lines, there is no solution. If they represent the same line, there are infinitely many solutions. This can be determined by comparing the ratios of the coefficients.
Substitute the obtained values of x and y back into the original equations to ensure both equations are satisfied.
Yes, the elimination method is more efficient when the coefficients of one variable are already aligned or can be easily manipulated to align, allowing for quick elimination.
The substitution method is preferable when one equation is easily solvable for one variable, making substitution straightforward.
The steps are:
- Multiply one or both equations to align coefficients of one variable.
- Add or subtract the equations to eliminate that variable.
- Solve the resulting single-variable equation.
- Substitute the found value into one of the original equations to find the other variable.
The elimination method focuses on eliminating one variable by adding or subtracting equations, whereas the substitution method involves expressing one variable in terms of the other and substituting it into the second equation.
In the substitution method:
- Solve one of the equations for one variable in terms of the other.
- Substitute this expression into the second equation.
- Solve the resulting single-variable equation.
- Use the obtained value to find the other variable
The primary algebraic methods for solving a pair of linear equations are:
- Substitution Method: Solve one equation for one variable and substitute this expression into the other equation.
- Elimination Method: Add or subtract equations to eliminate one variable, simplifying the system to a single-variable equation.
The graphical method can be imprecise when finding exact values, especially if the point of intersection is not on grid lines. It also becomes less practical when dealing with more complex systems or when precise solutions are required.
Yes, by comparing the ratios of the coefficients ,
, and
, we can determine the type of solution:
- If
, the lines intersect and there is a unique solution.
- If
, the lines are coincident and there are infinitely many solutions.
- If
, the lines are parallel and there is no solution.
If the equations have different slopes, it means the lines will intersect at a single point. Therefore, the system of equations will have a unique solution.
Infinitely many solutions occur when the two lines overlap completely, or in other words, they are coincident. This means every point on the line satisfies both equations, so there are infinitely many solutions.
A unique solution exists when the lines represented by the equations intersect at exactly one point. This means there is one specific pair of values for and
that satisfies both equations.
If two lines are parallel, it means that they will never intersect, indicating that there is no common solution to the equations. In this case, the equations are said to be an “inconsistent pair” and have no solution.
In the graphical method, the point of intersection represents the solution to the pair of equations. The coordinates of the intersection point satisfy both equations simultaneously.
The graphical method involves plotting each equation on a graph as a line and finding the point(s) of intersection. The coordinates of the intersection point represent the solution to the equations. If the lines intersect at a single point, there is a unique solution. If they are parallel, there is no solution, and if they coincide, there are infinitely many solutions.
A polynomial of degree 4 can have up to four real zeros.
Yes, a cubic polynomial can have one, two, or three real zeros, depending on how it intersects the x-axis.
If the quadratic polynomial’s discriminant is less than zero, the polynomial has no real roots, so the parabola does not intersect the x-axis.
A polynomial of degree 2 (quadratic polynomial) can have up to two real zeros.
This concept is widely used in algebra, calculus, and even fields like physics and engineering. For example, in circuit analysis, certain electrical parameters can be modeled using polynomial equations, and understanding the relationships between zeroes and coefficients can help solve complex problems efficiently.
For higher-degree polynomials (beyond cubic), similar relationships exist. The sum of zeroes, the sum of products of zeroes taken two at a time, and so on, can be related to the coefficients. However, the exact relationships depend on the polynomial’s degree and are more complex as the degree increases.
Yes, knowing the zeroes and their relationships with the coefficients allows us to construct polynomials. For example, if the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial are given as and
, we can write it as:
Expanding this will provide a polynomial with the desired zeroes.
This relationship allows us to determine properties of a polynomial without fully solving it. It is useful in factoring polynomials, solving equations, and understanding the behavior of polynomial functions in graphing and analysis.
For a linear polynomial , the zero is:
Yes, in a cubic polynomial , the sum of the products of zeroes taken two at a time is:
For a cubic polynomial , the product of the zeroes
,
, and
is given by:
For a cubic polynomial , if
,
, and
are the zeroes, then:
This is the sum of zeroes expressed in terms of the coefficients of and
.
For a quadratic polynomial , if
and
are the zeroes, then:
and
where represents the sum of zeroes, and
represents the product of zeroes.
No, polynomials only include terms with non-negative integer exponents.
The zero polynomial has no terms, so it doesn’t have the highest power. Hence, its degree is considered undefined.
The degree is the highest power of the variable present in the polynomial. For example, in , the degree is 3.
A polynomial consists only of non-negative integer powers of a variable and real-number coefficients, making it a specific type of algebraic expression.
Yes, if a number is a perfect square, its square root is rational (e.g., ).
The result is always irrational, as shown in examples like .
The square root of a prime number cannot be expressed as a fraction, so it’s irrational. We use proof by contradiction and Theorem 1 to prove this.
Prime factorization allows us to identify the common factors for HCF and all factors for LCM.
The uniqueness comes from the fact that no two different sets of prime numbers can be multiplied to produce the same composite number.
The theorem states that every composite number can be uniquely factorized as a product of prime numbers, apart from the order of factors.
Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction of two integers and have either terminating or repeating decimal expansions. Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions and have non-terminating, non-recurring decimals.
By expressing each number in terms of its prime factors, we can identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the numbers. Multiplying these factors gives the LCM.
Certain square roots cannot be expressed as a fraction because their decimal expansions are non-terminating and non-repeating. The proof often involves assuming the number is rational and reaching a contradiction.
Euclid’s Division Lemma allows us to systematically divide two numbers, using remainders to progressively reduce the numbers until we reach the HCF. This method is efficient and widely used in number theory.
Climate change alters habitats and ecosystems, forcing species to migrate or adapt. Many species may not survive these changes, leading to a loss of biodiversity and the extinction of certain species.
Biological magnification is the process by which harmful chemicals accumulate in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain. It is harmful because top predators, including humans, consume high concentrations of toxins, which can cause serious health problems.
Air pollution releases greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause global warming. This leads to rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and sea level rise.
Deforestation is the large-scale cutting down of forests. It leads to the loss of biodiversity, contributes to climate change by releasing carbon dioxide, and causes soil erosion.
Decomposers break down dead organisms into simpler substances, recycling nutrients like carbon and nitrogen back into the soil, which can then be absorbed by plants.
Producers, such as green plants and algae, are autotrophs that capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain and provide energy for all other organisms.
The two main components of an ecosystem are biotic components (living organisms) and abiotic components (non-living elements such as air, water, and soil).
An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature where living organisms interact with each other and with their non-living environment. These interactions involve the transfer of energy and cycling of nutrients, maintaining ecological balance.
Biological magnification causes harmful chemicals to accumulate at each trophic level. These chemicals become more concentrated in organisms at higher trophic levels, posing health risks to top predators, including humans.
Trophic levels represent the position of organisms in a food chain. Producers occupy the first level, herbivores the second, and carnivores the higher levels.
Biodegradable substances can be broken down by natural processes, while non-biodegradable substances cannot decompose easily and remain in the environment for a long time, causing pollution.
If a fuse blows, it breaks the circuit and stops the flow of current, protecting the appliances and preventing overheating or fire hazards. The fuse must be replaced to restore the connection.
Alternating current (AC) is used for domestic supply because it is more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances. AC can be easily transformed to different voltage levels, which reduces energy losses in transmission.
A fuse is a one-time safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if excess current flows. An MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) automatically trips during overload or short circuits but can be reset after the fault is corrected.
The earth wire provides a low-resistance path for leakage currents to flow into the ground. It protects users from electric shocks by safely directing excess current away from the appliance in case of a fault.
Appliances are connected in parallel in domestic circuits to ensure that each receives the same voltage and operates independently. This setup also allows individual control of devices, so if one appliance fails, the others continue to function.
Around a bar magnet, magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole, curve around the magnet, and enter the south pole. Inside the magnet, the lines continue from the south pole to the north pole, forming closed loops.
You can visualize magnetic field lines by sprinkling iron filings around a magnet or by using a small compass. The iron filings align themselves along the magnetic field lines, forming a pattern that reveals the field’s shape and direction.
Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines used to represent the strength and direction of a magnetic field. They help us visualize how the magnetic force behaves around a magnet or a current-carrying conductor.
An electric fuse protects appliances from damage by breaking the circuit if excessive current flows, preventing overheating and potential fires.
Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule is used to find the direction of force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. It’s applied in electric motors to understand the direction of motion.
Electromagnetic induction is used in devices like electric generators, transformers, and in technologies like magnetic levitation for high-speed trains (Maglev).
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces a current in a conductor. Michael Faraday discovered this phenomenon.
The magnetic field strength inside a solenoid increases as the number of turns increases, as each turn reinforces the magnetic field at the center of the solenoid.
Increasing the current increases the strength of the magnetic field around and at the center of the loop.
The magnetic field strength increases with a higher current and decreases as you move farther from the conductor.
Magnetic field lines never intersect because if they did, it would mean the magnetic field has two directions at the same point, which is physically impossible.
The Right-Hand Thumb Rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor. Point your right-hand thumb in the direction of the current, and your fingers will curl in the direction of the magnetic field lines.
A magnetic field around a conductor can be detected using a compass or by observing how iron filings arrange themselves around the conductor.
Hans Christian Oersted discovered in 1820 that an electric current can produce a magnetic field, revealing the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
When an electric current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. This magnetic effect is the basis for devices like electromagnets, electric motors, and generators.
A fuse works by using a thin wire with a low melting point. When excessive current flows through the fuse, the wire heats up due to the heating effect and melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to appliances.
Applications of the heating effect include electric heaters, electric irons, toasters, fuses, and filament bulbs. These devices convert electrical energy into heat energy for useful purposes.
High-resistance materials, like nichrome, are used in electric heaters because they generate more heat when current flows through them. This is because the heat produced is directly proportional to the resistance of the material.
The heat produced in a conductor is proportional to the square of the current flowing through it, the resistance of the conductor, and the time for which the current flows. It is given by the formula .
The heating effect of electric current refers to the phenomenon where heat is generated when an electric current flows through a conductor. This occurs due to collisions between electrons and atoms in the conductor.
Electric energy consumption is calculated using the formula E=P×t, where P is the power in watts and t is the time in hours. The result is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
The power rating of household appliances is usually mentioned on a label in watts or kilowatts. It indicates how much power the device consumes when operating at its rated voltage.
Power is the rate at which energy is consumed or produced, while energy is the total amount of work done over time. Power is measured in watts, and energy is measured in joules or kilowatt-hours.
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or produced in a circuit. It is measured in watts (W) and is given by the formula P=V×I.
In a series circuit, the current remains the same throughout all resistors, but the voltage is divided among them. In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across all resistors, but the current is divided among the different branches.
In a parallel circuit, the current has multiple paths to travel through. Even if one of the resistors has a high resistance, the presence of other resistors provides additional paths for the current, reducing the total resistance.
When more resistors are added in parallel, the total resistance decreases because the current has more paths to flow through, reducing the overall opposition to current flow.
When more resistors are added in series, the total resistance increases because the current has to pass through each resistor, increasing the overall opposition to current flow.
Resistivity is a material-specific property that measures how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its resistivity. Materials with low resistivity (like copper) have lower resistance, while materials with high resistivity (like rubber) have higher resistance.
For most conductors (such as metals), resistance increases with an increase in temperature due to more frequent collisions between electrons and atoms. However, some materials, like semiconductors, may exhibit decreased resistance with increasing temperature.
A thicker wire has a larger cross-sectional area, which provides more space for the flow of electric current, reducing the resistance. Resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area.
The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length. If the length of the conductor increases, the resistance increases.
If a component in a series circuit fails (e.g., if a bulb burns out), the entire circuit is interrupted, and current stops flowing through all components.
An ammeter is connected in series with the circuit components to measure the current flowing through the circuit.
A voltmeter is connected in parallel with the component or section of the circuit across which the potential difference (voltage) is to be measured.
Circuit diagrams simplify the understanding of electrical circuits by using symbols to represent components and connections. They help in the design, analysis, and troubleshooting of circuits and are universally understood.
In a series circuit, all components are connected in a single path, so the same current flows through each component. In a parallel circuit, components are connected across the same two points, providing multiple paths for current to flow.
Ohm’s Law states that the potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided the resistance remains constant. Mathematically, .
Electric potential at a point is the potential energy per unit charge at that point. The potential energy of a charge Electric potential at a point is the potential energy per unit charge at that point. The potential energy of a charge qqq at a point with electric potential V is given by . at a point with electric potential V is given by
.
Potential difference represents the energy required to move a unit charge between two points in an electric field or circuit. It is the driving force behind the flow of electric current in a circuit.
Potential difference is measured using a voltmeter. The voltmeter is connected in parallel across the two points between which the potential difference is to be measured.
The SI unit of potential difference is the volt (V).
A switch controls the flow of current by either completing or breaking the circuit. When the switch is closed, the circuit is complete, and current flows. When the switch is open, the circuit is incomplete, and current stops flowing.
The SI unit of electric current is the ampere (A). It is measured using an ammeter connected in series with the circuit.
Direct current (DC) flows in one direction, while alternating current (AC) changes direction periodically. Batteries produce DC, while power plants generate AC.
Electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is defined as the rate at which charge flows through a point in a circuit and is measured in amperes (A).
An electric fuse melts because of the heating effect of electric current. Excessive current generates heat that melts the fuse wire, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to appliances.
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or converted into other forms of energy. It is measured in watts (W).
In a series circuit, the components are connected end-to-end, and the current is the same through each component. In a parallel circuit, the components are connected across the same two points, and the voltage across each component is the same, but the current divides among the branches.
The SI unit of electric current is the ampere (A).
Yes, scattering can occur in any medium where light interacts with particles or irregularities. For example, scattering occurs in colloidal suspensions (like milk in water), glass (if it contains impurities), and even in water bodies with suspended particles.
Scattering can reduce visibility by causing light to be redirected in multiple directions. This is why fog, smog, or haze can make it difficult to see distant objects—light from these objects is scattered before reaching the observer.
Fog lights are typically yellow because longer wavelengths (like yellow light) scatter less than shorter wavelengths (like blue light). This allows yellow light to penetrate fog more effectively, improving visibility in foggy conditions.
At noon, the Sun is overhead, and its light travels through a shorter path in the atmosphere. As a result, all wavelengths of light scatter less, and the Sun appears white because all colors of light are reaching the observer in nearly equal amounts.
Although violet light scatters more than blue light, the sky does not appear violet because the human eye is less sensitive to violet light. Additionally, much of the violet light is absorbed by the upper atmosphere, making blue light more dominant.
Astronomers must account for atmospheric refraction when observing celestial bodies. The bending of light by the atmosphere causes objects to appear in slightly different positions than their true locations. This effect is especially significant for objects near the horizon.
A superior mirage occurs when the air near the surface is cooler than the air above it (the opposite of an inferior mirage). In this case, light rays bend downward, making distant objects appear elevated or floating in the sky. This phenomenon is commonly seen in polar regions.
Atmospheric refraction adds about 4 minutes to the length of the day—2 minutes for advanced sunrise and 2 minutes for delayed sunset. This extends the amount of visible daylight by bending the light from the Sun before it rises and after it sets.
Yes, atmospheric refraction affects the apparent position of all celestial objects, including the Moon. The Moon appears slightly higher in the sky than its actual position due to the bending of its light as it passes through the atmosphere.
Stars near the horizon twinkle more because their light passes through a larger portion of the Earth’s atmosphere, encountering more turbulence and refraction. This causes greater fluctuations in the brightness of the star.
A spectroscope uses a prism (or a diffraction grating) to disperse light into its component wavelengths. By analyzing the resulting spectrum, scientists can identify the specific wavelengths of light emitted by a substance, helping to determine its composition.
Yes, dispersion can occur in any transparent medium with varying refractive indices for different wavelengths. Water droplets, for example, cause dispersion, which leads to the formation of rainbows. Diamond, with its high refractive index, also causes significant dispersion.
Different colors of light have different wavelengths and refractive indices. Shorter wavelengths, like violet, have a higher refractive index and bend more, while longer wavelengths, like red, have a lower refractive index and bend less.
The order of colors in the spectrum formed by a glass prism is Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (VIBGYOR). Violet light bends the most, and red light bends the least.
Yes, prisms can be used to combine or separate different colors of light. In some optical instruments, prisms are used to merge multiple beams of light with different wavelengths into a single beam or to split light into its component wavelengths.
The refractive index of a prism is a measure of how much the prism slows down and bends light. It depends on the material of the prism and the wavelength of light.
Violet light has a shorter wavelength than red light, and light with shorter wavelengths is refracted more because it travels more slowly through the prism. This causes violet light to deviate more than red light.
Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its constituent colors when it passes through a prism due to different refractive indices for different wavelengths.
Laser surgery, such as LASIK, reshapes the cornea to correct its curvature, allowing light to focus correctly on the retina. This procedure can correct myopia, hypermetropia, and astigmatism, often eliminating the need for glasses or contact lenses.
Yes, astigmatism can occur alongside myopia or hypermetropia. In such cases, glasses or contact lenses can be designed to correct both defects simultaneously.
Spherical lenses (concave and convex) are used to correct simple vision defects like myopia and hypermetropia. Cylindrical lenses are used to correct astigmatism, as they focus light differently along different axes to correct irregularities in the curvature of the cornea or lens.
A virtual image cannot be projected on a screen because the light rays do not actually meet but only appear to diverge from a point behind the mirror. A real image, on the other hand, can be projected on a screen because the light rays actually converge at a point.
Mirrors have a smooth, shiny surface that causes most of the light falling on them to be reflected back according to the laws of reflection.
Lateral inversion is the phenomenon where the left side of an object appears as the right side in its mirror image, and vice versa.
The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, erect, laterally inverted, and of the same size as the object.
Yes, reflection occurs on all surfaces, but the nature of the reflection (regular or diffuse) depends on the smoothness of the surface.
No, convex mirrors always form virtual, erect, and diminished images, as the reflected rays appear to diverge from a point behind the mirror.
Concave mirrors form real images when the object is placed beyond the focus. The reflected rays actually converge and meet at a point, forming a real image.
The image is virtual, erect, and magnified.
The refractive index of air is almost equal to 1 because the speed of light in air is very close to its speed in a vacuum.
Total internal reflection is the phenomenon where light, traveling from a denser to a rarer medium, is completely reflected back into the denser medium when the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle.
Light bends during refraction because it changes speed when it passes from one medium to another. The bending occurs due to the difference in optical densities of the two media.
The refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a given medium. It indicates how much light slows down in that medium.
Planets do not twinkle because they are much closer to Earth and appear as extended sources of light, not point sources like stars. The variations in light from different parts of the planet cancel out, so the planet appears steady.
Presbyopia is caused by the gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles and the reduced elasticity of the lens, making it difficult to focus on nearby objects. It is corrected using bifocal or progressive lenses.
The near point is the closest distance at which an object can be seen clearly, typically about 25 cm for a normal adult. The far point is the farthest distance at which objects can be seen clearly, which is at infinity for a normal eye.
