What is Protozoa?
Protozoa are single-celled, eukaryotic organisms that can either live freely or as parasites. There are around 65,000 species of protozoa. They lack a cell wall and have various cell structures performing functions similar to higher animals’ organs. Protozoa can cause diseases like malaria (Plasmodium), sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma), and trichomoniasis (Trichomonas).
General Characteristics of Protozoa
- Habitat: Protozoa live in water environments, both fresh and salty. Some live freely, while others are parasitic. They can be aerobic or anaerobic, found in places like the human intestine.
- Size and Shape: Protozoa vary in size from microscopic to visible. They lack a rigid cell wall, making them flexible and variable in shape.
- Cell Structure: They are unicellular with a eukaryotic cell structure. They have one or more nuclei and various organelles for different functions. The plasma membrane surrounds the cell, and some have a pellicle for shape and movement.
- Nutrition: Protozoa are heterotrophic, consuming food through phagocytosis. They have structures like pseudopodia for capturing food.
- Locomotion: Protozoa move using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Sporozoa move slowly using subpellicular microtubules.
- Life Cycle: Protozoa alternate between a dormant cyst stage and a reproductive trophozoite stage.
- Reproduction: Mostly reproduce asexually through binary fission, with some capable of sexual reproduction.
Protozoa Classification and Examples
Protozoa are classified based on their structure and movement:
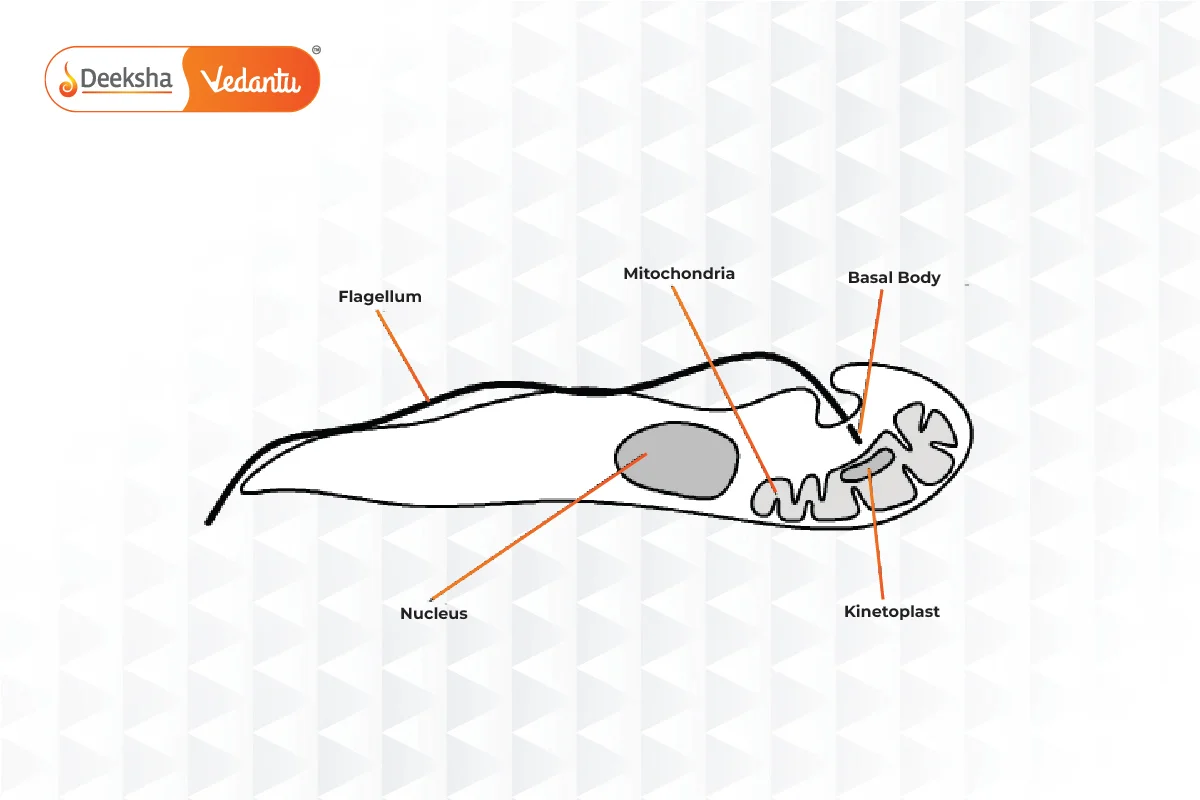
- Mastigophora (Flagellated Protozoans)
- Characteristics: Use flagella for movement, covered by a pellicle.
