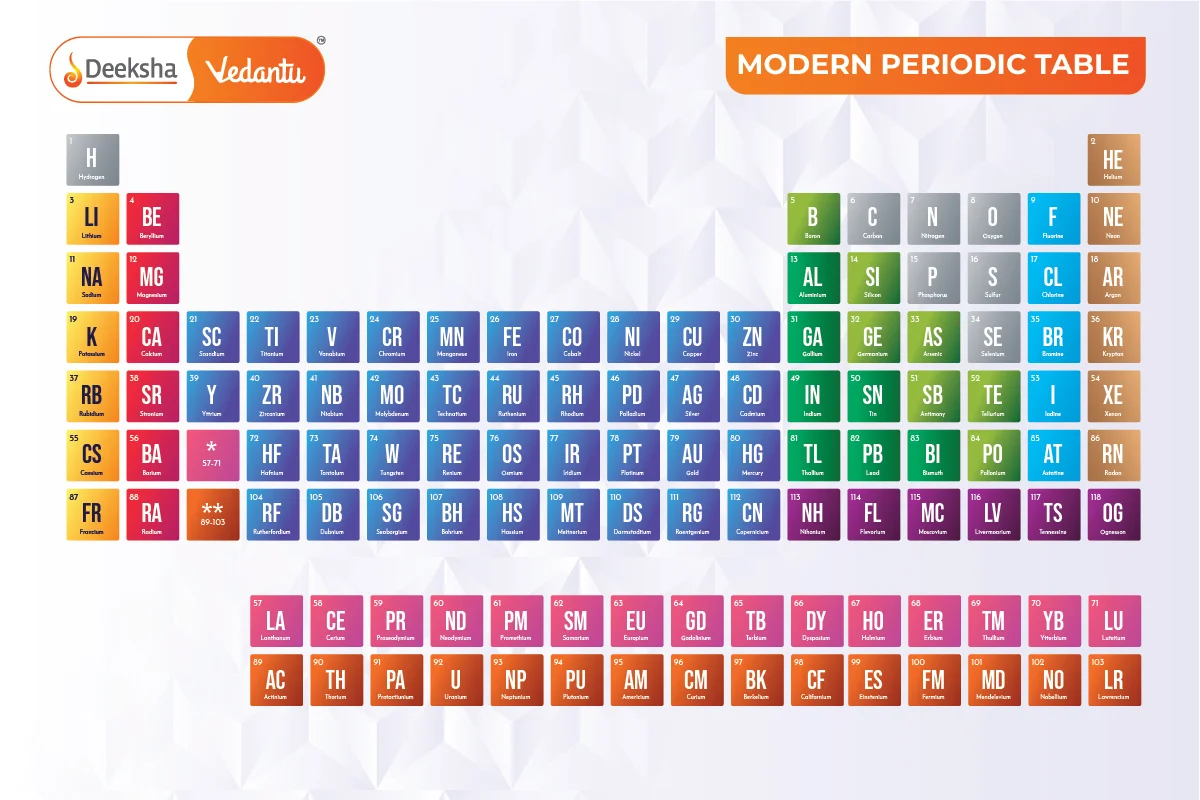
The periodic table is an essential tool widely used by scientists, professionals, teachers, and students of chemistry to find information about chemical elements. It was first developed by Dimitri Mendeleev, who is known as the Father of the Periodic Table. Mendeleev’s table was based on the atomic mass of the elements known at his time. The modern periodic table, however, is based on Henry Moseley’s periodic law, which states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. The periodic table now includes 118 elements.
Key Characteristics of the Periodic Table
- Order of Arrangement: Elements are arranged in increasing atomic numbers.
- Symbol Representation: Elements are denoted by unique symbols, typically one or two letters. Symbols may also have three letters for newly synthesized elements.
- Groups and Periods: Elements are organized in vertical columns called ‘Groups’ and horizontal rows called ‘Periods’.
- Periodic Trends: Elements are grouped based on similar properties and trends, such as elements in group 1A being soft metals that react with water.
118 Elements – Their Symbols and Atomic Number
| Element | Atomic Number | Element Symbol |
| Hydrogen | 1 | H |
| Helium | 2 | He |
| Lithium | 3 | Li |
| Beryllium | 4 | Be |
| Boron | 5 | B |
| Carbon | 6 | C |
| Nitrogen | 7 | N |
| Oxygen | 8 | O |
| Fluorine | 9 | F |
| Neon | 10 | Ne |
| Sodium | 11 | Na |
| Magnesium | 12 | Mg |
| Aluminum | 13 | Al |
| Silicon | 14 | Si |
| Phosphorous | 15 | P |
| Sulfur | 16 | S |
| Chlorine | 17 | Cl |
| Argon | 18 | Ar |
| Potassium | 19 | K |
| Calcium | 20 | Ca |
| Scandium | 21 | Sc |
| Titanium | 22 | Ti |
| Vanadium | 23 | V |
| Chromium | 24 | Cr |
| Manganese | 25 | Mn |
| Iron | 26 | Fe |
| Cobalt | 27 | Co |
| Nickel | 28 | Ni |
| Copper | 29 | Cu |
| Zinc | 30 | Zn |
| Gallium | 31 | Ga |
| Germanium | 32 | Ge |
| Arsenic | 33 | As |
| Selenium | 34 | Se |
| Bromine | 35 | Br |
| Krypton | 36 | Kr |
| Rubidium | 37 | Rb |
| Strontium | 38 | Sr |
| Yttrium | 39 | Y |
| Zirconium | 40 | Zr |
| Niobium | 41 | Nb |
| Molybdenum | 42 | Mo |
| Technetium | 43 | Tc |
| Ruthenium | 44 | Ru |
| Rhodium | 45 | Rh |
| Palladium | 46 | Pd |
| Silver | 47 | Ag |
| Cadmium | 48 | Cd |
| Indium | 49 | In |
| Tin | 50 | Sn |
| Antimony | 51 | Sb |
| Tellurium | 52 | Te |
| Iodine | 53 | I |
| Xenon | 54 | Xe |
| Cesium | 55 | Cs |
| Barium | 56 | Ba |
| Lanthanum | 57 | La |
| Cerium | 58 | Ce |
| Praseodymium | 59 | Pr |
| Neodymium | 60 | Nd |
| Promethium | 61 | Pm |
| Samarium | 62 | Sm |
| Europium | 63 | Eu |
| Gadolinium | 64 | Gd |
| Terbium | 65 | Tb |
| Dysprosium | 66 | Dy |
| Holmium | 67 | Ho |
| Erbium | 68 | Er |
| Thulium | 69 | Tm |
| Ytterbium | 70 | Yb |
| Lutetium | 71 | Lu |
| Hafnium | 72 | Hf |
| Tantalum | 73 | Ta |
| Tungsten | 74 | W |
| Rhenium | 75 | Re |
| Osmium | 76 | Os |
| Iridium | 77 | Ir |
| Platinum | 78 | Pt |
| Gold | 79 | Au |
| Mercury | 80 | Hg |
| Thallium | 81 | Tl |
| Lead | 82 | Pb |
| Bismuth | 83 | Bi |
| Polonium | 84 | Po |
| Astatine | 85 | At |
| Radon | 86 | Rn |
| Francium | 87 | Fr |
| Radium | 88 | Ra |
| Actinium | 89 | Ac |
| Thorium | 90 | Th |
| Protactinium | 91 | Pa |
| Uranium | 92 | U |
| Neptunium | 93 | Np |
| Plutonium | 94 | Pu |
| Americium | 95 | Am |
| Curium | 96 | Cm |
| Berkelium | 97 | Bk |
| Californium | 98 | Cf |
| Einsteinium | 99 | Es |
| Fermium | 100 | Fm |
| Mendelevium | 101 | Md |
| Nobelium | 102 | No |
| Lawrencium | 103 | Lr |
| Rutherfordium | 104 | Rf |
| Dubnium | 105 | Db |
| Seaborgium | 106 | Sg |
| Bohrium | 107 | Bh |
| Hassium | 108 | Hs |
| Meitnerium | 109 | Mt |
| Darmstadtium | 110 | Ds |
| Roentgenium | 111 | Rg |
| Copernicium | 112 | Cn |
| Nihonium | 113 | Nh |