Yes, a person can have both myopia and hypermetropia, particularly as they age. This condition is called presbyopia, and it is usually corrected using bifocal or progressive lenses.
The brain processes the signals received from the retina and flips the inverted image so that we perceive it as upright and correctly oriented.
As people age, the lens becomes less flexible, and the ciliary muscles weaken, reducing the eye’s ability to focus on nearby objects. This condition is called presbyopia, and it is corrected using reading glasses or bifocals.
The ciliary muscles adjust the shape of the lens, making it thicker for nearby objects and thinner for distant objects, allowing the eye to focus light properly on the retina.
The least distance of distinct vision, or the near point, is about 25 cm for a normal adult eye.
Genetic variation allows populations to adapt to changing environments. Natural selection acts on individuals with beneficial variations, allowing them to survive and reproduce. Over time, these beneficial traits become more common, driving evolution.
Mendel’s experiments with pea plants revealed that traits are inherited in predictable patterns. His laws of inheritance (dominance, segregation, and independent assortment) explain how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
Hereditary traits are characteristics passed from parents to offspring through genes. These traits include physical features, behaviors, and even susceptibility to certain diseases.
The environment determines which variations are beneficial. Individuals with traits that are well-suited to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, while those with less favorable traits may not survive as well.
Variation provides the raw material for natural selection. Individuals with favorable variations are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits to their offspring. Over time, this leads to the accumulation of beneficial traits in a population, driving evolution.
Sexual reproduction involves the mixing of genetic material from two parents, leading to a greater variety of genetic combinations. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves only one parent, so variation is limited to mutations in the DNA.
Variations occur due to mutations, recombination during meiosis, independent assortment of chromosomes, and the random fusion of gametes during fertilization. These processes introduce differences in the genetic material passed from parents to offspring.
Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity, including the Law of Dominance, the Law of Segregation, and the Law of Independent Assortment, by experimenting with pea plants.
The sex of a child is determined by the sex chromosomes. The mother always provides an X chromosome, while the father provides either an X (resulting in a female) or a Y (resulting in a male).
Dominant traits are expressed when at least one dominant allele is present, while recessive traits are only expressed when both alleles are recessive.
Heredity is the process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
Pollination is the process of transferring pollen from the male reproductive part of the flower (anther) to the female reproductive part (stigma). It is necessary for fertilization and the formation of seeds in flowering plants.
Genetic variation increases the ability of a population to adapt to changing environments. It ensures that some individuals have traits that may be beneficial for survival in new or challenging conditions.
Meiosis is the process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. It introduces genetic variation through crossing over and independent assortment of chromosomes.
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes from two parents, leading to genetic variation. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring.
Conjugation is a form of sexual reproduction that allows single-celled organisms to exchange genetic material, increasing genetic variation and enhancing their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
Asexual reproduction is energy-efficient and allows for rapid population growth, making it an ideal mode of reproduction for single-celled organisms that need to multiply quickly in favorable conditions.
In budding, a small outgrowth (bud) forms on the parent organism and grows into a new individual before detaching. In binary fission, the parent cell splits into two identical cells.
Binary fission is an asexual mode of reproduction where a single-celled organism divides into two identical daughter cells. It is common in organisms like bacteria, Amoeba, and Paramecium.
Variation allows some individuals in a population to survive better in changing environments. Over time, natural selection favors individuals with advantageous traits, leading to evolutionary changes in the population.
In asexual reproduction, variations are minimal and occur due to occasional mutations during DNA replication. In sexual reproduction, variations are more significant because the offspring inherit genetic material from two parents, resulting in genetic diversity.
Mutations introduce variations in the genetic material of organisms. While most mutations are neutral or harmful, some may provide an advantage that helps the organism adapt to its environment, leading to evolutionary changes.
Organisms don’t create exact copies due to small variations that occur during DNA replication. These variations are a result of mutations that introduce slight differences between parent and offspring.
Reproduction ensures the continuation of species by producing new individuals. It also introduces variations that allow organisms to adapt to changes in their environment, enhancing their chances of survival.
DNA copying ensures that genetic information is passed from parent to offspring. Although the copying process is precise, minor errors (mutations) can occur, leading to genetic variation.
Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genes from two parents, leading to genetic diversity among offspring. This variation allows populations to adapt to changing environments and is the basis of evolution.
Thyroxine regulates metabolism, ensuring that the body’s cells receive enough energy for normal functioning.
Estrogen (in females) and testosterone (in males) regulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics, such as breast development in girls and facial hair in boys, during puberty.
Adrenaline increases heart rate, breathing rate, and blood glucose levels to prepare the body for the “fight-or-flight” response in stressful situations.
Insulin helps lower blood glucose levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy or stored as glycogen.
Thigmotropism is the growth response of plants to touch. Climbing plants like peas and vines use thigmotropism to wrap their tendrils around supports, allowing them to grow upwards and access more sunlight for photosynthesis.
During drought, the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) causes stomata to close, reducing water loss through transpiration. This helps the plant conserve water and survive during dry conditions.
Gibberellins are responsible for promoting stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering. They help break seed dormancy and enable plants to grow taller, which is beneficial for accessing light.
Reflex actions are faster because they are processed by the spinal cord and do not involve the brain. This allows the body to respond quickly to harmful stimuli without conscious thought.
The CNS (Central Nervous System) consists of the brain and spinal cord, which process and coordinate information. The PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) consists of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body, carrying sensory and motor signals.
The nervous system detects changes in the environment (stimuli) through sensory receptors, processes the information in the brain and spinal cord, and generates an appropriate response through motor neurons.
The synapse is the junction between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle. It allows electrical impulses to be transmitted from one neuron to another or from a neuron to a muscle via chemical neurotransmitters.
Hormones like growth hormone (from the pituitary gland) and thyroxine (from the thyroid gland) regulate physical growth, metabolic rate, and development.
Plants respond to light through phototropism, a process regulated by auxins. Auxins cause the cells on the shaded side of the plant to elongate more, making the plant bend towards the light.
The cerebrum is responsible for higher cognitive functions like thinking, memory, decision-making, and voluntary actions like movement.
Insects excrete uric acid because it is less toxic and conserves water. This is particularly beneficial for insects living in dry environments, as they need to minimize water loss.
Oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released into the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata, located on the surface of leaves.
Nephrons filter blood through the glomerulus, where small molecules like water, salts, urea, and glucose pass into the Bowman’s capsule. This filtrate is then processed in the tubules, where essential substances are reabsorbed, and waste products are concentrated into urine.
Urea is formed in the liver through the urea cycle when excess amino acids are broken down. The nitrogen from amino acids is converted into ammonia, which is toxic. The liver converts ammonia into urea, which is less toxic and can be safely excreted by the kidneys.
The main excretory products in humans are urea, excess salts, water, and nitrogenous waste. Urea is produced by the liver during the breakdown of proteins and is excreted in urine.
Transpiration creates a suction force that pulls water upward from the roots to the leaves through the xylem. This process helps in the absorption and distribution of water and minerals throughout the plant.
The lymphatic system helps in draining excess fluid from tissues, absorbing fats from the intestines, and fighting infections through lymph nodes and lymphocytes.
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen in the lungs and transports it to the tissues. It also helps in transporting carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs for exhalation.
Breathing is the physical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide, while respiration is the biochemical process of breaking down glucose to release energy.
Muscle cramps are caused by the accumulation of lactic acid during anaerobic respiration in the muscles. When oxygen supply is insufficient, muscles switch to anaerobic respiration, leading to the production of lactic acid, which causes cramps.
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and produces more energy, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and produces less energy. Aerobic respiration results in carbon dioxide and water, while anaerobic respiration in muscles results in lactic acid, and in yeast, it produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Autotrophs synthesize their food through processes like photosynthesis, while heterotrophs rely on other organisms for their food.
Nutrition provides organisms with the necessary energy to carry out life processes, promotes growth, and maintains the body’s functions.
Enzymes act as catalysts that break down complex food molecules into simpler ones, which can then be absorbed and used by the body for energy and growth.
Specialized tissues, such as xylem in plants for water transport and red blood cells in animals for oxygen transport, allow organisms to efficiently carry out life processes and sustain themselves.
Energy is produced through the breakdown of glucose during respiration. This process generates ATP, which is used by cells to perform various functions.
Life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion ensure that organisms maintain homeostasis, grow, and reproduce. Without these processes, organisms would not be able to survive.
Double circulation ensures that oxygen-rich blood is separated from oxygen-poor blood, improving the efficiency of oxygen delivery to body tissues.
While photosynthesis produces glucose (food), respiration breaks down glucose to release energy for cellular activities. Both processes are necessary for survival.
Enzymes catalyze the breakdown of large food molecules into smaller, absorbable molecules. For example, amylase breaks down starch into maltose.
Detergents do not react with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, so they do not form scum. This makes them more effective cleaners in areas with hard water.
A micelle is a spherical structure formed by soap or detergent molecules, with hydrophobic tails trapping grease and hydrophilic heads interacting with water. This allows dirt to be washed away easily.
In hard water, calcium and magnesium ions react with soap molecules to form an insoluble precipitate called scum, which reduces the soap’s effectiveness.
Esterification reactions produce esters, which have pleasant fragrances and are widely used in the perfume and food industries as flavoring agents.
When ethanol reacts with sodium, it forms sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. This reaction shows ethanol’s weakly acidic properties.
Ethanol is a renewable resource, and its combustion produces fewer pollutants compared to fossil fuels, making it an eco-friendly alternative for fuel.
Ethanol () is oxidized to form ethanoic acid (
) when treated with an oxidizing agent such as potassium dichromate or potassium permanganate.
In an addition reaction, new atoms are added to a compound (typically across double or triple bonds in unsaturated hydrocarbons). In a substitution reaction, one atom (usually hydrogen) is replaced by another atom, such as a halogen.
Hydrocarbons burn in oxygen during combustion, producing carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of heat and light. The carbon in the compound reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, while hydrogen forms water.
Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes) contain double or triple bonds.
Catenation allows carbon to form long chains, branched chains, and rings, which are the basis for many organic compounds found in nature and industry.
Carbon’s versatility arises from its ability to form stable covalent bonds with itself and other elements. Its tetravalency and capacity for catenation lead to an immense variety of compounds.
A single bond involves sharing one pair of electrons, a double bond involves two pairs, and a triple bond involves three pairs of electrons shared between two atoms.
A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons, allowing both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell, and it is energetically unfavorable for it to either gain or lose four electrons to form an ion. Therefore, carbon shares electrons and forms covalent bonds.
Soaps are natural salts of fatty acids, while detergents are synthetic and work better in hard water.
Alkanes have single bonds between carbon atoms, alkenes have double bonds, and alkynes have triple bonds.
Carbon’s tetravalency and catenation properties allow it to form a wide variety of compounds with different elements.
Anodizing increases the thickness of the oxide layer on metals like aluminum, protecting the metal from further oxidation and corrosion.
Zinc is more reactive than iron. When it is used to coat iron, it corrodes first, protecting the iron from rusting. This process is known as galvanization.
Iron is reactive and combines with oxygen and water to form rust. Gold is an unreactive metal, and it does not react with oxygen, even at high temperatures.
Copper sulfate loses its water of crystallization upon heating, turning from blue (hydrated form) to white (anhydrous form).
Water of crystallization refers to water molecules that are chemically bonded within the structure of a salt.
Example: Copper sulfate pentahydrate ().
A neutral salt is formed from the reaction of a strong acid and a strong base, with a pH close to 7.
Example: Sodium chloride ().
Salts are ionic compounds formed when an acid reacts with a base, typically producing salt and water.
Soil pH affects the availability of nutrients. If the pH is too acidic or too alkaline, plants may not be able to absorb the nutrients they need to grow.
Pure water has a pH of 7, which is neutral.
A universal indicator changes color depending on the pH of the solution, providing a visual way to determine whether the solution is acidic, neutral, or basic.
Strong acids have a pH close to 0 (e.g., hydrochloric acid).
The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions () in a solution, determining whether the solution is acidic, neutral, or basic.
Yes, acids and bases react in a neutralization reaction to form salt and water, canceling each other’s properties.
Both acids and bases dissociate into ions ( in acids and
in bases), which allows them to conduct electricity.
All bases release hydroxide ions () when dissolved in water and turn red litmus paper blue.
All acids release hydrogen ions () when dissolved in water and turn blue litmus paper red.
Carbon dioxide turns limewater milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
Indicators change color in the presence of an acid or a base, helping to identify whether a solution is acidic or basic.
Acids donate hydrogen ions () in water. When they react with metals, the hydrogen ions are reduced to hydrogen gas.
Antacids neutralize excess stomach acid by reacting with it to form salt and water.
pH is used to maintain soil quality, ensure safe drinking water, and manage health through the proper use of antacids.
Acids release hydrogen ions (), which react with litmus, causing it to turn red.
A neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
Example:
Sets can be represented in statement form, roster form, or set-builder form, depending on how their elements are defined.
A subset includes all elements of another set, including possibly being the same set, while a proper subset includes all elements but is not identical to the set.
The Cartesian product of two sets and
, denoted as
, is the set of all ordered pairs where the first element is from
and the second element is from
.
Sets are used in various fields like data science, logic, computer science, database management, probability, and statistics. For example, sets are used to group data, perform operations on databases, and calculate probabilities in statistical models.
The union of two sets includes all elements that are in either of the sets or in both. It is denoted by .
Some common types of sets are finite sets, infinite sets, empty sets (null sets), universal sets, power sets, subsets, and equal sets.
A set is a collection of distinct and well-defined objects, called elements. These elements can be anything from numbers to letters or even other sets.
The Tyndall effect is the scattering of light by particles in a mixture. It occurs in suspensions due to the larger size of their particles, which scatter light.
Yes, the solid particles in a suspension can be separated by filtration, unlike solutions where the solute is dissolved.
In a suspension, the particles are large and settle over time, while in a solution, the solute is completely dissolved and does not settle out.
Stabilizing agents like surfactants or thickeners are added to prevent the solid particles from settling out too quickly.
Common examples include sand in water, muddy water, paint, and certain medicines like antacids.
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid or gas but do not dissolve. Over time, the solid particles settle out if left undisturbed.
Noble gases have a full valence shell of electrons, which makes them highly stable and unreactive compared to other elements.
Rare earth elements mostly comprise the lanthanide series, which are key components in various electronic devices and are known for their magnetic and luminescent properties.
While Mendeleev’s table was organized by increasing atomic mass, the modern table is organized by increasing atomic number, which resolves many of the inconsistencies in the earlier arrangements.
Moseley’s discovery established the atomic number as the basis for organizing the periodic table, leading to a clearer and more accurate understanding of element properties and their relationships.
The modern periodic table helps predict the chemical behavior of elements, organize elements with similar properties, and guide the discovery of new elements. It is a critical tool for chemists.
As you move across a period, the number of protons increases, which increases the nuclear charge. This pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus, reducing the atomic radius.
Periods are horizontal rows, and groups are vertical columns. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells, while elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
The periodic law states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. This means that elements show recurring patterns in their properties when arranged by atomic number.
Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number (number of protons). This arrangement leads to periodic trends in properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
Yes, apparent weight can change when an object accelerates (e.g., feeling heavier or lighter in an elevator).
Acceleration can be measured using an accelerometer or by calculating the change in velocity over time using speed-measuring devices.
Gravity is a type of acceleration, specifically 9.8 m/s² downward near Earth’s surface, affecting all objects in free fall.
Uniform acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity changes by the same amount in equal intervals of time.
Negative acceleration (or deceleration) occurs when an object slows down, meaning its velocity decreases over time.
Yes, an object can have acceleration even if its speed is constant, as in the case of centripetal acceleration, where only the direction of velocity changes (e.g., circular motion).
Speed is the rate of change of distance, while acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared ().
Pascal’s Law states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. This principle is used in hydraulic systems like car lifts and braking systems.
A sharp knife has a smaller surface area in contact with the object, which increases the pressure for a given force, making it easier to cut.
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the Earth’s atmosphere on all objects. It is approximately at sea level.
The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa), which is equivalent to one Newton per square meter .
Hydraulic systems use pressure applied at one point to be transmitted through a fluid to another point, effectively multiplying the force applied. This principle allows for mechanisms like hydraulic lifts and brakes to function effectively.
Pressure cookers increase the boiling point of water by increasing the pressure inside the cooker. This allows food to cook faster and more efficiently at higher temperatures.
In the context of atmospheric and fluid pressures, negative pressure typically refers to a partial vacuum. However, absolute negative pressure is not physically meaningful in those contexts.
Atmospheric pressure variations are crucial in weather formation. Low pressure often leads to cloud formation and precipitation, while high pressure tends to bring clear skies.
In fluids, pressure increases with depth due to the weight of the fluid above increasing the force over a given area.
The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number of turns in the coil or by increasing the current flowing through the coil.
An electromagnet is a type of magnet created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire wound around a soft iron core.
A permanent magnet retains its magnetism over time, while a temporary magnet only behaves like a magnet when placed in a strong magnetic field.
Every magnet has two poles: a north pole and a south pole. These poles exert the strongest magnetic force.
No, only ferromagnetic metals like iron, nickel, and cobalt are strongly attracted to magnets. Other metals like aluminum and copper are not attractive.
Neodymium magnets should be recycled properly due to their rare-earth elements. Contact local recycling centers or return them to the manufacturer for proper handling.
To maintain their strength and prevent unwanted attraction of metal objects, keep magnets in a dry, mild temperature environment and store them in pairs with opposing poles facing each other.
Magnets themselves do not generate electricity, but they can be used in generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
High temperatures can weaken magnets by causing the random thermal motion of atoms, disrupting the magnetic domains.
Conserving energy is crucial for sustaining natural resources, reducing environmental impact, and maintaining ecological balance.
Renewable energy sources are those that can be replenished naturally over short timescales and include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy.
The relationship between energy and mass is famously explained by Einstein’s theory of relativity, specifically through the equation:
Where:
is the energy,
is the mass of the object,
is the speed of light in a vacuum (
).
While kinetic and potential are the primary categories, energy can manifest in various specific forms like nuclear, magnetic, or ionization energy, each associated with particular physical phenomena.
Energy is the capacity to do work, while power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred.
Energy transfer occurs when work is done on an object, transferring energy from one form to another (e.g., from potential to kinetic energy).
Mechanical energy is the sum of an object’s kinetic and potential energy.
No, according to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion, while potential energy is the stored energy due to an object’s position or configuration.
Average velocity over multiple intervals can be calculated by dividing the total displacement by the total time taken for the journey.
A change in direction affects velocity since velocity is a vector. Even if the speed remains constant, a change in direction means a change in velocity.
In projectile motion, velocity has both horizontal and vertical components, and the magnitude and direction of the velocity change over time due to gravity.
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific moment in time.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. If acceleration is positive, the velocity increases, and if acceleration is negative (deceleration), the velocity decreases.
Average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time taken. It gives the overall rate of change of position over a time interval.
The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s).
Yes, velocity can be negative if the object is moving in the opposite direction relative to a chosen reference point.
Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction.
Periscopes use a system of plane mirrors set at precise angles that allow light to enter from one end, reflect twice, and exit from the other end, enabling views over obstacles or from hidden positions.
Yes, when the object is placed between the focal point and the mirror, concave mirrors produce virtual, erect, and magnified images.
Mirrors actually do not reverse images left to right; they reverse front to back. This common misconception arises because we interpret our reflection as another person facing us.
Lateral inversion refers to the phenomenon where the left and right sides of an object are reversed in the image. This is a common property of plane mirrors and explains why words appear backward when viewed in a mirror.
The mirror formula is , where
is the focal length,
is the image distance, and
is the object distance. It is used to calculate the position and nature of the image formed by concave and convex mirrors.
Convex mirrors are used in vehicle rearview mirrors to provide a wider field of view, and they are also installed in stores and at intersections for security and safety purposes.
A real image is formed when light rays actually meet after reflection or refraction. It can be projected onto a screen and is inverted. A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point behind the mirror; it cannot be projected onto a screen and is always upright.
Concave mirrors can focus light rays to form real images when the object is beyond the focal point. However, convex mirrors cause light rays to diverge, so they always form virtual images behind the mirror, making them useful for a wider field of view.
Yes, the concept of power is also applicable in mechanical contexts, such as calculating the power output of engines or the rate at which a person does physical work.
A watt-hour measures the amount of energy used over time. Specifically, it represents the energy consumption of one watt over one hour.
Knowing about power consumption helps in estimating energy usage, managing electricity costs, and making informed decisions about using electrical appliances efficiently.
Watts are used universally in the scientific measurement of power, providing a standard unit based on the metric system. Horsepower is traditionally used in the automotive and machinery industries due to historical conventions.
Power is the rate at which energy is used or work is done, while energy is the capacity to perform work.
Examples of ideal solutions include benzene and toluene, hexane and heptane. Examples of non-ideal solutions include ethanol and acetone, phenol and aniline, and chloroform and acetone.
Non-ideal solutions show positive or negative deviations from Raoult’s law because the intermolecular interactions between solute and solvent are either weaker (positive deviation) or stronger (negative deviation) than those between the pure components.
Yes, non-ideal solutions can form azeotropes, which are mixtures that boil at a constant temperature and retain the same composition in the vapor phase as in the liquid phase.
In ideal solutions, the total vapor pressure is the same as predicted by Raoult’s law. In non-ideal solutions, the total vapor pressure is either higher or lower than the value predicted by Raoult’s law.
A non-ideal solution is one that does not obey Raoult’s law. It may show positive or negative deviation from Raoult’s law, and the enthalpy and volume changes upon mixing are not zero.
An ideal solution is a solution where the intermolecular interactions between solute-solute (A-A) and solvent-solvent (B-B) are similar to the interaction between solute-solvent (A-B). It obeys Raoult’s law, has zero enthalpy and volume change upon mixing.
Euglena is cultivated for commercial production of paramylon and has potential applications in nutrition and biotechnology due to its unique metabolic properties.
The pellicle is a flexible outer membrane composed of proteinaceous strips and microtubules, providing flexibility and shape change.
Yes, Euglena contain chloroplasts with chlorophyll, allowing them to perform photosynthesis.
The eyespot, or stigma, helps Euglena detect light and move towards it (phototaxis).
Euglena reproduce asexually through binary fission, dividing longitudinally.
Euglena are found in freshwater, saltwater, marshes, and moist soil.
Euglena are unicellular microorganisms classified under euglenoids, exhibiting both plant and animal characteristics.
Selectable markers are genes, such as antibiotic resistance genes, that allow researchers to identify cells that have taken up the plasmid.
Plasmids are important because they can be easily modified, replicated, and used to transfer genes. This makes them valuable tools in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
Ti plasmids are found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. They are used to transfer genes to plants, creating transgenic plants. They contain T-DNA and virulence genes.
The ORI is a sequence of DNA where replication begins, allowing the plasmid to replicate independently within the host cell.
A recombinant plasmid is a plasmid into which a foreign DNA fragment has been inserted. This allows for the replication and expression of the foreign gene in the host cell.
Plasmids are used as vectors to transfer and clone genes. They can be modified to carry specific genes, which are then introduced into host cells for replication and expression.
The main function of plasmids is to carry genes that can provide advantages such as antibiotic resistance. They are also used as cloning vectors in genetic engineering.
Plasmids are small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules found in bacteria and some eukaryotes. They replicate independently of chromosomal DNA.
DNA polymerases contribute to genetic variation by their role in DNA repair and replication. Errors during replication can lead to mutations, which are a source of genetic diversity.
DNA polymerase III is the primary enzyme responsible for DNA replication in E. coli. It has high processivity and a proofreading function to ensure replication accuracy.
DNA polymerases need a primer to provide a 3’-OH group for the addition of nucleotides. They cannot initiate DNA synthesis de novo.
DNA polymerase 𝝳 is the primary enzyme responsible for DNA replication in eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes, like E. coli, have five main DNA polymerases: DNA polymerase I, II, III, IV, and V, each with specific functions in replication and repair.
DNA polymerases have proofreading abilities. They possess 3’→5’ exonuclease activity that removes mismatched nucleotides and replaces them with the correct ones.
DNA polymerases are responsible for synthesizing DNA during replication and repairing damaged DNA, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic information.
Checkpoints in the cell cycle (G1, G2, and M checkpoints) ensure that the cell is ready to proceed to the next phase, preventing errors and ensuring proper cell division.
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I of meiosis, leading to genetic variation.
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through cleavage, while in plant cells, a cell plate forms to divide the cytoplasm.
Centromeres hold sister chromatids together and attach to spindle fibers, ensuring proper chromosome separation.
The stages of mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, followed by Cytokinesis.
Meiosis produces haploid gametes, ensuring genetic diversity and the correct chromosome number in offspring.
DNA replication occurs, doubling the DNA content while maintaining the same chromosome number.
Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse haploid cells.
The main phases are Interphase (G1, S, G2) and M Phase (Mitosis).
The cell cycle is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction. It ensures genetic continuity and the proper function of cells.
Polytene chromosomes are large chromosomes found in some Dipteran insects with multiple chromonemata. Lampbrush chromosomes are found in oocytes of vertebrates and invertebrates, resembling a brush due to their lateral loops.
Karyotyping is a technique used to study the structure of chromosomes and identify chromosomal abnormalities.
Nucleosomes are the basic unit of chromatin, consisting of DNA wound around histone proteins. They help in packaging DNA into a compact structure.
Heterochromatin is a darkly stained, condensed region of chromatin that is genetically inactive. Euchromatin is a light-stained, diffused region of chromatin that contains genetically active, loosely packed DNA.
The centromere joins sister chromatids and is the attachment site for spindle fibers during cell division. It plays a crucial role in the movement of chromosomes.
The main parts of a chromosome include chromatids, centromere, kinetochore, secondary constriction, nucleolar organizer, telomere, and chromatin.
Chromosomes were first observed by Karl Nägeli in 1842. W. Waldeyer coined the term ‘chromosome’ in 1888.
Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus that carry genetic information from one generation to another. They play a vital role in cell division, heredity, variation, mutation, repair, and regeneration.
Hemoglobin levels are used to diagnose various conditions such as anemia and diabetes (HbA1c levels indicate average blood glucose levels). It is also used to assess overall health and oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Some common Hemoglobin disorders include sickle cell anaemia and thalassemia, both of which affect the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Oxygen binds to the iron atom in the heme group of Hemoglobin. The binding is cooperative, meaning the binding of one oxygen molecule increases the affinity of the remaining sites for oxygen.
The primary function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from the lungs to various tissues in the body and to carry carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
The normal hemoglobin level ranges from 12 to 20 g/dL. In males, it is typically 13.5 to 17.5 g/dL, and in females, it is 12 to 15.5 g/dL.
Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells (RBCs) and constitutes about 90-95% of the dry weight of RBCs. It is also found in certain other cells such as macrophages, neurons, and alveolar cells.
The primary function of Hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from the lungs to various tissues in the body and to carry carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
Common species include Nostoc commune, Nostoc azollae, Nostoc punctiforme, Nostoc flagelliforme, and Nostoc pruniforme.
Nostoc can be found in freshwater environments, on tree trunks, rocks, and as symbionts in lichens and certain bryophytes.
Nostoc are important for nitrogen fixation, enriching soil nutrients. They also have potential uses in biofuel production, bioremediation, and the pharmaceutical industry due to their antibacterial and antiviral properties.
Nostoc reproduces vegetatively through fragmentation and asexually by forming akinetes. They also reproduce using heterocysts.
Nostoc is a genus of blue-green algae or cyanobacteria, found mainly in freshwater environments. They are capable of photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation.
Dicot leaves (dorsiventral) have reticulate venation, differentiated mesophyll (palisade and spongy cells), and more stomata on the lower surface. Monocot leaves (isobilateral) have parallel venation, undifferentiated mesophyll, and stomata equally distributed on both surfaces.
Lenticels are small openings on the surface of stems that allow for gas exchange between the internal tissues and the external environment, facilitating respiration and transpiration.
Secondary growth in dicot stems is due to the activity of the vascular cambium and cork cambium, which increase the thickness (girth) of the stem by forming secondary xylem and phloem.
Xylem conducts water and minerals from roots to stems and leaves, while phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Plant tissues are classified into two main types: Meristematic tissue (actively dividing cells) and Permanent tissue (cells that don’t divide further). Permanent tissue is further classified into Simple tissue (one type of cell) and Complex tissue (more than one type of cell).
The shape of bacteria is a fundamental characteristic used in their classification and identification. Along with staining properties, metabolic activities, and genetic analysis, the shape helps microbiologists categorize bacteria into different genera and species, aiding in diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections.
- Cocci: Streptococcus pneumoniae causes pneumonia.
- Bacilli: Bacillus anthracis causes anthrax.
- Spirilla: Helicobacter pylori causes stomach ulcers.
- Vibrio: Vibrio cholerae causes cholera
Spiral-shaped bacteria, such as spirilla and spirochetes, often have unique flagellar arrangements that allow them to move in corkscrew-like motions. This type of movement is efficient in viscous environments, helping them navigate through mucus and tissues.
Yes, some bacteria are pleomorphic, meaning they can change shape in response to environmental conditions, such as nutrient availability, temperature, and pressure. This ability allows them to adapt and survive in diverse environments.
The shape of bacteria is influenced by their genetic makeup, the structure of their cell wall, and their environmental adaptations. Rod-shaped bacteria (bacilli) often have an advantage in motility and surface attachment, while spherical bacteria (cocci) are more resistant to mechanical stress.
Different bacterial shapes contribute to their adaptability and evolutionary success. For example, the spiral shape of spirochetes allows them to move through viscous environments, while the compact shape of cocci helps them survive harsh conditions. The ability to change shape, as seen in pleomorphic bacteria, enhances their survival under varying environmental stresses.
Coccus-shaped bacteria are classified based on their arrangement as follows:
- Monococcus: Single spherical cell.
- Diplococcus: Pair of cocci.
- Streptococcus: Chain of cocci.
- Tetrads: Group of four cells.
- Staphylococcus: Irregular clusters.
- Sarcinae: Group of eight cells.
The bacterial cell wall, primarily composed of peptidoglycan, provides structural support and determines the shape of the bacteria. Variations in the composition and thickness of the peptidoglycan layer contribute to the different shapes and rigidity of the bacterial cell wall.
The shape of bacteria affects their motility, ability to adhere to surfaces, and how they interact with their environment. For instance, rod-shaped bacteria like Bacillus are often more motile due to their flagella, while spherical bacteria like Streptococcus are better at withstanding desiccation. Shape can also influence the effectiveness of antibiotics and the bacteria’s ability to evade the immune system.
The primary shapes of bacteria are spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), spiral (spirilla and spirochetes), and comma-shaped (vibrio).
Pulmonary circulation involves the exchange of gases in the lungs, while systemic circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the body and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Hypertension is caused by factors like genetics, lifestyle, stress, and underlying health conditions.
An ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart used to detect heart conditions.
The heart’s activity is regulated by the sinoatrial node (pacemaker) and the autonomic nervous system.
The Rh factor determines compatibility for blood transfusions; mismatched Rh factors can lead to immune reactions.
Oxygen is primarily transported by hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Blood consists of plasma (fluid part) and formed elements (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets).
Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Marchantia exhibits a haplodiplontic life cycle, alternating between a dominant haploid gametophyte and a short-lived diploid sporophyte.
Rhizoids anchor the plant to the substratum and absorb water and minerals.
The male antheridia and female archegonia, located on antheridiophore and archegoniophore stalks, respectively.
Through gemmae, which are multicellular buds formed in gemma cups on the gametophyte’s dorsal surface.
Marchantia thrives in moist and shady environments.
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between the air and the blood.
Asthma is caused by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty in breathing, often triggered by allergens, pollutants, or respiratory infections.
Residual volume is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forceful expiration. It prevents lung collapse and ensures continuous gas exchange even between breaths.
The diaphragm contracts during inspiration, increasing thoracic cavity volume and reducing pressure to draw air into the lungs. It relaxes during expiration, reducing volume and increasing pressure to expel air from the lungs.
Oxygen is transported in the blood primarily by binding to haemoglobin in red blood cells, forming oxyhaemoglobin.
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases, mainly oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment.
Leaf venation is important for the distribution of nutrients and water throughout the leaf. It also provides structural support to the leaf.
The two main types of inflorescence are racemose and cymose.
The stem supports the plant by providing structural support, allowing it to stand upright. It also transports water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and the leaves.
The different types of roots are tap root, fibrous root, and adventitious root.
The main function of the root in flowering plants is to anchor the plant in the soil, absorb water and nutrients, and sometimes store food.
The key features include growth, reproduction, responsiveness to stimuli, metabolism, self-organization, and mortality.
Zoological parks provide a controlled environment where the behavior and characteristics of animals can be studied, aiding in their classification and conservation.
Taxonomy focuses on the identification, naming, and classification of organisms, while systematics also includes studying their evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomic aids are tools and techniques like herbariums, museums, zoological parks, and botanical gardens used for the identification and classification of organisms.
Protoplasm is the living part of a cell where all life processes occur, making it essential for the organism’s survival and function.
Binomial nomenclature provides a standardized way to name species, ensuring each has a unique and universally recognized name.
Selective permeability is crucial because it allows the cell to maintain homeostasis by controlling the entry and exit of substances, ensuring the internal environment remains stable and suitable for cellular functions.
The fluid mosaic model is a scientific description of the plasma membrane structure, depicting it as a dynamic and fluid combination of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that move laterally within the layer.
The plasma membrane maintains fluidity through the presence of cholesterol among the phospholipids and the unsaturated fatty acid tails of phospholipids, which prevent the membrane from becoming too rigid.
The plasma membrane is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, integral and peripheral proteins, and carbohydrates.
The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell by forming a barrier between the cell’s internal environment and the external environment. It regulates the transport of materials, facilitates cell communication, and maintains the cell’s structural integrity.
Aerenchyma cells have large intercellular spaces that facilitate buoyancy and gas exchange, allowing aquatic plants to float and maintain sufficient oxygen levels for respiration.
Parenchyma cells retain their ability to divide even at maturity, which helps in wound healing and regeneration of plant tissues.
Types of parenchyma cells include chlorenchyma, transfer cells, vascular parenchyma, storage parenchyma, prosenchyma, aerenchyma, epidermis parenchyma, and conjunctive parenchyma.
Parenchyma cells are involved in storage, transport of nutrients and water, photosynthesis, gas exchange, protection, buoyancy, mechanical support, and healing and regeneration.
Parenchyma cells are found throughout the plant in the pith, cortex of stems and roots, mesophyll of leaves, flesh of fruits, and endosperm of seeds.
Parenchyma cells are living, undifferentiated cells that make up a significant portion of ground tissue in plants, performing various essential functions such as storage, photosynthesis, and regeneration.
The main types are lactic acid fermentation, alcohol fermentation, acetic acid fermentation, and butyric acid fermentation.
No, fermentation is an anaerobic process and occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Butyric acid fermentation, carried out by Clostridium bacteria, produces butyric acid, which is essential for colon health and energy.
Fermented foods improve digestion by maintaining healthy intestinal bacteria and enhancing the immune system.
Fermentation is used to produce wine, beer, biofuels, yogurt, pickles, bread, certain antibiotics, and vitamins.
Yeast converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde and CO2, and then to ethanol, regenerating NAD+ in the process.
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is reduced to lactic acid, regenerating NAD+ for glycolysis.
Fermentation is an enzyme-catalyzed metabolic process where organisms convert sugars or starches into alcohol or acid anaerobically, releasing energy.
Connective tissues like blood and lymph play crucial roles in transporting immune cells and fighting infections.
Collagen fibers provide flexibility and high tensile strength to connective tissues, making them strong and durable.
Common disorders include Marfan syndrome, epidermolysis bullosa (EB), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and scleroderma.
There are three main types: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Connective tissues support and connect various tissues and organs, providing structural integrity, protection, and insulation.
The wavelength of light determines the spacing of the fringes. Different wavelengths result in different fringe spacings, affecting the overall interference pattern.
Constructive interference occurs when the path difference is an integer multiple of the wavelength, resulting in bright fringes. Destructive interference occurs when the path difference is an odd multiple of half the wavelength, resulting in dark fringes.
The introduction of a transparent plate causes a shift in the fringe pattern towards the side with the plate, altering the path difference.
Fringe width is calculated using the formula , where
is the wavelength,
is the distance to the screen, and d is the separation between the slits.
The experiment demonstrated the wave nature of light, showing that light can exhibit interference patterns, a characteristic of waves.
Resonance describes the situation where more than one valid Lewis structure can represent a molecule, indicating delocalized electrons.
Lewis structures represent the valence electrons of atoms, showing how they share or transfer electrons to form bonds.
They are weak intermolecular forces caused by temporary dipoles in atoms or molecules, significant in nonpolar substances.
Bond enthalpy is the energy required to break one mole of a specific type of bond in a compound.
The main types are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds.
Chemical bonding refers to the attractive force that holds atoms, molecules, or ions together in a compound.
Outliers can skew the results of the correlation coefficient, making the relationship appear stronger or weaker than it actually is.
A zero correlation indicates that there is no linear relationship between the variables.
No, the correlation coefficient can indicate the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables but it cannot establish causality.
A correlation coefficient of +0.8 suggests a strong positive relationship between the variables, meaning as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well.
Pascal’s Triangle is a geometric representation of the binomial coefficients used in the theorem, where each number is the sum of the two directly above it.
Yes, the theorem can be extended to work with any real or complex exponent by using the concept of infinite series for convergence within specific bounds.
For the even value of , the middle term is the
th term. If
is odd, the middle terms are the
th term and
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \displaystyle \boldsymbol{\left[\left(\frac{n+1}{2}\right) + 1\right]}](https://deekshalearning.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5fcf241138d0d5c3c081615c0a73771a_l3.png)
They determine the weights of individual terms in the expansion, reflecting combinations in which components can occur.