- Examples: Trypanosoma, Trichomonas, Giardia.
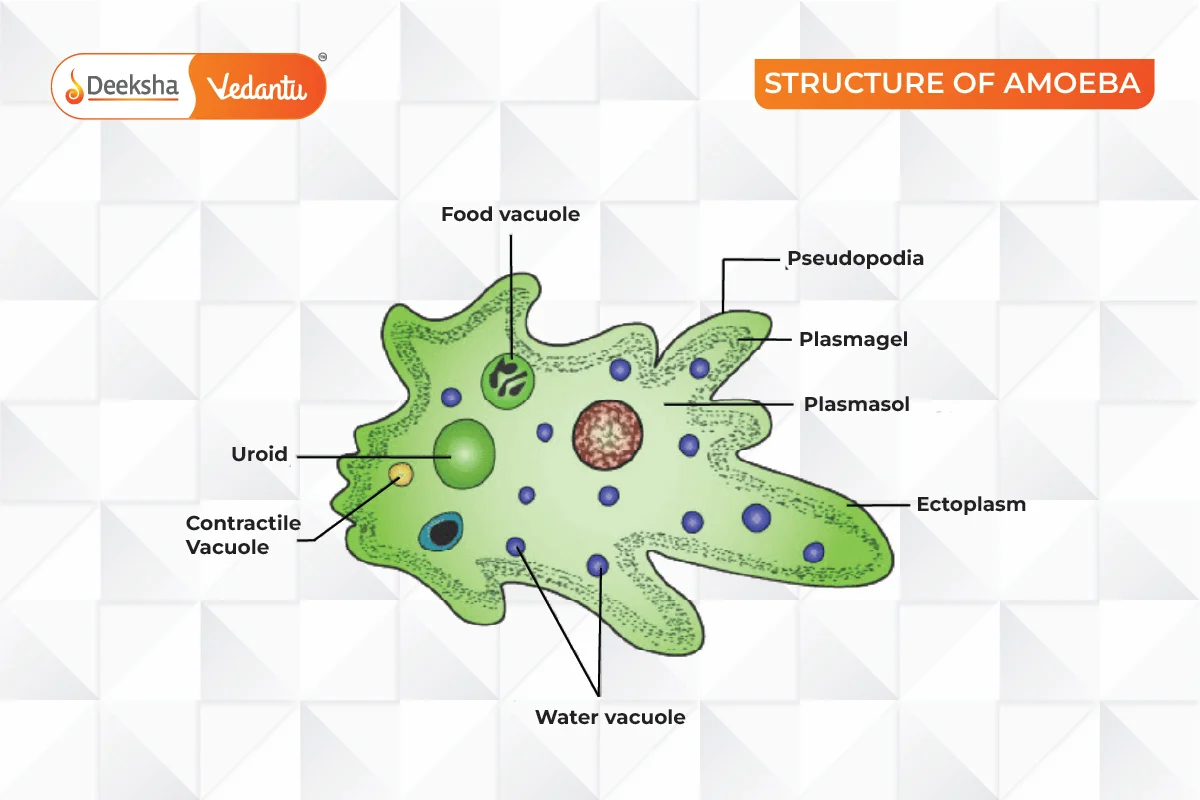
- Sarcodina (Amoeboids):
- Characteristics: Move using pseudopodia, lack a definite shape.
- Examples: Amoeba, Entamoeba.