| Flerovium | 114 | Fl |
| Moscovium | 115 | Mc |
| Livermorium | 116 | Lv |
| Tennessine | 117 | Ts |
| Oganesson | 118 | Og |
Symbols of Elements
A chemical element’s symbol is a shorthand notation, usually consisting of one or two letters derived from its English name. Some symbols are derived from Latin or Greek names, like ‘Au’ for gold (Aurum) and ‘Fe’ for iron (Ferrum).
Conventions for Symbols
- The first letter of a symbol is capitalized, and any subsequent letters are lowercase (e.g., ‘Ca’ for Calcium, ‘He’ for Helium).
- Single-letter symbols are always capitalized (e.g., ‘N’ for Nitrogen, ‘O’ for Oxygen).
Importance for Students
Understanding and memorizing the symbols and valency of the 118 elements is crucial for writing chemical formulas and equations efficiently.
Valency of an Element
Valency is the ability of an atom to gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable configuration, often similar to noble gases. The valency is determined by the number of electrons in the outermost shell (valence electrons).
Atomic Number
The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is denoted by ‘Z’. It determines the chemical properties of an element.
Occurrence of Elements
Out of the 118 elements:
- 98 are found in nature (Hydrogen ‘H’ to Californium ‘Cf’).
- The rest are synthesized in laboratories (e.g., Einsteinium ‘Es’, Fermium ‘Fm’, and Nobelium ‘No’).
Nature of Occurrence
- Noble gases and some metals like gold, silver, and copper occur in their pure form.
- Most elements occur naturally but not in their native form; they are usually found as compounds.
FAQs
Some element symbols are derived from their Latin names. For example, the symbol for sodium is Na, from the Latin word “Natrium.”
The heaviest naturally occurring element is Uranium (U), with an atomic number of 92.
Synthetic elements are those not found naturally and have been created artificially in laboratories. They generally have higher atomic numbers, such as Einsteinium (Es) and Fermium (Fm).
Elements are categorized as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals are typically shiny, conductive, and malleable. Nonmetals are diverse in appearance and properties, while metalloids have characteristics of both metals and nonmetals.
Groups are the vertical columns in the periodic table and indicate elements with similar chemical and physical properties. Periods are the horizontal rows and represent elements with increasing atomic numbers and different properties.
Elements are represented by one or two-letter symbols, which are often derived from their English or Latin names. For example, Hydrogen is represented as H, and Gold as Au (from Latin “Aurum”).
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.
The periodic table provides each element’s atomic number, symbol, name, and atomic mass. It may also show other properties such as electron configuration and valency.
There are 118 confirmed elements in the periodic table.
The first periodic table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, based on atomic masses and properties of elements.
The Periodic Table of Elements is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements, organized by increasing atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Related Topics
- Classification of Carbohydrates and its Structure
- Understanding the Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
- Metals and Non-Metals
- Types of Chemical Reactions
- Reactivity Series
- Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Versatile Nature Of Carbon
- Modern Periodic Table
- Acids and Bases
- Chemical Properties Of Carbon Compounds
- Chemical Formula
- Natural Resources
- Corrosion
- Chemistry FAQs
- How Strong Are Acid Or Base Solutions?












Get Social