Yes, the rank of a matrix is zero if and only if the matrix is a null matrix, containing all zero entries.
A square matrix is invertible if and only if its rank equals the number of its columns (or rows), meaning it has full rank.
A matrix has full rank if its rank equals the maximum possible rank it can have, which is the lesser of its number of rows or columns. This condition indicates that the matrix’s column vectors are linearly independent.
Temperature can affect the interactions between molecules in a solution, potentially leading to deviations from the predictions of Raoult’s Law.
While Raoult’s Law deals with the vapor pressure of the solvent in a solution, Henry’s Law focuses on the solubility of gases in liquids at constant temperature.
Yes, if the solute is non-volatile, Raoult’s Law can predict the decrease in vapor pressure due to the solute.
For non-ideal solutions, corrections are made using activity coefficients to account for deviations from ideal behavior.
While the effects are not directly observable in everyday life, the principle influences the development of technologies like semiconductors and lasers, which form the basis of various modern devices.
No, the principle applies to all quantum entities but is most noticeable in particles like electrons due to their small mass.
It is essential for understanding the limits of what we can know about the properties of particles at the quantum level. It reshapes our understanding of measurement, prediction, and control in quantum physics.
Some electromagnetic waves, like ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays, can be harmful due to their high energy, which can cause damage to biological tissues.
The electromagnetic spectrum is essential for understanding fundamental physical processes and is used extensively in scientific research, from astronomy to molecular chemistry.
Different types of electromagnetic waves are used in everyday technology; for example, microwaves in cooking, X-rays in medical diagnostics, and radio waves in communications.
Electromagnetic waves vary in wavelength and frequency, with radio waves having the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, and gamma rays having the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a classification of all electromagnetic waves by their respective wavelengths and frequencies, encompassing types from radio waves to gamma rays.
Normality itself does not change with temperature; however, the volume of the solvent and the dissociation of substances can be temperature-dependent, indirectly affecting the calculated normality.
Yes, normality can vary depending on the reaction it is used for because it is based on the number of equivalents, which changes with the reaction’s stoichiometry.
Normality provides a direct measure of reactive species in a solution, making it essential for achieving accurate stoichiometry in titrations.
Silicon and germanium are the most widely used elemental semiconductors, while compounds like gallium arsenide are crucial for specific applications like LEDs and lasers.
Yes, intrinsic semiconductors can conduct electricity but much less efficiently than extrinsic semiconductors, which are enhanced by doping.
N-type semiconductors have extra electrons as charge carriers, making them negatively charged. P-type semiconductors have holes as charge carriers, giving them a positive charge.
As temperature increases, more electrons gain enough energy to jump from the valence band to the conduction band, decreasing the material’s overall resistance.
A semiconductor is defined by its band gap which is small enough to allow the excitation of electrons from the valence band to the conduction band under normal conditions.
Redox reactions are used in processes like water purification and waste treatment to remove contaminants and toxins.
Balancing ensures that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed, and it allows for the quantitative analysis of the reaction.
Yes, substances like hydrogen peroxide can act as both depending on the chemical environment and the reacting species.
The oxidizing agent gains electrons and is reduced, while the reducing agent loses electrons and is oxidized.
A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons between two substances, resulting in changes in their oxidation states.
- Coulomb’s constant (k) determines the magnitude of the electrostatic force in a given medium. It varies with the permittivity of the medium, being higher in a vacuum and lower in other media.
- Coulomb’s Law not only helps in understanding the natural phenomena related to charges but also serves as a building block for more complex theories in electromagnetism and quantum physics, highlighting the interconnectivity of science across various domains.
Coulomb’s Law can be applied to spheres if they are considered as point charges located at their centers, provided the distance between them is much greater than their radii.
The force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. As the distance increases, the force decreases rapidly.
Yes, Coulomb’s Law applies to both attractive and repulsive forces. The force is attractive between opposite charges and repulsive between like charges.
Coulomb’s Law is used to calculate the electrostatic force between two point charges. It is fundamental in fields such as chemistry, physics, and electrical engineering.
De Morgan’s Theorems help transform logical expressions involving AND and OR gates into expressions using only NAND or NOR gates, facilitating simpler and more efficient circuit designs.
XOR gates are pivotal in arithmetic operations in computers, while XNOR gates are crucial for error detection and correction in digital communication systems.
Logic gates are integral to devices like computers, mobile phones, and automated systems, where they process digital signals to perform specific functions.
NAND and NOR gates are called universal because they can be used to implement any other basic logic gate, making them crucial for digital circuit design.
Basic logic gates, including OR, AND, NOT, and XOR, perform fundamental operations on binary inputs to produce a single output, based on Boolean algebra.
Isotopes are crucial for various scientific applications, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, carbon dating in archaeology, and tracing environmental changes.
Bohr’s model introduced quantum mechanics into the atomic structure, proposing that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed paths or shells and can jump between these shells by emitting or absorbing energy.
Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus of the atom and proposed that atoms consist mostly of empty space, with a dense central nucleus.
J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897 during his experiments with cathode rays.
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus, while electrons orbit this nucleus.
SHM is foundational in designing clocks, electronic oscillators, sensors, and various other devices that require precise periodic movements or signal generation.
The period (T) of SHM is the time it takes to complete one full cycle, and the frequency (f) is the number of cycles per second. These are related by the equations and
Examples of SHM include the motion of a mass attached to a spring and the swinging of a pendulum in small angular displacements.
While all SHM is oscillatory and periodic, not all oscillatory motions are SHM. SHM is characterized by its sinusoidal motion and unique stability at the equilibrium position.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement and acts in the direction towards the equilibrium position.
Common problems include indigestion, heartburn, constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These can be caused by a variety of factors, including diet, stress, and underlying medical conditions.
The large intestine absorbs water and salts from the material that has not been digested as food, and is thus crucial for maintaining the body’s fluid balance. It also serves as a storage place for waste before it is excreted from the body.
The small intestine is crucial for digestion and absorption. It is where most of the nutrients from ingested food are absorbed into the bloodstream. It utilizes enzymes secreted by the pancreas and bile from the liver to digest food completely.
The stomach mixes food with gastric juices, turning it into a semi-liquid substance called chyme. It also uses its muscular walls to physically break down food and uses enzymes and acids to perform chemical digestion.
The digestive process involves several steps: ingestion (eating), propulsion (moving food through the digestive system), mechanical digestion (breaking down food into smaller pieces), chemical digestion (breaking down food into simple molecules), absorption (taking nutrients into the bloodstream), and excretion (eliminating waste).
The human digestive system is primarily responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair. It also plays a critical role in the excretion of waste products.
Neuronal plasticity allows the brain to adapt to new information, learn from experiences, and recover from injuries, profoundly influencing behavior and cognitive functions.
The three primary types are sensory neurons, which detect environmental stimuli; motor neurons, which control muscle movements; and interneurons, which connect neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
The main parts include dendrites, which receive signals; the cell body, which processes signals; and the axon, which transmits signals to other neurons or muscles.
Neurons communicate via electrical and chemical signals. Electrical signals travel within the neuron, and chemical signals, or neurotransmitters, are released to communicate between neurons at synapses.
Neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system that transmit information throughout the body, essential for all bodily functions, from movement to cognitive processes.
Reducing noise pollution can be achieved by using soundproof materials in construction, regulating noise levels in urban areas, and promoting quieter technologies in transport and industry.
Causes of soil pollution include industrial waste, agricultural chemicals, and improper disposal of hazardous materials.
Water pollution can cause waterborne diseases, affect marine life, and lead to ecosystem imbalances.
Air pollution can lead to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and can exacerbate asthma and other lung conditions.
The main types of pollution include air, water, soil, and noise pollution.
Yes, mitosis occurs in almost all eukaryotic cells, excluding germ cells which undergo meiosis.
Both mitosis and meiosis involve prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase as part of their processes.
Meiosis produces gametes with half the chromosome number of parent cells, essential for sexual reproduction and ensuring genetic variation in offspring.
Meiosis introduces genetic diversity through processes like crossing over and independent assortment during the formation of gametes.
Mitosis serves to grow and repair tissues by producing two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell.
Mitosis occurs in most eukaryotic cells except for sex cells which undergo meiosis to produce gametes.
Errors during mitosis can lead to conditions such as cancer if cells divide uncontrollably, or genetic disorders if chromosomes are not distributed correctly.
Mitosis results in two genetically identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four genetically unique cells with half the number of chromosomes, contributing to sexual reproduction.
Cells use spindle fibers to align and pull apart chromosomes during mitosis, ensuring each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
Mitosis begins following the completion of the G2 phase of interphase, triggered by specific genetic and molecular signals that ensure the cell is ready to divide.
While naturally beneficial, an enhanced greenhouse effect due to human activity is harmful as it leads to global warming and climate change.
Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by using energy-efficient appliances, reducing waste, recycling, and opting for public transport or carpooling.
The enhanced greenhouse effect, due to increased levels of greenhouse gases from human activities, leads to global warming.
Key gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases.
It’s a natural process where gases in Earth’s atmosphere trap the Sun’s heat, maintaining the planet’s temperature.
Avoiding pollutants, not smoking, regular exercise, and a healthy diet are key to maintaining respiratory health.
Common disorders include asthma, COPD, bronchitis, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
Major parts include the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and alveoli.
Air enters through the nose or mouth, travels down the trachea to the lungs, and reaches the alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
The main function is to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment.
Dysfunctional mitochondria can lead to reduced energy production, affecting organ function and leading to symptoms like muscle weakness, neurological disorders, and organ failure.
Mitochondria are inherited maternally, which means they are passed from mothers to their children through the egg cell.
Currently, there is no cure for most mitochondrial diseases, but treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell because they produce the majority of the ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell, through the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
Enzymes are used in various industries for their catalytic properties. They are used in the food industry to enhance flavors and textures, in detergents to break down stains, and in pharmaceuticals for drug manufacture.
Enzymes are sensitive to pH and temperature because changes in these conditions can alter the enzyme’s structure. Extreme temperatures and pH levels can unfold the enzyme, rendering it inactive.
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that can decrease or block the activity of an enzyme. They are crucial in regulating enzyme activity in the body and are often used as drugs to treat diseases by inhibiting specific enzyme-targeted pathways.
Yes, enzymes can be reused. They are not consumed in the reactions they catalyze and can continue to act repeatedly on multiple substrate molecules.
Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required, facilitating the transformation of substrates into products more efficiently.
The heart ensures all bodily tissues receive adequate oxygen and nutrients and helps in the removal of metabolic wastes, which is crucial for maintaining overall health.
The heart is involved with pulmonary circulation (between the heart and lungs), systemic circulation (throughout the body), and coronary circulation (blood supply to the heart itself).
The heart is located in the middle of the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, slightly tilted towards the left.
The human heart has four chambers: two atria on the top and two ventricles on the bottom.
The main function of the human heart is to pump blood throughout the body, facilitating the circulation of oxygen, nutrients, and the removal of wastes.
Fungi play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and decomposition, making them essential for ecosystem health.
Fungi are used to produce antibiotics like penicillin and other drugs that treat various diseases.
No, while some mushrooms are edible and highly valued, others are toxic and can be fatal if consumed.
While mushrooms can be seen without aid, many fungi, such as molds and yeasts, require magnification to be observed clearly.
Fungi lack chlorophyll, do not perform photosynthesis, and have chitin in their cell walls, unlike plants.
Rainwater harvesting can be implemented in almost any type of building, but the effectiveness and capacity are influenced by factors like roof area, local rainfall patterns, and available space for tanks or other infrastructure.
Rainwater harvesting is an effective way to mitigate the effects of drought by providing an alternative water source that can be used for various non-potable and, with proper treatment, potable purposes.
Yes, challenges include the initial cost of installation, the need for regular maintenance, the dependence on rainfall patterns which can be unpredictable, and potential health risks if the water is not properly filtered or stored, leading to mosquito breeding and waterborne diseases.
Benefits include reducing water bills, increasing water availability, conserving energy, improving the quality of groundwater, and providing a reliable water supply for agricultural and landscape irrigation.
A typical system includes a catchment area to collect rainwater, a conveyance system to transport the water, a filter to remove pollutants, and storage tanks to hold the water until it is needed. Some systems include recharge structures to help replenish groundwater.
Harvesting rainwater helps mitigate water scarcity, reduces dependence on groundwater, and can significantly decrease water bills. It also lessens the impact of runoff on the environment, helping to prevent erosion and pollution.
Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting, storing, and utilizing rainwater from surfaces like rooftops and land surfaces. It helps conserve water by using it for various purposes like irrigation, washing, and even drinking, after proper treatment.
Chloroplasts are critical for photosynthesis, where plants convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in molecules of glucose.
Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, while smooth ER is involved in lipid synthesis and does not have ribosomes.
Ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis. They read the genetic instructions to build proteins from amino acids.
Mitochondria generate energy through the process of cellular respiration, converting nutrients into ATP, a molecule that powers cellular functions.
The nucleus functions as the control center of the cell, housing genetic material (DNA) and coordinating activities like growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Decomposers break down dead and decaying organisms, recycling essential nutrients back into the ecosystem, thus facilitating nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
Food chains illustrate the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another within an ecosystem, highlighting the interdependence of different species and helping maintain ecological balance.
A food chain is a linear sequence showing energy flow between organisms. A food web is a complex network of many interconnected food chains showing the various paths through which energy and nutrients flow in an ecosystem.
Consumers are classified into several types based on their diet:
- Herbivores: Consume plants.
- Carnivores: Eat other animals.
- Omnivores: Eat both plants and animals.
- Scavengers: Feed on dead organisms.
Parasites: Live off other living organisms, often harming them.
A food chain starts with producers, such as plants and algae, that generate food through photosynthesis. It ends with decomposers like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter.
A food chain describes the sequence of who eats whom in an ecosystem to show the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
Effective management of the nitrogen cycle involves practices like precision farming, using nitrogen-fixing crops to naturally enrich the soil, and regulating the use of nitrogenous fertilizers to prevent excess runoff. These practices help maintain ecological balance and reduce pollution.
The nitrogen cycle impacts the environment significantly, particularly through the leaching and runoff of excess nitrogen from agricultural fields into waterways, which can lead to eutrophication and the disruption of aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, nitrogen oxides from industrial processes contribute to air pollution and acid rain.
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a form that plants can use, such as ammonia. This process is primarily carried out by symbiotic bacteria known as diazotrophs, which include genera like Rhizobium in leguminous plants.
Plants primarily obtain nitrogen through the soil in the form of nitrates and ammonium ions, which they absorb through their roots. These forms of nitrogen are made available through the process of nitrification and nitrogen fixation by bacteria.
Nitrogen is a vital component of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are essential for the growth and function of all living organisms. It is a fundamental building block of life.
The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that transforms nitrogen and its compounds through various environmental and biological processes, including fixation, nitrification, and denitrification, making it usable for living organisms.
This law explains how genes for different traits can separate independently during gamete formation, leading to new combinations of genes and contributing to genetic diversity.
A true-breeding plant is one that, when self-pollinated, consistently produces offspring with the same traits as the parent.
Pea plants have distinct, easily observable traits, they can self-pollinate and be cross-pollinated, and they have a short generation time, making them perfect for genetic studies.
Yes, Mendel’s laws apply to all sexually reproducing organisms, including humans. However, human genetics can be more complex due to multiple genes influencing most traits.
Mendel’s laws of inheritance provide the basic framework for understanding how traits are passed from parents to offspring, which is crucial for genetics, medicine, and evolutionary biology.
Yes, imaginary numbers, like the square root of -1 (denoted as i), are not real numbers. They form part of the complex numbers when combined with real numbers.
Zero is the additive identity in real numbers, meaning any real number added to zero equals the number itself.
Yes, real numbers can be both positive and negative, including zero.
Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction with both numerator and denominator as integers, and the denominator is not zero. Irrational numbers have non-repeating, non-terminating decimals.
A real number can be any rational or irrational number. It includes all the numbers on the number line.
Yes, mensuration formulas can be extended to irregular shapes using advanced mathematical techniques like calculus, particularly for integrating areas and volumes.
The volume of a 3D object is the space it occupies, measured in cubic units, while the surface area is the total area covered by the surface of the object, measured in square units.
The area of a circle can be calculated using the formula , where “r” is the radius of the circle.
Mensuration is vital for practical applications in fields like engineering, construction, and daily life tasks such as calculating space in home projects or material requirements.
Mensuration is the branch of mathematics that deals with the measurement of various parameters of geometric figures, including area, volume, and perimeter.
It is used in various practical fields like construction, navigation, and physics to calculate distances and verify measurements.
No, Pythagoras Theorem is specifically applicable only to right-angled triangles.
The theorem can be proved by equating the area of the square on the hypotenuse with the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Pythagoras Theorem describes the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle, stating that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Complementary events are two outcomes of an event that sum to a probability of 1, such as passing or failing a test.
No, probability values range from 0 to 1.
A common example is tossing a coin, where the probability of getting heads is 0.5.
Calculate probability using the formula P(E)=(Total number of outcomes)/(Number of favorable outcomes).
Probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring, ranging from 0 (impossible) to 1 (certain).
For two functions, f and g, the quotient rule states that the derivative of their quotient is
The chain rule is used to find the derivative of composite functions. It multiplies the derivative of the outer function by the derivative of the inner function.
Trigonometric functions such as sine and cosine have specific derivatives: sin(x) differentiates to cos(x), and cos(x) differentiates to −sin(x).
The power rule states that the derivative of is
While MCQs are a crucial part of CBSE exams and practicing them can significantly boost your score, they should not be your sole focus. A well-rounded preparation strategy includes studying theoretical concepts, practicing subjective questions, and solving past papers along with MCQs. MCQs help with quick revision and testing your knowledge, but understanding the underlying concepts is key to answering both objective and descriptive questions effectively. Combine MCQ practice with a solid grasp of the syllabus for the best results in your CBSE exams.
Yes, practicing MCQs from previous years’ exams is incredibly beneficial. These questions give you insight into the types of questions that are frequently asked and the level of difficulty you can expect. They also familiarize you with the exam pattern and help identify important topics that are repeatedly tested. Additionally, practicing past MCQs under timed conditions helps build your speed and accuracy. Reviewing these questions allows you to understand the examiners’ mindset and prepares you for surprises, making your preparation more targeted and effective.
To use MCQs effectively for revision, start by selecting a chapter and attempt its corresponding MCQs without prior preparation to gauge your understanding. Analyze the results to identify weak areas and focus your revision on those topics. Revisit the chapter, making notes on key concepts. After thorough revision, reattempt the MCQs to measure your improvement. Regular practice with chapter-wise MCQs consolidates your learning and helps you retain information longer, ensuring a more comprehensive grasp of the subject material before exams.
The best approach to tackling difficult MCQs is to first eliminate options that are clearly incorrect. This increases your chances of selecting the correct answer from the remaining choices. If you’re unsure, mark the question and move on to avoid wasting time. Return to it later with a fresh perspective. During revision, focus on strengthening your weak areas so that you’re better prepared for tough questions. Finally, practice regularly with timed quizzes to build confidence and improve your ability to handle challenging MCQs under exam pressure.