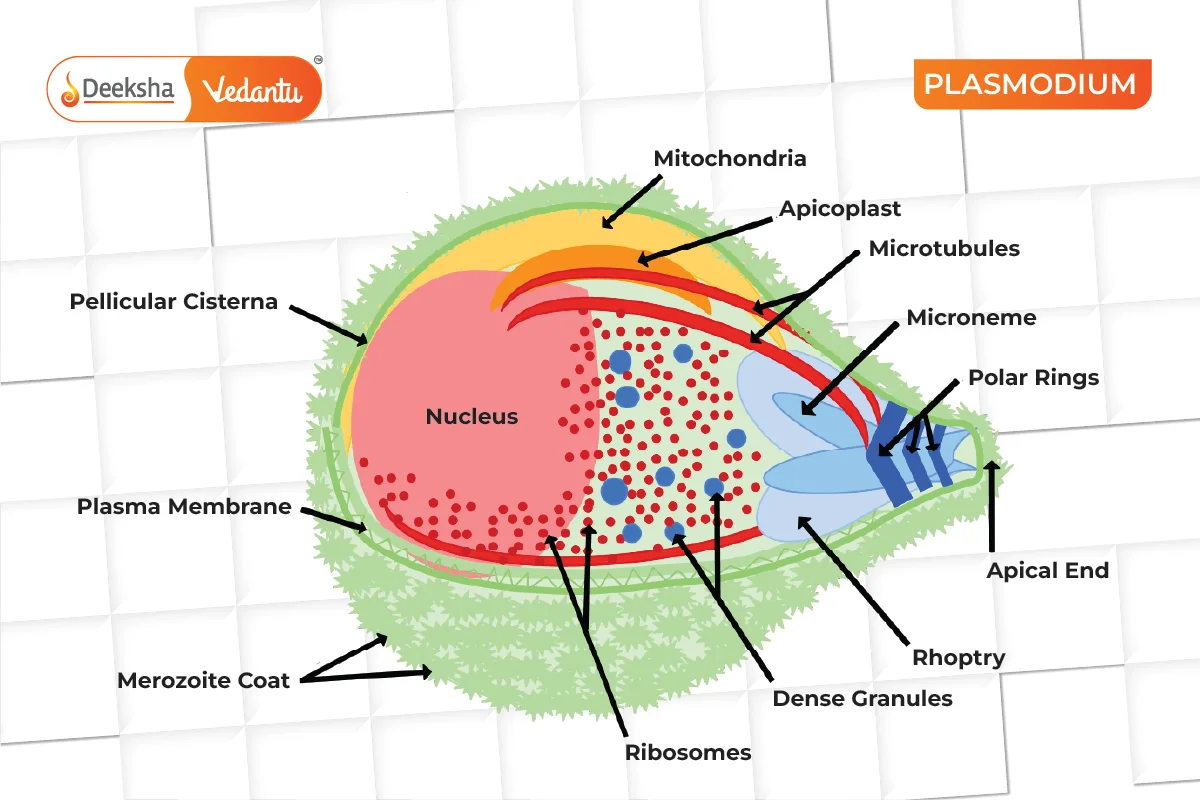
- Sporozoa (Sporozoans):
- Characteristics: Endoparasitic, no specialized movement organelles.
- Examples: Plasmodium, Myxidium.