Absolutely! Regular MCQ practice can significantly improve your accuracy, speed, and confidence, leading to better performance in exams.
Review the correct answer and the related concept. Re-attempt the question after revising the topic.
Aim to practice MCQs daily or at least thrice a week to keep the concepts fresh in your mind.
The difficulty of the CBSE Science paper can vary from year to year. However, with proper preparation and practice, students generally find the paper manageable. Being well-versed with the syllabus and practicing different types of questions can significantly ease the exam pressure.
Many students find “Heredity and Evolution” or “Light – Reflection and Refraction” to be among the hardest chapters in Science, due to the abstract concepts and the need for strong analytical skills. Regular practice and conceptual clarity are key to mastering these topics.
CBSE board checking for Science follows a strict marking scheme, but it is fair. Examiners are trained to award marks based on the quality of answers, adherence to the marking scheme, and presentation. It’s important to write clear and concise answers, stick to the points, and ensure all diagrams are labeled properly to score well.
To prepare for the Class 10 Science board exam, create a study schedule that covers all the chapters, with extra focus on the difficult ones. Regularly practice important questions, revise key concepts, and solve sample papers to familiarize yourself with the exam pattern. Ensure you get plenty of rest and stay calm during your study sessions.
The toughest chapter in Class 10 Science can vary from student to student. For some, chapters like “Heredity and Evolution” or “Carbon and its Compounds” may be difficult due to the complexity of the concepts. However, regular practice and understanding can make these topics easier to handle.
To score 90+ in Class 10 Science, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the concepts, practice regularly with previous years’ question papers, and take mock tests. Time management during the exam is key, so practice solving problems within a set time. Regular revision and clarification of doubts will help in achieving a high score.
Class 10 Science can be challenging for some students, particularly if they struggle with understanding the core concepts in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. However, with regular practice and a strong focus on understanding rather than rote learning, the subject becomes much more manageable.
The toughest chapter in Class 10 Maths can differ for each student. However, chapters like Trigonometry and Quadratic Equations are often considered challenging due to their complex concepts and the application of multiple formulas. Regular practice and conceptual clarity can make these topics easier to tackle.
The difficulty of the CBSE Maths paper can vary from year to year, but it is generally designed to test a student’s understanding of the subject. With proper preparation, practice, and time management, students often find the paper manageable. The key is to be well-versed with the syllabus and practice different types of questions.
The most failed subject in high school often varies by region and student demographics, but Maths tends to be a common challenge for many. The abstract nature of the subject and the need for strong problem-solving skills can make it difficult for students who struggle with the basics.
Whether History is harder than Maths depends on a student’s individual strengths and interests. History requires memorization of dates, events, and interpretations, while Maths requires logical thinking and problem-solving skills. Some students might find one easier than the other based on their learning preferences.
CBSE board paper checking is systematic and follows a strict marking scheme, but it is also fair. Examiners are trained to award marks based on the quality of answers, adherence to the marking scheme, and presentation. It’s essential to write clear, concise answers and stick to the points to score well.
The hardest subject in Class 10 varies from student to student, depending on their strengths and interests. While some find Maths or Science challenging due to their problem-solving nature, others may struggle with subjects like History or Literature, which require a lot of memorization.
To score 95+ in Class 10 CBSE Maths, focus on understanding each concept thoroughly. Regularly solve sample papers, previous years’ question papers, and take mock tests. Time management is crucial, so practice solving problems within a set time. Also, ensure you revise all formulas and theorems frequently and clarify any doubts immediately.
CBSE 10th Maths can be challenging for some students, especially if they lack clarity in fundamental concepts. The key to overcoming this difficulty is regular practice and understanding the concepts rather than rote learning. With the right approach and dedication, many students find the subject quite doable.
Class 10 CBSE Maths can be manageable if you build a strong foundation in the basics and practice regularly. The syllabus is designed to strengthen your understanding of core mathematical concepts, which are essential for higher studies. With proper guidance, consistent effort, and solving a variety of problems, you can find the subject easier than it seems.
If you find a question challenging, revisit the related concept in your textbook, seek help from a teacher, or use online resources to clarify your doubts. Practice similar questions until you feel confident in that area.
Important questions are typically those that cover fundamental concepts, are frequently asked in past exams, or are known to be challenging. They are carefully selected by our experienced educators to ensure they reflect the key areas of the curriculum.
Currently, we provide important questions for Maths and Science. However, we are continually updating our resources, and other subjects may be included in the future. Stay tuned!
While important questions are a critical part of your preparation, they should be complemented with a thorough study of the entire syllabus. Use them as a tool to focus your revision and to practice difficult concepts.
It’s recommended to integrate the practice of important questions into your daily study routine. Aim to solve a set of questions for each subject every day, gradually increasing the difficulty level as your understanding improves.
Studying biology enhances analytical, problem-solving, observational, and experimental skills. It also fosters a deeper understanding of scientific processes and critical thinking abilities applicable in various careers.
Biology provides insights into ecosystem functions and biodiversity, essential for developing effective conservation strategies, managing natural resources, and addressing issues like climate change and pollution.
Recent advancements include CRISPR gene editing technology, developments in stem cell research, and breakthroughs in synthetic biology which are revolutionizing medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
Biology impacts daily life in numerous ways, from the food we eat and the medicine we take, to understanding our own health and the sustainability of our environment.
Biology has wide applications across various fields including medicine, environmental management, agriculture, and biotechnology. It helps in developing new drugs, improving crop yields, managing natural resources, and conserving wildlife.
Major branches include botany, zoology, microbiology, genetics, and ecology. Each focuses on different aspects of life and organisms.
Biology has evolved from ancient natural philosophy to a rigorous science that includes molecular biology and biotechnology, significantly expanding our understanding of life.
Careers include healthcare, research, environmental conservation, biotechnology, and education.
It helps us understand the natural world, from individual organisms to entire ecosystems, and addresses practical challenges in health, environment, and agriculture.
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, and interaction with the environment.
Deeksha Learning continuously updates its content to align with the latest educational standards and real-world applications. They incorporate new teaching methods and technologies to ensure the material is engaging, effective, and comprehensive.
Mathematics opens the door to numerous careers in engineering, economics, data science, actuarial science, academic research, and more. Proficiency in math is also highly valued in fields like finance, consulting, and technology.
Yes, with discipline and access to the right resources, students can self-teach mathematics. Platforms like Deeksha Learning provide comprehensive materials that students can use at their own pace to build and enhance their mathematical knowledge.
Many students find mathematics challenging due to a lack of foundational understanding, math anxiety, or previous negative experiences with the subject. Personalized learning approaches, like those offered by Deeksha Learning, can help overcome these barriers.
Deeksha Learning offers a range of interactive and engaging resources that simplify complex concepts and provide extensive practice in a structured manner. Their materials cater to different learning styles and help students grasp foundational concepts and advanced topics effectively.
Basic math concepts like counting and number recognition can be introduced as early as preschool. As children grow, more complex topics can be gradually introduced to align with their cognitive development and curiosity.
Mathematics helps in managing budgets, home improvement projects, cooking, and understanding data in the news. It fosters critical thinking and decision-making skills that are vital in everyday choices.
Effective strategies include practicing regularly, understanding the concepts rather than memorizing procedures, and applying mathematics to real-life situations to better understand its usage. Additionally, seeking help when needed and using educational resources like Deeksha Learning can be very beneficial.
Parents can help by encouraging a positive attitude towards mathematics, providing a quiet study space, and ensuring their child practices regularly. Engaging in games and activities that require mathematical thinking, like puzzles or building blocks, can also enhance a child’s learning.
Mathematics is crucial because it is the foundation of sciences and technology. It teaches problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and the ability to think in abstract ways. Mathematics is used in every aspect of life, including finance, engineering, and the social sciences.
Careers in chemistry range from research and development, pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and academia to roles in government and private sectors focusing on chemical engineering, toxicology, and more.
Chemistry affects everyday life in numerous ways, including food preparation, healthcare, cleaning, and environmental management.
The main branches of chemistry include organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and biochemistry.
Chemistry is known as the central science because it connects physics with other natural sciences, such as biology and environmental science, bridging various disciplines to provide a full understanding of the natural world.
Chemistry is the science of studying substances, focusing on how they interact, combine, and change to form new materials.
They are used to indicate positions in races, ranks in classes, floors in buildings, and places in lines.
Yes, typically, ordinal numbers are written with the numeral followed by the suffix (st, nd, rd, th), such as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th.
The ordinal number for 25 is “Twenty-Fifth” (25th).
Nominal numbers are used to name or identify objects, such as vehicle registration numbers and postal codes.
Sure! “Ram finished first in his class,” and “Sarita was the third girl in line.”
Ordinal numbers indicate position or order (e.g., 1st, 2nd, 3rd), while cardinal numbers indicate quantity (e.g., 1, 2, 3).
Ordinal numbers are numbers that indicate the position or rank of something in a list, such as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc.
Yes, Kirchhoff’s Laws can be applied to both AC and DC circuits to analyze current and voltage distributions.
The negative sign in KVL indicates the direction of voltage drops and gains around the loop, ensuring the conservation of energy.
To apply KVL, identify closed loops in the circuit, choose a direction to traverse the loop, sum the voltages around the loop considering the sign of each voltage drop, and set the sum equal to zero.
To apply KCL, identify all junctions in the circuit, assign current directions, write the KCL equation for each junction, and sum the currents entering and leaving the junction to set the sum equal to zero.
Kirchhoff’s Laws are essential for analyzing and understanding electrical circuits, allowing for the calculation of current and voltage in complex networks.
Kirchhoff’s Laws were discovered by Gustav Robert Kirchhoff, a German physicist, in 1845.
Kirchhoff’s Laws consist of Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL). KCL states that the total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it, while KVL states that the sum of all voltages around a closed loop is zero.
Projectile motion is observed in various activities like throwing a ball, launching a rocket, or shooting an arrow, where gravity influences the object’s path.
Projectile motion is influenced by the initial velocity, the angle of projection, and the acceleration due to gravity.
Projectile motion is the curved path an object follows when it is thrown near the Earth’s surface, moving under the influence of gravity alone.
Full wave rectifiers are used in power supplies for electronic devices, battery charging circuits, and any application requiring a steady DC voltage.
Full wave rectifiers have higher efficiency, lower ripple factor, and provide higher output voltage and power compared to half wave rectifiers.
The rectification efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2%, which is higher than the 40.6% efficiency of a half wave rectifier.
A full wave rectifier uses either a center-tapped transformer with two diodes or a bridge configuration with four diodes to rectify both halves of the AC cycle, providing a continuous DC output.
A full wave rectifier converts the entire cycle of alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC), utilizing both halves of the AC cycle.
Ionization isomerism occurs when compounds give different ions in solution despite having the same composition.
Enantiomers are optical isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images, differing in their optical activity.
Stereoisomerism occurs when compounds have the same formula but different spatial arrangements of atoms.
Structural isomerism occurs when atoms and functional groups are connected differently.
The main types are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Isomerism is when compounds with the same chemical formula have different structures or arrangements of atoms.
Congruence can help in solving problems involving shapes and structures in geometry, ensuring designs are accurate and matching parts fit together perfectly.
CPCT stands for “Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles”
The main rules are SSS (Side-Side-Side), SAS (Side-Angle-Side), ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), AAS (Angle-Angle-Side), and RHS (Right angle-Hypotenuse-Side).
Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal, meaning they have the same shape and size.
Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions with non-zero denominators, while irrational numbers cannot be written as simple fractions and have endless, non-repeating decimals.
Rational numbers can be positive or negative. Positive if both numerator and denominator have the same sign, negative if they have opposite signs.
A number is rational if it can be written as p/q with q≠0 and can be simplified to a decimal form.
Yes, zero is a rational number because it can be expressed as 0/1.
A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where q is not zero.
Protozoa mainly reproduce asexually through binary fission. Some species can also reproduce sexually through conjugation, syngamy, or gametocytes formation.
Examples of protozoa include Trypanosoma, Amoeba, Plasmodium, and Paramecium.
Protozoa can cause diseases like malaria, amoebic dysentery, and African sleeping sickness.
Protozoa have a life cycle alternating between a dormant cyst stage and a reproductive trophozoite stage.
Protozoa move using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Some protozoa, like sporozoans, use subpellicular microtubules for slow movement.
Protozoa are found in aquatic environments, both fresh and salty. They can live freely or as parasites in plants and animals.
Protozoa are single-celled, eukaryotic organisms that can live freely or as parasites. They lack a cell wall and have various cell structures for different functions.
Ciliated epithelium, with hair-like cilia, helps move mucus and other substances in specific directions, found in respiratory and reproductive tracts.
Glandular epithelial cells are specialized for secretion. They can be unicellular (single cells like goblet cells) or multicellular (clusters like salivary glands).
Mucous membranes line cavities opening outside and secrete mucus for protection and lubrication. Serous membranes line cavities not opening outside and secrete fluid to reduce friction.
Epithelial cells include squamous (thin and flat), cuboidal (short and cylindrical), and columnar (long and cylindrical). They can form simple (single layer) or compound (multiple layers) epithelium.
Epithelial tissue consists of tightly packed cells with specialized junctions, forming a continuous layer. One surface is exposed, and the other is attached to underlying tissue.
Epithelial tissue protects against injury and infection, absorbs nutrients and water, regulates substance exchange, senses stimuli, and secretes hormones and enzymes.
Epithelial tissue forms the outer layer of the skin and lines body cavities, covering organs and structures. It protects, absorbs, senses, and secretes.
Avalanche breakdown occurs at higher voltages and involves electron collisions, while Zener breakdown occurs at lower voltages with a strong electric field breaking valence electrons free.
The Zener effect is the phenomenon where a Zener diode breaks down and allows current to flow in reverse when the reverse voltage reaches a certain level.
Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, over-voltage protection, and in clipping circuits to modify AC waveforms.
In reverse bias, a Zener diode allows a small leakage current until the breakdown voltage is reached, then it permits a stable current flow to regulate voltage.
A Zener diode is a semiconductor device designed to operate in reverse bias, allowing current to flow when the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage.
The number of questions varies, but the weightage table provides an average count based on the last five years of NEET exams, helping students understand the distribution.
The NEET 2025 syllabus has been updated to reflect the latest educational standards and topics, ensuring students prepare for current and relevant material.
Key chapters in Zoology for NEET 2025 include Animal Kingdom, Biotechnology – Principles and Processes, and Biomolecules.
Key chapters in Botany for NEET 2025 include Molecular Basis of Inheritance, Principles of Inheritance and Variation, and Cell Cycle and Cell Division.
You can download the NEET Biology Chapter Wise Weightage PDF from educational websites or coaching institutes’ resources.
Use the weightage to allocate more study time to chapters with higher weightage, ensuring thorough preparation of important topics likely to appear in the exam.
NEET Biology Chapter Wise Weightage indicates the importance of each chapter based on the number of questions typically asked in the NEET exam. This helps students prioritize their study topics.
Knowing the chapter-wise weightage helps students focus on high-priority topics, ensuring efficient study planning and better preparation for the NEET exam.
Peat is a dark substance formed from the compression and partial decomposition of mosses, used as fuel and in various industries.
Bryophytes are used in medicine, research, packing materials, as indicators of soil conditions, and in horticulture.
Bryophytes help in soil formation, prevent erosion, aid in bog succession, and recycle nutrients.
Bryophytes are classified into three classes: Hepaticopsida (liverworts), Anthocerotopsida (hornworts), and Bryopsida (mosses).
Bryophytes have a thallus-like body, lack vascular tissue, and show alternation of generations with a dominant gametophyte stage.
They are called amphibians because they live on land but require water for sexual reproduction.
Bryophytes are small, non-vascular plants including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts that thrive in damp and shady environments.
Mutual induction in transformers refers to the process where a change in current in the primary coil induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary coil through a shared magnetic field.
The main types of transformers are step-up transformers, step-down transformers, air core transformers, iron core transformers, autotransformers, power transformers, distribution transformers, measurement transformers, and protection transformers.
Transformers are used in power transmission, voltage regulation, and devices that require multiple voltage levels.
The main components are the core, windings (primary and secondary), and insulation agents.
Transformers operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction and mutual induction.
A step-up transformer increases the output voltage and decreases the output current, while a step-down transformer decreases the output voltage and increases the output current.
The primary purpose of a transformer is to change the voltage level in an AC circuit, either stepping it up or stepping it down.
Decibels (dB) measure the intensity of sound, with higher dB levels indicating louder sounds that can contribute to noise pollution.
Dense tree cover can absorb and reduce noise, helping to prevent noise pollution.
Preventive measures include banning honking in sensitive areas, installing soundproofing, controlling musical instrument volume, planting trees, and avoiding explosives in certain areas.
It can cause hypertension, hearing loss, sleep disorders, and cardiovascular issues.
Common sources include vehicles, industrial machinery, loudspeakers at events, and construction sites.
The main types are transport noise, neighborhood noise, and industrial noise.
Noise pollution is unwanted or harmful noise that disrupts the environment and can cause health problems in humans.
Forests provide clean air, help maintain ecological balance, and are a source of many resources. They need to be conserved to prevent deforestation and environmental degradation.
Only 2% of Earth’s water is freshwater, which is essential for drinking, agriculture, and other uses. Conservation efforts are important to protect this limited resource.
Clean air is essential for the health and survival of plants, animals, and humans. Reducing air pollution helps protect this vital resource.
Renewable resources can be replenished and are available in infinite quantities, like water and wind. Non-renewable resources are limited and cannot be replenished once consumed, like fossil fuels and minerals.
Natural resources are materials or substances that occur naturally in the environment and are not made by humans. Examples include air, water, soil, plants, and minerals.
Used in pathology labs for disease identification, forensic labs for fingerprint detection, microbiology for studying bacteria and viruses, and in educational institutions for academic purposes.
It offers detailed magnification, built-in light sources, and ease of use.
The main parts include the base, arm, stage, body tube, objective lenses, eyepiece, diaphragm, condenser, and reflector.
It uses an objective lens to form a real image of the specimen and an eyepiece to magnify this image into a virtual one, viewed by the observer.
A compound microscope is an optical device with high resolution that uses two sets of lenses to magnify specimens, providing a 2-dimensional image.
Carbohydrates break down to release energy, providing fuel for various bodily functions and activities.
Common sources include potatoes, maize, milk, popcorn, and bread.
Types include monosaccharides (single unit), disaccharides (two units), and polysaccharides (many units).
Carbohydrates are classified based on their structures into simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starch, cellulose).
The general formula is Cx(H2O)y, originally thought to be hydrates of carbon.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds found in living tissues and foods, breaking down to release energy. They include sugars, starch, and cellulose.
Understanding the marks vs rank data helps aspirants gauge the scores needed to achieve a specific rank, aiding in setting realistic goals and preparing effectively for the exam.
Visit the official JEE Advanced 2024 website, enter your roll number, date of birth, and registered phone number, and submit. Your result will be displayed, which you can download and print for future reference.
The minimum percentage of marks required in each subject and aggregate marks for different categories are:
- Common Rank List (CRL): 10% in each subject, 35% aggregate
- GEN-EWS and OBC-NCL: 9% in each subject, 31.5% aggregate
- SC, ST, and PwD: 5% in each subject, 17.5% aggregate
JEE Advanced ranks are determined based on the total aggregate marks out of 360. In case of a tie, higher positive marks, Mathematics marks, and Physics marks are considered sequentially to break the tie.
Limitations include errors from lead and contact resistance in low resistance measurements, insensitivity in high resistance measurements, and resistance changes due to the heating effect of current.
The Wheatstone bridge is used for precise measurement of low resistance, measuring physical parameters like temperature and strain, and determining impedance, inductance, and capacitance.
The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null deflection. When the ratio of resistances in one leg equals the ratio in the other leg, no current flows through the galvanometer, indicating the bridge is balanced.
The Wheatstone bridge was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie in 1833 and later popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1843.
The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which includes the unknown resistance.
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity in 1896.
Max Planck proposed the quantum theory of energy, which significantly advanced the understanding of atomic and subatomic processes.
Ernest Rutherford is known as the father of nuclear physics.
Albert Einstein developed the General and Special theory of relativity and introduced the concept of mass-energy equivalence (E = mc^2).
J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897.
Acids are used in food preservation, batteries, and soft drinks. Bases are used in soap making, bleaching powder, and antacids.
Conjugate acids and bases are pairs of substances that differ by one proton. An acid becomes its conjugate base after donating a proton, and a base becomes its conjugate acid after accepting a proton.
Common acids: Citric acid (in citrus fruits), acetic acid (in vinegar), lactic acid (in sour milk).
Common bases: Sodium hydroxide (in soap), calcium hydroxide (in bleaching powder), magnesium hydroxide (in antacids).
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a substance, ranging from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic).
Acids taste sour and turn blue litmus paper red, while bases taste bitter, feel slippery, and turn red litmus paper blue.
Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions (H+), and bases are substances that accept hydrogen ions.
Abscisic acid inhibits growth, induces seed dormancy, promotes leaf fall, and helps plants tolerate stress by closing stomata during water scarcity.
Plant hormones can act synergistically or antagonistically, meaning they can work together to enhance effects or oppose each other to balance growth and development processes.
Ethylene regulates fruit ripening, leaf fall, stress responses, and stimulates root hair formation.
Cytokinins promote cell division, shoot growth, delay leaf aging, and help overcome apical dominance.
Gibberellins promote stem elongation, break seed dormancy, delay aging, and induce flowering in certain plants.
Auxins promote cell elongation, maintain apical dominance, prevent premature leaf drop, and help in rooting and fruit development.
Plant hormones, or phytohormones, are chemical compounds present in low concentrations in plants, regulating growth, development, and responses to stimuli.
Common examples include batteries, mobile phones, flashlights, flat-screen TVs, and electric vehicles.
AC is converted to DC using a rectifier, which allows current to flow in only one direction.
The typical frequency of AC is either 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the country.
Most household appliances run on AC, but devices like mobile phones, laptops, and some electric vehicles use DC, often converting AC to DC for their operation.
AC is used for long-distance power transmission because it can be easily transformed to high voltages, reducing energy loss during transmission.
The main difference is that AC current changes direction periodically, while DC current flows steadily in one direction.
The area of a triangle is measured in square units, such as square meters (m²) or square centimeters (cm²).
If two sides and the included angle are known, the area can be found using ½ b c sinA, where A is the included angle, and b and c are the sides.
Heron’s formula calculates the area of a triangle when the lengths of all three sides are known. It is , where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle.
Yes, the formula applies to all types of triangles, including scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles.
The basic formula to find the area of a triangle is
Faraday concluded that a relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field changes the flux linkage, producing a voltage across the coil.
Faraday’s law is applied in transformers, induction cookers, electromagnetic flowmeters, electric guitars, and Maxwell’s equations.
Increasing the number of turns in the coil increases the induced EMF.
Lenz’s law states that the induced EMF will always oppose the change in magnetic flux that caused it.
The first law states that an EMF is induced when a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field. The second law quantifies the EMF as the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage.
Faraday’s law states that a changing magnetic field creates an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
The hydrogen spectrum problem refers to the fact that Rutherford’s model could not explain why hydrogen atoms emit light at specific wavelengths, forming a series of discrete spectral lines. This was later explained by Bohr’s model using quantum theory.
According to classical physics, orbiting electrons should continuously emit energy and lose speed, eventually collapsing into the nucleus. This would make atoms unstable, which contradicts the observed stability of matter.
Rutherford’s model laid the groundwork for future atomic theories by introducing the concept of a nucleus. It was later refined by Niels Bohr, who incorporated quantum theory to explain the stability of atoms and the hydrogen spectrum.
The nucleus is important because it contains almost all the mass of the atom and the positive charge, which influences the behavior and arrangement of the electrons.
Rutherford developed his model based on the gold foil experiment conducted in 1909. This experiment involves bombarding a thin gold foil with alpha particles and observing their scattering patterns.
Rutherford’s atomic model, also known as the nuclear atom or planetary model, describes the atom as having a small, dense nucleus at the center, containing all the positive charge, with electrons orbiting around it, similar to how planets orbit the sun.
Power is calculated by dividing the work done by the time taken. The formula is P = W / t
Power indicates how quickly work is done or energy is used, making it essential for understanding the efficiency of machines and systems.
Energy can be kinetic or potential. Other types include mechanical, chemical, electric, magnetic, radiant, nuclear, and thermal energy.
No, if there is no displacement, no work is done regardless of the force applied.
The SI unit for work and energy is the Joule (J). The SI unit for power is the Watt (W).
Energy is the ability to do work. When work is done, energy is transferred or transformed from one form to another.
Work is done when a force moves an object in the direction of the force. It is calculated as the product of force and displacement.
The order in electronic configurations follows the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first. This order determines the chemical properties and reactivity of the elements.
The subshell labels (s, p, d, f) represent different types of atomic orbitals that vary in shape and energy levels. Each subshell can hold a different maximum number of electrons: s (2), p (6), d (10), and f (14).
The electronic configuration can be written using the nearest noble gas as a prefix. For example, the electronic configuration of sodium (Na) can be written as [Ne] 3s1, where [Ne] represents the configuration of neon.
The electronic configuration of an element describes the distribution of electrons in its atomic orbitals. It is written using the subshell labels (s, p, d, f) and the number of electrons in each subshell as superscripts.
Conjugation in Paramecium is a form of sexual reproduction where two complementary cells exchange genetic material, resulting in genetic variation.
Trichocysts are defensive organelles embedded in the ectoplasm of Paramecium, used for protection.
Nutrient-rich water is drawn into the Paramecium by ciliary movement, enters the oral groove, and is digested within food vacuoles.
Paramecium are heterotrophic and primarily feed on bacteria, algae, yeast, and other microorganisms through a process called holozoic nutrition.
Cilia cover the body of Paramecium and are used for locomotion and feeding by moving water containing food particles into the oral groove.
Yes, Paramecium can reproduce sexually through conjugation, where two cells exchange genetic material, and through less common methods like autogamy and cytogamy.
Paramecium primarily reproduces asexually through binary fission, where a single cell divides into two identical cells.
Paramecium is classified in the kingdom Protista, under the phylum Ciliophora. Common species include Paramecium aurelia, Paramecium caudatum, Paramecium woodruffi, and Paramecium trichium.
Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliated protozoa found in various aquatic environments. They are characterized by their slipper shape and are covered with cilia.
Seismographs measure and record the ground motions caused by seismic waves, helping to determine the characteristics of an earthquake.
The Richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on the amplitude of seismic waves recorded by seismographs.
Earthquakes can cause ground shaking, structural damage, fires, chemical spills, landslides, and tsunamis.
Stay indoors, take cover under sturdy furniture, avoid heavy objects, and if outside, move to an open area away from hazards.
Have a readiness plan with essential supplies, secure gas lines with flexible connections, consult experts for building safety, and educate your community.
The two main types of seismic waves are S waves (side-to-side motion) and P waves (back-and-forth motion).
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy due to tectonic movements within the Earth’s crust, often at plate boundaries.
A reaction where oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. Example: Copper oxide reacting with hydrogen.
A reaction where two or more substances combine to form a compound. Example: Magnesium burning in oxygen.
A reaction where a compound breaks down into simpler substances. Example: Electrolysis of water.
A chemical reaction is a process where reactants undergo chemical changes to form products.
A chemical reaction is a process where reactants undergo chemical changes to form products.
Key enzymes in the Krebs Cycle include citrate synthase, aconitase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, succinate dehydrogenase, fumarase, and malate dehydrogenase.
NADH and FADH2 are high-energy molecules produced during the Krebs Cycle. They carry electrons to the electron transport chain, where their energy is used to generate additional ATP.
The Krebs Cycle is a key part of cellular respiration, a process that converts nutrients into energy (ATP) in the presence of oxygen. It follows glycolysis and the formation of acetyl-CoA and precedes the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation.
Each turn of the Krebs Cycle produces 2 molecules of CO2, 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2. Since each glucose molecule results in two acetyl-CoA, the cycle runs twice per glucose, yielding 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2.
The Krebs Cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells.
The Krebs Cycle is crucial for energy production in cells. It produces ATP and high-energy molecules (NADH and FADH2) that are used in the electron transport chain to generate more ATP.
The Krebs Cycle, also known as the Citric Acid Cycle, is a series of enzyme-driven reactions in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidized to produce carbon dioxide, NADH, FADH2, and ATP.
A chromatogram is a recorded plot showing the separation of components in chromatography based on their retention times.
Chromatography separates, isolates, and purifies proteins from complex mixtures, essential in protein purification strategies.
Differential extraction separates organic compounds from an aqueous solution using an immiscible organic solvent.
The main types are adsorption chromatography, thin layer chromatography, column chromatography, and partition chromatography.
Chromatography is a technique for separating, purifying, and testing compounds by using a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
There are several types of hypotheses, including simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and associative/causal hypotheses. Each type serves a specific purpose in hypothesis testing and research design.
Hypotheses can arise from various sources, including observations of phenomena, previous research findings, scientific theories, and general patterns influencing thinking processes.
Key characteristics include clarity, precision, specificity, and simplicity. A hypothesis should be clear and concise, stating the relationship between variables and allowing for further testing and analysis.
In scientific terms, a hypothesis is a testable statement or assumption about the relationship between two or more variables. It serves as a proposed explanation for observed phenomena and can be tested through experimentation or observation.
A hypothesis is an assumption made based on evidence, serving as a starting point for investigations. It’s crucial in research as it guides the direction of inquiry, allows for predictions, and provides a framework for testing relationships between variables.
Hybridization helps predict the shape and bond angles of molecules, making it easier to understand molecular geometry and bonding properties.
Yes, fully filled orbitals with slightly different energies can participate in hybridization, along with half-filled orbitals.
sp3 hybridization occurs when one s and three p orbitals mix to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals, resulting in a tetrahedral shape with 109.5° bond angles. Examples include CH4 and C2H6.
sp2 hybridization involves the mixing of one s and two p orbitals to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals, creating a trigonal planar shape with 120° bond angles. Examples include BF3 and C2H4.
sp hybridization occurs when one s and one p orbital mix to form two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals, resulting in a linear molecular shape with a 180° bond angle. Examples include BeF2 and C2H2.
There are several types of hybridization, including sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, and sp3d2, each involving different combinations of s, p, and d orbitals.
Hybridization is the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals to create new hybrid orbitals with different energies and shapes, helping to explain atomic bonding and molecular geometry.
Yes, there are changes in weightage, with some subjects seeing an increase or decrease in specific areas to balance the syllabus.
Staying updated helps students focus on relevant topics, streamline their preparation, and avoid wasting time on outdated material.
Topics such as certain experimental skills in Physics, some parts of Three Dimensional Geometry in Mathematics, and specific chapters in Chemistry have been removed or merged.
The JEE Main 2025 syllabus includes new updates like the reduction in certain topics, merging and splitting of chapters, and changes in weightage across subjects.
Yes, normalization can affect ranks as it accounts for variations in difficulty levels across different exam sessions, ensuring fair assessment.
Understanding this relationship helps students gauge their performance, set realistic goals, and make informed decisions about their future academic pursuits.
The expected cut-off varies annually. Reviewing past cut-off trends can provide a general idea of the probable cut-off for the current year.
You can download your rank card by visiting the official NTA website, logging in with your roll number and date of birth, and downloading the rank card from the link provided.
Factors include the total number of registered candidates, number of questions in the exam, difficulty level of the test, collective performance of candidates, and historical data trends.
The JEE Main marks vs. rank table helps students estimate their probable rank based on their scores. This understanding aids in setting realistic expectations and planning for the next steps in their academic journey.
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies are found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells.
The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell.
Eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually through processes like mitosis and meiosis.
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, a form of asexual reproduction.
The main difference is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both.
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They include plants, animals, and other unicellular organisms with a nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells are simple, ancient cells without a nucleus. They include bacteria and archaea.
Diverse ecosystems are more productive and resilient to environmental stress, supporting essential services for human survival.
Ecological diversity includes the variety of ecosystems in a region and the interactions among species within these ecosystems.
Genetic diversity involves the variations in the genetic makeup within species, leading to differences among individuals.
Species diversity refers to the different types of species found in a particular area. Each species shows variability among its individuals.
Biodiversity provides resources for food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and other products. It also supports tourism and recreational activities.
Biodiversity is essential for ecological stability, economic resources, and maintaining cultural and ethical values. It supports ecosystems that humans rely on for survival.
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including all plants, animals, and microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
- Treat sewage waste before releasing it into water bodies.
- Use plants like Water Hyacinth to absorb toxic chemicals.
- Apply chemical methods like precipitation and reverse osmosis.
- Reduce, reuse, and recycle materials to minimize waste.
The Ganges is heavily polluted due to industrial effluents and religious practices like burials and cremations. This pollution poses serious health risks and threatens local wildlife.
Toxic substances like cadmium and lead enter the food chain through contaminated water and accumulate in animals, disrupting the food chain at higher levels and affecting human health.
Contaminated water can cause diseases such as hepatitis, cholera, and other infectious diseases. Long-term exposure can lead to chronic health issues.
Pollution can harm aquatic animals’ health, behavior, and reproductive systems, often leading to death. Toxins accumulate in the food chain, impacting both aquatic and terrestrial life.
- Urbanization
- Deforestation
- Industrial effluents
- Social and religious practices
- Use of detergents and fertilizers
- Agricultural run-offs
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies by harmful substances, affecting all life forms that depend on water.
UV radiation affects planktons, crucial organisms in the aquatic food chain, potentially disrupting marine ecosystems.
Higher UV radiation can harm plant growth, reduce photosynthesis, and affect forest ecosystems.
Increased UV radiation can cause skin and eye cancer in animals and disrupt their natural habitats.
Depletion of the ozone layer increases UV radiation exposure, leading to higher risks of skin diseases, cancer, sunburns, cataracts, premature aging, and weakened immune systems.
Ozone layer depletion is primarily caused by chemicals containing bromine and chlorine, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), used in aerosols, refrigerants, and industrial processes.
The ozone layer absorbs most of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing it from reaching the Earth’s surface and protecting living organisms from its harmful effects.
The ozone layer is a region in the Earth’s stratosphere with high concentrations of ozone that protect the Earth from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Types include leucoplasts (storage), chloroplasts (photosynthesis), and chromoplasts (pigment storage).
Xylem cells transport water and minerals from the roots, while phloem cells transport food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
The central vacuole stores substances and helps maintain turgor pressure against the cell wall.
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis, where plants produce food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the plant cell.
Main components include the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, plastids, central vacuole, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes.
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a nucleus and specialized organelles, distinct from animal cells by the presence of a cell wall.
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they produce energy.
The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities.
Cells reproduce through mitosis (asexual reproduction) and meiosis (sexual reproduction).
Cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Cell organelles are specialized structures within a cell, each performing specific functions (e.g., mitochondria produce energy, lysosomes digest waste).
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell and provides protection.
There are two main types: Prokaryotic cells (without a nucleus) and Eukaryotic cells (with a nucleus).
A cell is the smallest unit of life, capable of performing all life processes independently.
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem.
Ecosystems maintain balance through the cycling of nutrients, energy flow, and interactions among organisms.
An ecological pyramid graphically represents the number, biomass, and energy at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
A food chain is the flow of energy from producers (plants) to consumers (herbivores, carnivores) and decomposers.
Decomposers break down dead matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: Forests, grasslands, deserts, tundra.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Freshwater (lakes, rivers) and marine (seas, oceans).
- Biotic Components: Living things (plants, animals, microorganisms).
- Abiotic Components: Non-living elements (air, water, soil, sunlight)
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their non-living environment.
Factories and industries emit large amounts of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and other chemicals that degrade air quality.
Air pollution releases chlorofluorocarbons and other chemicals that deplete the ozone layer, allowing harmful UV rays to reach Earth, causing skin diseases and eye problems.
Air pollution increases greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which traps heat and raises Earth’s temperature, leading to global warming.
Air pollution is the contamination of air by harmful substances such as gases, dust, and smoke, which can harm humans, animals, and plants.
Air pollution causes respiratory disorders, heart diseases, lung cancer, pneumonia, and asthma. It can also increase mortality rates.
Primary Pollutants: Directly cause air pollution (e.g., sulfur dioxide).
Secondary Pollutants: Formed by reactions of primary pollutants (e.g., smog).
Air pollution is the contamination of air by harmful substances such as gases, dust, and smoke, which can harm humans, animals, and plants.
Global warming affects human health by changing heat and humidity patterns, increasing the spread of diseases, and causing more frequent natural disasters.
Natural causes include volcanic eruptions, water vapour, melting permafrost, and forest fires, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Industrial activities release large amounts of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, contributing significantly to the increase in Earth’s temperature.
Vehicles burn fossil fuels, releasing CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere, which increases the greenhouse effect and raises Earth’s temperature.
Deforestation reduces the number of trees that absorb CO2 and release oxygen, leading to higher levels of CO2 in the atmosphere and increased global temperatures.
Man-made: Deforestation, vehicle emissions, industrial development, excessive use of CFCs, agriculture, and overpopulation.
Natural: Volcanic eruptions, water vapour, melting permafrost, and forest fires.
Global warming is the gradual increase in Earth’s temperature caused by the greenhouse effect from higher levels of CO2, CFCs, and other pollutants.
The formula to convert centimeters to inches is:
inches = cm × 0.393701
Knowing how to convert inches to centimeters is important for understanding and comparing measurements between the Imperial and Metric systems. This is especially useful in fields like science, engineering, construction, and international trade, where different measurement systems are used.
To use an online inches to centimeters converter, simply enter the number of inches you want to convert, and the tool will automatically calculate and display the equivalent value in centimeters.