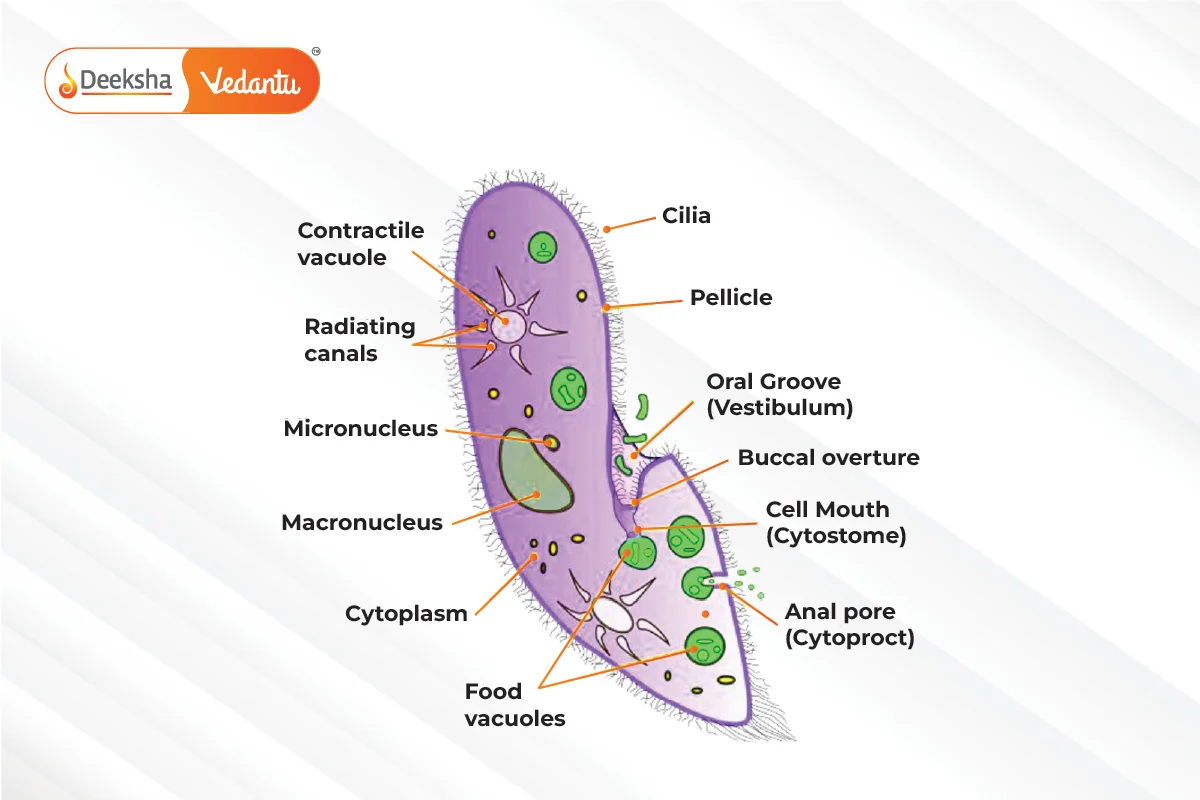
- Ciliophora (Ciliated Protozoans):
- Characteristics: Move using cilia, have a fixed shape due to pellicle.
- Examples: Paramecium, Vorticella.
Protozoan Diseases in Humans
Protozoa can cause diseases when they become parasites in humans, leading to illnesses like malaria, amoebic dysentery, and sleeping sickness. These protozoa can multiply in humans, spreading through contaminated water, food, or insect bites.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria
Bacterial diseases are caused by harmful bacteria releasing toxins. Examples include bacterial meningitis, diphtheria, tetanus, cholera, and tuberculosis.
Diseases Caused by Fungi
Fungal infections, or mycosis, are caused by fungi reproducing through spores. These infections can affect the skin, nails, or internal organs. Examples include ringworm, athlete’s foot, and candidiasis.
FAQs
Protozoa mainly reproduce asexually through binary fission. Some species can also reproduce sexually through conjugation, syngamy, or gametocytes formation.
Examples of protozoa include Trypanosoma, Amoeba, Plasmodium, and Paramecium.
Protozoa can cause diseases like malaria, amoebic dysentery, and African sleeping sickness.
Protozoa have a life cycle alternating between a dormant cyst stage and a reproductive trophozoite stage.
Protozoa move using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Some protozoa, like sporozoans, use subpellicular microtubules for slow movement.
Protozoa are found in aquatic environments, both fresh and salty. They can live freely or as parasites in plants and animals.
Protozoa are single-celled, eukaryotic organisms that can live freely or as parasites. They lack a cell wall and have various cell structures for different functions.
Related Topics
- DNA Polymerases
- Types of Fermentation
- Plant Hormones
- Difference between Ideal Solution and Non-ideal Solution
- Euglena
- Krebs Cycle
- Connective Tissue
- Marchantia
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Paramecium
- Epithelial Tissue
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Chromosome Structure
- What is Hemoglobin
- Bryophytes
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Body Fluids and Circulation











Get Social