The formula to convert inches to centimeters is:
Cm = inches × 2.54
To convert centimeters to inches, multiply the number of centimeters by 0.393701. For example, to convert 10 centimeters to inches:
10 cm × 0.393701 inches/cm = 3.93701 inches
There are 2.54 centimeters in one inch.
To convert inches to centimeters, multiply the number of inches by 2.54. For example, to convert 10 inches to centimeters:
10 inches × 2.54 cm/inch = 25.4 cm
Double angle identities express trigonometric functions of double angles:
Sum and difference identities are used to find the sine and cosine of the sum or difference of two angles:
Periodicity identities allow shifting angles by , etc.:
Reciprocal identities relate trigonometric functions to their reciprocals:
The basic trigonometric functions are:
The largest number typically written with Roman numerals is 3,999, which is MMMCMXCIX. Larger numbers are usually written using a bar over the numeral, indicating multiplication by 1,000.
100 is written as C in Roman numerals.
The Roman numeral system does not have a symbol for zero. The concept of zero was introduced later by Indian mathematicians and was not part of the Roman numeral system.
Roman numerals are used for various purposes today, such as in clock faces, book chapter titles, movie sequels, and to denote significant events or dates like the year of construction on buildings.
Roman numerals are a number system that originated in ancient Rome and are used throughout Europe until the late Middle Ages. They use combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet (I, V, X, L, C, D, and M) to represent numbers.
Percentages are preferred because they provide a common base (100), making it easier to compare different quantities directly.
Percentages are used in various real-life situations such as calculating discounts, interest rates, grades, statistics, and comparing data.
Percentages standardize different quantities for comparison. For instance, comparing test scores as percentages rather than raw marks can show performance more clearly.
To calculate a percentage, divide the part by the total and then multiply by 100.
Percentage =( Part / Total )×100
A percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. It is denoted by the symbol %. For example, 50% means 50 out of 100.
Yes, metals high in the reactivity series, such as sodium and calcium, can react with water to form hydroxides and release hydrogen gas.
Metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series can react with acids to release hydrogen gas, while metals below hydrogen do not react with acids in this way.
Hydrogen is included in the reactivity series as a reference point. Metals above hydrogen can displace hydrogen from acids, while those below cannot.
Metals like platinum and gold are at the bottom of the reactivity series. These metals are very unreactive.
Metals like caesium, francium, and potassium are at the top of the reactivity series. These metals are highly reactive.
The reactivity series helps predict how metals will react with water, acids, and in single displacement reactions. It also indicates which metals can displace others from their compounds.
The reactivity series, also known as the activity series, is a list of metals arranged in order of their reactivity from highest to lowest.
Quantum numbers are crucial because they provide a unique address for each electron in an atom, defining its energy, position, and behavior. They help predict and explain the arrangement of electrons in atoms and the resulting chemical properties.
The spin quantum number (ms) describes the intrinsic spin of the electron within an orbital. It can have one of two values: +1/2 (spin up) or -1/2 (spin down).
The magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of an orbital in space relative to the other orbitals. Its values range from -l to +l. For instance, if l=1, ml can be -1, 0, or 1.
The azimuthal quantum number (l), also known as the angular or orbital quantum number, defines the subshell and shape of the orbital. It ranges from 0 to n-1. For example, for n=3, l can be 0, 1, or 2.
The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level or shell of an electron within an atom. It can be any positive integer (1, 2, 3,…).
There are four quantum numbers:
- Principal quantum number (n)
- Azimuthal quantum number (l)
- Magnetic quantum number (ml)
- Spin quantum number (ms)
Quantum numbers are a set of values that describe the position and energy of an electron in an atom. They define the properties of atomic orbitals and the electrons in those orbitals.
Bohr’s model was eventually replaced by the quantum mechanical model, which provides a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of electron behavior and atomic structure, accounting for the principles of quantum mechanics and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
Bohr’s model is based on a simple system with one electron (like hydrogen). Larger atoms have more complex electron interactions and energy levels, which Bohr’s model could not accurately describe.
Bohr’s model explained atomic stability by proposing that electrons move in fixed orbits with specific energy levels, preventing them from spiraling into the nucleus due to electrostatic attraction.
Electrons can move from a lower to a higher energy level by absorbing energy. Conversely, they can move from a higher to a lower energy level by releasing energy. This absorption or emission of energy often results in the emission of light at specific wavelengths, forming an atomic spectrum.
Quantum numbers in Bohr’s model represent the energy levels of the orbits around the nucleus. The number (n) indicates the orbit’s distance from the nucleus and its energy level, with n=1 being the closest and lowest energy level.
Rutherford’s model described the atom with a central nucleus and electrons around it but did not explain how electrons are arranged. Bohr introduced the concept of fixed orbits with specific energy levels, providing a clearer structure for the arrangement of electrons.
Bohr’s model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1915, describes an atom with a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons moving in fixed orbits (shells) around it. Each orbit has a specific energy level.
Soil contamination occurs when harmful substances reach high concentrations. It can be due to human activities like industrial waste disposal, agricultural chemicals, improper waste management, or natural processes.
Industrial pollution contributes by discharging waste into the soil, including chemicals from mining and manufacturing. These wastes can stay on the soil surface for long periods, degrading its quality and fertility.
Agricultural activities contribute through the excessive use of pesticides and insecticides. These chemicals can degrade soil quality, reduce fertility, and become pollutants when they seep into the soil and water.
Pesticides are substances used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. While they target pests, they can unintentionally spread into the environment, causing soil and water pollution and posing health risks to humans.
Improper disposal of plastics, batteries, and other solid wastes leads to soil pollution. Harmful chemicals from these wastes can leach into the soil, making it toxic.
Acid rain occurs when pollutants in the air mix with rain and fall to the ground. It can dissolve essential soil nutrients and alter soil structure, making it unsuitable for agriculture.
Soil pollution is the presence of toxic chemicals in the soil at concentrations high enough to pose a risk to human health and the ecosystem. It is often caused by human activities that alter the natural soil composition.
The tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional folding of a polypeptide chain, stabilized by various interactions like hydrogen bonds, electrostatic forces, disulfide linkages, and van der Waals forces.
Mutations in the DNA can change the amino acid sequence in the protein’s primary structure, potentially altering its folding and function, leading to genetic disorders.
The quaternary structure refers to the spatial arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains or subunits in a protein, resulting in a functional protein complex.
The tertiary structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds, electrostatic forces, disulfide linkages, and van der Waals forces, which maintain the protein’s unique shape.
An α-helix is a right-handed spiral formed by hydrogen bonds between the -NH group of one amino acid and the -CO group of another. A β-pleated sheet consists of polypeptide chains laid side by side, bonded by hydrogen bonds, creating a sheet-like structure.
The secondary structures of proteins are local folded shapes within a polypeptide chain, such as α-helix and β-pleated sheet, stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms.
The amino acid sequence is crucial because it dictates the protein’s final three-dimensional shape, which is essential for its specific function. Any change in this sequence can alter the protein’s function.
The primary structure of a protein is the exact sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain. This sequence determines how the protein will fold and function.
Elements have different oxidation states due to their ability to lose or gain different numbers of electrons. This variability depends on the element’s electron configuration and its position in the periodic table.
Yes, many elements can have multiple oxidation states. Transition metals, in particular, often exhibit a variety of oxidation states due to their complex electron configurations.
Within a group, the number of valence electrons remains the same, so elements in the same group typically exhibit similar valency and oxidation states.
As you move from left to right across a period, the number of valence electrons increases from 1 to 8. The oxidation state can vary, usually increasing in a similar pattern until reaching group 14, then decreasing.
Valency is a specific case of oxidation state where the atom’s combining capacity is considered without assigning charges. Oxidation state, on the other hand, always involves the effective charge due to electron gain or loss.
For s-block and p-block elements, valency is typically the number of valence electrons or eight minus the number of valence electrons. For d-block and f-block elements, valency includes electrons in both valence and d or f orbitals.
The oxidation state of an atom indicates the number of electrons an atom has gained or lost. It represents the effective charge of an atom in a compound due to the transfer of electrons.
Valency is the measure of an element’s ability to combine with other elements. It represents the number of electrons an atom needs to gain, lose, or share to achieve a stable electron configuration.
The atomic mass in amu is numerically equivalent to the mass in grams of one mole of atoms of an element. For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu, so one mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 grams.
The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is an average based on natural isotope abundances and generally does not change. However, variations can occur in different samples due to isotopic enrichment or depletion.
Different isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons, which results in different atomic masses. For instance, carbon-12 has six neutrons, while carbon-13 has seven neutrons.
The atomic mass unit (amu) is a standard unit of mass that quantifies the mass of atoms and subatomic particles. 1 amu is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Atomic mass is usually not a whole number because it is a weighted average of all the isotopes of an element, each with a different mass and natural abundance.
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus and defines the element. The atomic mass includes the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, representing the element’s isotopic composition.
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of that element, measured in atomic mass units (amu). It accounts for both the mass and the relative abundance of each isotope.
The periodic table arranges elements in order of increasing atomic number, and elements with similar properties are grouped together. This arrangement helps predict an element’s reactivity, state of matter, and other chemical properties based on its position.
- Gases: Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (F), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar).
- Liquids: None.
- Solids: Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Boron (B), Carbon (C), Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Chlorine (Cl), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca).
- Hydrogen (H): Fuel, hydrogenation processes.
- Helium (He): Balloons, cooling superconducting magnets.
- Carbon (C): Organic compounds, fuels.
- Oxygen (O): Breathing, combustion.
- Sodium (Na): Table salt (NaCl), street lights.
- Calcium (Ca): Bones, teeth, cement.
Noble gases are inert, non-reactive gases located in group 18 of the periodic table. Among the first 20 elements, the noble gases are Helium (He), Neon (Ne), and Argon (Ar).
The electronic configuration is determined by the number of electrons, which is equal to the atomic number. Electrons fill energy levels (shells) around the nucleus in a specific order, following the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle.
These elements are fundamental in chemistry and biology. They include essential elements for life, such as Oxygen (O) for respiration, Carbon (C) for organic compounds, and Calcium (Ca) for bones.
Element symbols are usually derived from their English names, often using the first one or two letters (e.g., H for Hydrogen, He for Helium). Some symbols are derived from Latin names (e.g., Au from Aurum for Gold, Fe from Ferrum for Iron).
The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It determines the element’s identity and its position in the periodic table. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom, influencing the element’s chemical properties.
The first 20 elements are Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Boron (B), Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (F), Neon (Ne), Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Chlorine (Cl), Argon (Ar), Potassium (K), and Calcium (Ca).
Some element symbols are derived from their Latin names. For example, the symbol for sodium is Na, from the Latin word “Natrium.”
The heaviest naturally occurring element is Uranium (U), with an atomic number of 92.
Synthetic elements are those not found naturally and have been created artificially in laboratories. They generally have higher atomic numbers, such as Einsteinium (Es) and Fermium (Fm).
Elements are categorized as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals are typically shiny, conductive, and malleable. Nonmetals are diverse in appearance and properties, while metalloids have characteristics of both metals and nonmetals.
Groups are the vertical columns in the periodic table and indicate elements with similar chemical and physical properties. Periods are the horizontal rows and represent elements with increasing atomic numbers and different properties.
Elements are represented by one or two-letter symbols, which are often derived from their English or Latin names. For example, Hydrogen is represented as H, and Gold as Au (from Latin “Aurum”).
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.
The periodic table provides each element’s atomic number, symbol, name, and atomic mass. It may also show other properties such as electron configuration and valency.
There are 118 confirmed elements in the periodic table.
The first periodic table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, based on atomic masses and properties of elements.
The Periodic Table of Elements is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements, organized by increasing atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Force can be measured using instruments such as a spring balance or a force sensor. The deformation of the spring or the sensor is used to calculate the magnitude of the force.
The principle of superposition states that when two or more forces act on an object, the resultant force is the vector sum of the individual forces.
Gravitational force is a non-contact force that attracts any two objects with mass. The strength of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them.
The basic formula for force is given by Newton’s second law of motion:
F=ma, where
F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration.
Force can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, change its speed, change its direction, or change its shape. The effect of force on an object’s motion is described by Newton’s laws of motion.
Yes, a venturi meter uses Bernoulli’s principle to measure the flow rate of fluid through a pipe. As the fluid flows through a constricted section of the pipe, its speed increases and pressure decreases. The pressure difference is used to calculate the flow rate.
Bernoulli’s principle explains how lift is generated on an airplane wing. Airflow over the top of the wing moves faster than the airflow below, creating lower pressure above the wing and higher pressure below, resulting in an upward lift force.
The main assumptions for Bernoulli’s principle are:
- The fluid is incompressible.
- The fluid flow is steady.
- The fluid is non-viscous.
- The flow is along a streamline.
Bernoulli’s equation is derived from the principle of conservation of energy. For a flowing fluid, the total mechanical energy (comprising pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy) remains constant along a streamline.
Bernoulli’s principle states that as the speed of a fluid increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases. This principle helps explain the behavior of fluids in motion and is fundamental in fluid dynamics.
The second law dictates that natural processes tend to move towards a state of greater entropy or disorder. It explains why heat flows from hot to cold objects and why certain reactions occur spontaneously while others do not.
The first law of thermodynamics, or conservation of energy, can be seen in many everyday situations, such as heating water on a stove (converting electrical energy to thermal energy) or riding a bicycle (converting chemical energy from food into mechanical energy).
Thermal equilibrium occurs when two systems in contact with each other cease to exchange heat, resulting in the same temperature throughout both systems.
A thermodynamic system is a specific portion of matter or a space chosen for analysis. It is separated from its surroundings by a boundary which can be real or imaginary, fixed or movable.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. It quantifies how much energy in a system is unavailable for doing work and tends to increase in isolated systems.
The brain processes the electrical signals received from the retina and combines them with information from other sensory modalities to form a coherent visual image. This process involves complex neural pathways and areas of the brain dedicated to visual processing.
The optic nerve carries electrical signals from the retina to the brain, where they are interpreted as visual information. It serves as the primary pathway for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain.
The blind spot in our vision is caused by the absence of photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) where the optic nerve exits the retina. However, our brains compensate for this blind spot by filling in the missing information based on the surrounding visual information.
Rods and cones are photoreceptor cells located in the retina. Rods are responsible for vision in low light conditions and detecting motion, while cones are responsible for color vision and visual acuity in bright light.
The lens of the eye is flexible and can change shape to focus on objects at different distances. This process, known as accommodation, is controlled by the ciliary muscles surrounding the lens. When we look at objects up close, the ciliary muscles contract, causing the lens to become thicker. Conversely, when we look at distant objects, the ciliary muscles relax, causing the lens to become thinner.
The cornea is the transparent outer layer of the eye that helps to focus light onto the retina. It acts as a protective barrier and also contributes to the eye’s ability to refract light.
The main parts of the human eye include the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, and optic nerve. Each part plays a crucial role in the process of vision. The cornea and lens focus light onto the retina, while the iris and pupil control the amount of light entering the eye. The retina contains photoreceptor cells that convert light into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve for processing.
Yes, Fleming’s rules can be applied to any direction of current and magnetic field, as long as the correct orientation of the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger is maintained.
Yes, Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule can be used to determine the direction of the induced current in both AC and DC generators as long as the direction of motion and the magnetic field are known.
The left-hand rule applies to situations involving the motor effect (force on a current-carrying conductor), while the right-hand rule applies to electromagnetic induction (induced current). Using different hands helps distinguish between these two different phenomena.
The left-hand rule is used for motors to determine the direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor, while the right-hand rule is used for generators to find the direction of the induced current.
Extend the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your right hand perpendicular to each other. The thumb points in the direction of the conductor’s movement, the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, and the middle finger points in the direction of the induced current.
Extend the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand perpendicular to each other. The thumb points in the direction of the force (motion), the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, and the middle finger points in the direction of the current.
Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule is used to determine the direction of the induced current when a conductor moves through a magnetic field.
Newton’s First Law is called the Law of Inertia because it describes the inherent property of objects to resist changes in their motion. This concept of inertia is central to understanding why objects remain in their current state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an external force.
According to Newton’s Second Law, the acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to its mass. This means that heavier objects (with more mass) will accelerate less than lighter objects when the same amount of force is applied.
Friction is an external force that acts opposite to the direction of motion, causing objects to slow down and eventually stop. Without friction, an object in motion would continue moving indefinitely at a constant speed and direction.
A common example of Newton’s Third Law is the interaction between a swimmer and the water. When a swimmer pushes against the water with their hands, the water pushes back with an equal and opposite force, propelling the swimmer forward.
In the equation F = m x a, the proportionality constant is 1 when using SI units. This simplifies the relationship to a direct proportionality between force, mass, and acceleration, making it easier to calculate one if the other two are known.
Inertia is the property of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. It is the tendency of an object to remain at rest if it is at rest, or to continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed if it is in motion.
Convex mirrors are used in applications requiring a wide field of view, such as rear-view mirrors and security mirrors, due to their ability to provide a broad reflection of the scene.
Images formed by convex mirrors are always virtual, erect, and diminished, regardless of the object’s position relative to the mirror.
Convex mirrors form virtual images through reflection. Regardless of the object’s position relative to the mirror, convex mirrors always produce virtual, erect, and diminished images.
A convex mirror is a curved mirror with a reflecting surface that curves outward, resembling the outer surface of a sphere.
Concave mirrors are used in various applications, including telescopes, shaving mirrors, and headlights, due to their ability to focus light to a point.
Images formed by concave mirrors can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished, depending on the object’s position relative to the mirror.
Concave mirrors form images through reflection. Depending on the object’s position relative to the mirror, concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images.
A concave mirror is a curved mirror with a reflecting surface that curves inward, resembling the inner surface of a hollow sphere.
Temperature affects the conductivity and mobility of charge carriers in a semiconductor, thereby influencing the electrical characteristics of a P-N junction device. In general, higher temperatures lead to increased conductivity and current flow.
The depletion region is a region near the junction where charge carriers are depleted due to the combination of majority carriers from both sides. It plays a crucial role in determining the electrical behavior of the junction.
P-N junctions are used in various electronic devices, including diodes, transistors, photodiodes, solar cells, LED lighting, rectifiers, and varactors.
In forward bias, the diode conducts current easily as the external voltage reduces the potential barrier at the junction. In reverse bias, the diode blocks current flow due to the increased potential barrier, except for a small reverse saturation current.
The operating regions of a P-N junction diode are zero bias, forward bias, and reverse bias. These conditions determine the behavior of the diode with respect to current flow and voltage applied.
A P-N junction is typically formed through a process called doping, where specific impurities are introduced into a semiconductor material to alter its electrical properties and create regions of excess positive and negative charge carriers.
A P-N junction is the boundary interface between a p-type semiconductor (with excess positive charge carriers) and an n-type semiconductor (with excess negative charge carriers) within a semiconductor device.
Ohm’s Law can be applied to AC circuits, but because AC circuits involve time-varying voltages and currents, the calculations may become more complex, especially when dealing with reactive components like capacitors and inductors.
Ohm’s Law may not be suitable for components with non-linear characteristics or unilateral elements like diodes. Additionally, it assumes constant resistance, which may not hold true in certain situations.
Ohm’s Law is applicable to most passive electrical components like resistors, conductors, and simple circuits. However, it may not apply to complex components like diodes and transistors, which exhibit non-linear behavior.
Ohm’s Law is used in various applications, including designing electrical circuits, troubleshooting faults, calculating power dissipation, and selecting appropriate resistors for specific voltage and current requirements.
Ohm’s Law can be remembered using various mnemonic devices, such as the acronym VIR (Voltage equals Current times Resistance) or the “magic triangle” visualization, where you cover up the variable you want to find and see what’s left in the equation.
Voltage is measured in volts (V), current in amperes (A), and resistance in ohms (Ω).
Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. It states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Cracking KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) in a week is challenging, but with focused and strategic preparation, improvement is possible. Here are some tips to make the most of your time:
- Mock Tests and Previous Papers: Take mock tests and solve previous years‘ question papers to understand the exam pattern and identify weak areas. This helps in improving time management.
- Focus on Weak Areas: Concentrate on the subjects or topics where you feel less confident. Prioritize areas with higher weightage in the exam.
- Revision: Revise essential formulas, concepts, and key points. Create concise notes for quick reference.
- Time Management: Plan your study schedule efficiently. Allocate dedicated time to each subject and take short breaks to maintain focus.
- Stay Healthy: Ensure proper sleep, hydration, and nutrition. A healthy body and mind enhance learning and retention.
- Guidance: Seek guidance from teachers, classmates, or online resources for clarification on doubts and challenging topics.
While it’s ambitious to prepare comprehensively in a week, a targeted approach can yield positive results. Keep in mind that consistent preparation over a more extended period generally leads to better outcomes. If you’re aiming to ace the KCET exam, consider joining Deeksha’s KCET Crash Course program. With over 200 contact hours and comprehensive coverage of the syllabus, this crash course is designed to enhance your performance and boost your confidence for the upcoming KCET exam. Benefit from rigorous training, experienced faculty, and a structured approach that aims to maximize your preparation in a short span. To give your best shot at KCET, explore the advantages of Deeksha’s Crash Course and set yourself on the path to success.
The age limit for KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) is a minimum of 17 years. However, there is no upper age limit specified for candidates appearing in the KCET exam. This means that candidates must be at least 17 years old to be eligible to take the KCET exam, and there is no maximum age restriction.
It’s important to note that the eligibility criteria may vary, and candidates should refer to the official KCET guidelines and notifications for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding age requirements.
Determining the “best” engineering colleges under KCET can depend on various factors such as faculty, infrastructure, placement opportunities, and overall reputation. Here are some notable engineering colleges in India that accept KCET scores:
- Visvesvaraya Technological University
- Ramaiah Institute of Technology
- ACS College of Engineering, Bangalore
- RV College of Engineering
- PES University
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology
It’s essential to research each college individually, considering your preferences and goals. Factors like location, course offerings, campus facilities, placements and alumni networks also play a crucial role in determining the best fit for you.
The number of people writing the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) varies each year. For KCET 2023, approximately 2,61,610 candidates applied for the exam, and 2,44,345 candidates appeared for it. The number of test-takers can fluctuate annually based on factors such as academic interest, eligibility criteria, and other circumstances.
The importance of 11th-grade marks for the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) varies. While KCET primarily assesses a candidate’s knowledge in subjects like Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics (PCM), 11th-grade marks does not directly contribute to the KCET ranking. The eligibility criteria usually focus on the 12th-grade syllabus.
However, it’s crucial to note that a strong foundation in 11th-grade topics can significantly enhance a student’s performance in the KCET exam. Understanding and mastering fundamental concepts from the 11th-grade curriculum can provide a solid base for tackling the more advanced topics in the 12th-grade syllabus, which directly contributes to KCET.
In summary, while 11th-grade marks might not be explicitly considered in the KCET ranking, a thorough understanding of the 11th-grade curriculum can positively impact overall preparation and success in the examination.
There is no specific limit on the number of attempts for the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET). Candidates can appear for the exam as many times as they wish. The eligibility for KCET is based on educational qualifications, and there is no age limit or restriction on the number of attempts
When aiming to clear the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) in the first attempt, enrolling in Deeksha’s KCET Crash Course proves to be a valuable decision. Deeksha’s Crash Course is designed to guide aspirants through effective preparation strategies, focusing on intensive practice sessions to enhance performance on the final day. With over 200 contact hours and a module-wise syllabus coverage, the course ensures comprehensive preparation within a condensed time frame. The crash course provides a structured approach to tackle the KCET exam, helping students build confidence and competence. Taking advantage of Deeksha’s expertise and resources in exam preparation increases the likelihood of success in the KCET on the first attempt.
The KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in its examination. The test covers subjects like Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, and Biology depending on the course chosen. Each subject has 60 questions, and candidates are required to choose the correct answer from the provided options. The exam pattern may involve three sessions covering Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry.
It is important for candidates to refer to the KCET syllabus and previous year question papers for a comprehensive understanding of the question types and exam structure.
The advantages of taking the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) include:
- Admission into Various Courses: KCET allows candidates to secure admission into various undergraduate courses, particularly in the field of Engineering and Technology.
- Lower Fees for Karnataka Domicile Holders: KCET provides advantages in terms of fee structure, especially for Karnataka domicile holders. The fees for candidates who qualify through KCET may be comparatively lower.
- Government-Based Merit Seats: KCET is conducted to secure government-based merit seats in engineering colleges. A good rank in the KCET exam enhances the chances of obtaining a merit seat in prestigious institutions.
- Wide Range of Course Options: KCET allows candidates to explore a wide variety of courses and programs, providing flexibility in choosing a career path aligned with their interests and goals.
- Gateway to Prestigious Engineering Colleges: KCET is crucial for securing admission to prestigious engineering colleges in Karnataka, serving as a gateway to a promising academic and professional journey.
The total marks in KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) is 180. The exam consists of three subjects: Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics, each carrying 60 marks. Therefore, the overall maximum marks a candidate can score in KCET is 180.
A good score in KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) typically falls within the range of 170 to 175 marks. Scoring within this range is considered commendable and can lead to a competitive ranking in the KCET exam. It’s important to note that the exact definition of a “good score” may vary based on factors like the difficulty level of the exam and the overall performance of test-takers in a particular year.
To understand the relationship between KCET marks and rank, it’s essential to consider the following analysis:
| Marks Range | Rank Range |
| 170 – 175 | Top 10 |
| 160 – 169 | 10 – 50 |
| 150 – 159 | 50 – 200 |
| 140 – 149 | 200 – 500 |
| 130 – 139 | 500 – 1000 |
| Below 130 | 1000+ |
Preparing for the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) without coaching is entirely feasible. Many students successfully crack the KCET through self-study and strategic preparation. Tips for preparing without coaching include creating a well-structured study plan, solving previous year papers and mock tests, and managing time effectively. While coaching can provide guidance and support, it is not mandatory for KCET preparation. The key lies in understanding the exam pattern, dedicating ample time to self-study, and staying consistent with preparation strategies
On the other hand, for those who feel the need for coaching, we at Deeksha, offer a comprehensive coaching program for KCET, combining academic excellence with advanced teaching methodologies. Our crash program for CET has gained recognition for its success in preparing students effectively. Deeksha’s unique blend of technology and academics aims to bridge the gap between board exams and competitive entrance tests. The institute focuses on nurturing students by providing additional practice sets, video explanations, and personalized attention. With a reputation for helping students excel in competitive exams like KCET, JEE, NEET, and CET, Deeksha’s coaching methodology ensures a holistic approach to preparation, addressing the specific needs of students. Enrolling in Deeksha’s KCET coaching program is a strategic choice for those seeking a well-rounded and supportive learning environment to ace the KCET exam 2024.
No, the use of a calculator is not allowed in the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET). The Karnataka Examination Authority strictly prohibits the use of calculators or any other electronic devices during the KCET exam. Candidates are expected to perform all calculations manually, and the exam provides rough sheets for any necessary calculations. This policy is in line with the regulations set by the examination authorities to ensure fairness and integrity in the examination process.
Based on the paper analysis and student feedback, the difficulty level of KCET Chemistry appears to vary. The overall sentiment suggests that the Chemistry section in the KCET exam is often considered moderate in difficulty. However, the specific perception of difficulty can vary from individual to individual. Some students may find certain topics or questions more challenging than others. To enhance preparedness, it is recommended for KCET aspirants to thoroughly understand the syllabus, focus on key concepts, and practice with previous years‘ papers and mock tests
Yes, Class 12 marks do matter in the KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) admission process. While the primary focus is on the performance in the KCET exam, some colleges may consider Class 12 marks as part of their admission criteria. It is advisable for candidates to check the specific admission requirements of the colleges they are interested in, as the importance of Class 12 marks may vary among institutions. However from the KCET rank perspective, class 12 marks do matter.
Deeksha Learning fosters Class 12 academic excellence with a holistic coaching approach, bridging the gap between board and competitive exam preparation. Using proven methodologies, Deeksha imparts strategic insights, enabling students to excel in board exams. The track record, demonstrated by successful toppers, highlights the effectiveness of their approach. Offering guidance in study techniques, time management, and subject-specific nuances, Deeksha prepares students for both board exams and diverse competitive challenges. With a focus on holistic development, Deeksha creates a nurturing environment, paving the way for students’ academic success and a promising future.
Yes, KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) does have Biology as one of the subjects. The examination is conducted in four subjects: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, and Biology. Biology is a relevant subject for candidates aspiring to pursue courses in fields such as Medicine, Pharmacy, and other life sciences. The syllabus for Biology in KCET covers topics such as the Living World, Plant Kingdom, Body Fluids and Circulation, Cell Division, and more. Students preparing for KCET are advised to refer to the official syllabus and exam pattern to ensure comprehensive coverage of the Biology section.
At Deeksha, we offer effective strategies to excel in the Biology section of the KCET exam. Our proven methodology bridges the gap between board and competitive exam preparation. Utilizing careful planning and study plans, students can optimize their performance in KCET Biology.
The Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) is conducted in offline mode. As per the KCET exam pattern, the test is pen and paper-based, with candidates marking their answers on OMR sheets. This offline mode allows students to answer multiple-choice questions in a traditional exam format.
To enhance your preparation for KCET, you may consider joining Deeksha Learning’s KCET coaching program. Deeksha has earned a reputation for effectively blending technology with academics, offering comprehensive coaching for various competitive exams, including KCET. Our coaching program is designed to bridge the gap between board exams and competitive entrance tests, providing students with a well-rounded preparation. With experienced faculty, a structured curriculum, and a supportive learning environment, Deeksha’s KCET coaching equips students with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in the entrance exam and secure a successful future.
KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) does not have negative marking. In the KCET exam, candidates are awarded 1 mark for each correct answer, and there is no penalty for incorrect answers or unanswered questions. This marking scheme provides candidates the opportunity to attempt all questions without the fear of losing marks for incorrect responses.
The rank for the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) is calculated based on the scores obtained by the candidates in the test. The detailed process of calculating the CET rank involves considering the marks obtained in the PU examination. The marks vs. rank analysis is a significant aspect, where candidates can predict their ranks by understanding the correlation between their scores and the expected rank range. The calculation of the KCET merit list involves providing equal weightage, usually in a 50:50 ratio, to the marks obtained by the applicants in the KCET exam. The rank predictor tools available online can also aid candidates in estimating their probable ranks based on their scores.
Cracking KCET requires strategic preparation and a strong understanding of the exam pattern. While it may be challenging for some, effective study methods, regular revisions, and solving mock tests can enhance success rates.
By providing specialized coaching, Deeksha aims to bridge the gap between regular board exams and competitive entrance tests like KCET. Our methodology focuses on coaching students for KCET, JEE, NEET, and CET, empowering them for success in these challenging exams. The personalized approach and experienced faculty at Deeksha contribute to students’ comprehensive understanding of the syllabus, increasing their scores in the KCET exam.
Yes, while the KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) primarily focuses on the syllabus of Class 12 (2nd PUC), there are fundamental concepts that are picked up for evaluation from class 11 as well. The exam considers the subjects studied in Class 11 & 12, including Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, or Biology, depending on the chosen course. The KCET exam is typically based on the syllabus covered in the Class 11 and Class 12. For more information on the syllabus for KCET refer to the page here.
Yes, KCET (Karnataka Common Entrance Test) is open to non-Karnataka students. Eligibility criteria, including academic qualifications and other requirements, may vary for non-Karnataka students, but they are permitted to participate in the examination. It is essential for non-Karnataka students to refer to the official KCET website or contact the relevant authorities to obtain specific details regarding eligibility and admission criteria.
As of the 2024 exam, there is no specified attempt limit for the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET). Candidates are allowed to take the KCET exam any number of times without facing any restrictions on the total attempts. This lack of attempt limit provides candidates with the flexibility to appear for the KCET multiple times to improve their scores or qualifications.
To be eligible for KCET 2024, candidates must meet the following criteria:
- Educational Qualification: Candidates should have passed the 2nd PUC / class 12 or an equivalent examination.
- Mandatory Subjects: Candidates must have completed their qualifying exam with Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and Biology as compulsory subjects.
- Minimum Marks: A minimum aggregate of marks is required. For example, candidates should have secured at least 45% marks in aggregate in Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and Biology.
- Board Recognition: The qualification should be from a recognized board or institution.
- Additional Requirements: Specific documents such as a valid email ID, valid mobile phone number, and educational qualification documents are essential for the application process.
As of the latest information available, Kannada is not compulsory for all candidates appearing in the Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET). The eligibility criteria may have exemptions for candidates who have studied in the Kannada language for a certain number of academic years or those from specific regions.
It’s crucial to check the official KCET eligibility criteria provided by the Karnataka Education Authority (KEA) to confirm any recent updates or changes regarding the Kannada language requirement.
Yes, it is generally acceptable to take a gap year for KCET preparation. Many students opt for a gap year to focus on their studies and enhance their preparation for the exam. However, it’s essential to consider various factors such as the specific requirements of the college or university you plan to apply to and the impact on future placements.
With Deeksha you can prepare for both with our integrated coaching model which has a well balanced approach when it comes to pre university and competitive exam coaching.
It’s advisable to maintain continuous communication with the academic institutions and understand their policies regarding gap years. Additionally, ensure that you utilize the gap year effectively for comprehensive preparation.
Scoring above 150 in KCET demands a strategic approach to your preparation. Here are key tips to achieve this target and how Deeksha can assist you in reaching your goals:
- Thorough Syllabus Understanding: Understand the complete KCET syllabus and exam pattern to identify important topics and allocate your study time effectively.
- Create a Comprehensive Study Plan: Develop a well-structured study plan covering all subjects with a focus on high-weightage topics. Allocate sufficient time for each subject to ensure thorough coverage.
- Regular Practice with Mock Tests: Practice with KCET mock tests and previous year papers to familiarize yourself with the exam pattern. Deeksha provides additional practice sets to strengthen your preparation.
- Expert Guidance from Deeksha: Deeksha, a reputable coaching institute, offers expert guidance and comprehensive study materials to enhance your preparation for KCET.
- Personalized Learning at Deeksha: Deeksha provides personalized classes, offering ease of learning and expert guidance to help you understand complex topics effectively.
- Consistent Support and Practice: Joining Deeksha ensures consistent support, regular practice, and personalized attention, creating an environment conducive to achieving the required marks in KCET.
Remember, success in KCET requires not only hard work but also smart and focused preparation. Deeksha’s approach aims to provide students with the necessary tools and guidance to excel in the examination.
Cracking KCET in 15 days is a challenging task, but with a strategic approach, it’s possible to make efficient use of this time. Here are some tips:
- Create a Study Schedule: Allocate specific time slots for each subject based on your strengths and weaknesses. Focus on high-weightage topics.
- Practice Previous Years’ Papers: Utilize previous years’ KCET question papers for practice. It helps in understanding the exam pattern and familiarizing yourself with potential question types.
- Mock Tests: Take mock tests to simulate exam conditions. This aids in time management and enhances your problem-solving skills.
- Focused Study: Concentrate on essential topics rather than trying to cover the entire syllabus. Prioritize subjects based on their weightage in the exam.
- Seek Expert Guidance: If possible, consult with teachers or experts to clarify doubts quickly.
- Stay Healthy: Ensure proper sleep and maintain a healthy lifestyle to stay focused during your intense preparation period.
For KCET preparation, consider the following recommended books for each subject. These resources cover key topics and provide comprehensive content for effective KCET exam readiness.
Physics
- “Concepts of Physics” by H.C. Verma
- “Fundamentals of Physics” by Halliday, Resnick & Walker
Chemistry
- “Modern ABC Chemistry” by S.P. Jauhar
- “Principles of Physical Chemistry” by Puri, Sharma, and Pathania
Mathematics
- “New Course Mathematics” by S. Chand (V.K. Kapoor)
- “Higher Engineering Mathematics” by B.S. Grewal
Biology
- “NCERT Biology Textbooks” for Class 11 and 12
- “Trueman’s Elementary Biology” by K.N. Bhatia
Note: The above recommended books are just for information. To get the best book to suit your needs, consult your guide for more.
Yes, you can prepare for KCET at home. To excel in KCET from the comfort of your home, Deeksha provides effective methods to prepare for the KCET exam. Explore study tips, time management techniques, and resources to excel in the Karnataka Common Entrance Test. Our guidance and study materials can complement your preparation, ensuring a holistic approach to success.
- Understand the Syllabus: Thoroughly grasp the KCET exam syllabus.
- Devote Adequate Time: Dedicate 6-8 hours daily to your exam preparation, with short breaks in between.
- Practice Previous Year Papers: Enhance your preparation by practicing KCET previous year question papers and sample papers. When attempting sample papers, use a timer to improve speed and time management.
To prepare for KCET 2024, follow these key strategies:
- Understand the Syllabus and Exam Pattern: Know the exam structure and focus on essential topics.
- Practice Previous Year Papers: Solve KCET sample papers to familiarize yourself with the exam format.
- Create a Study Plan: Devote equal time to each subject based on the syllabus.
- Mock Tests: Take mock tests for effective time management and preparation.
The Karnataka Common Entrance Test (KCET) application process typically involves the following steps:
- Registration: Create an account on the official KCET website.
- Filling the Application Form: Provide personal, educational, and contact details.
- Uploading Documents: Upload scanned images of your photograph, signature, and other required documents.
- Payment of Fees: Pay the application fee online.
- Final Submission: Review and submit the application.
- Printout: Take a printout of the application form for future reference.
Remember to check the eligibility criteria before applying and adhere to the specified. To know more read our detailed guide on KCET Application Process



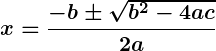
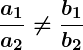 , the lines intersect and there is a unique solution.
, the lines intersect and there is a unique solution.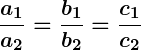 , the lines are coincident and there are infinitely many solutions.
, the lines are coincident and there are infinitely many solutions.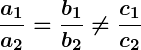 , the lines are parallel and there is no solution.
, the lines are parallel and there is no solution.







Get Social