Introduction to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
All living organisms, from tiny bacteria to giant trees, are made up of cells, the basic units of life. Cells were first observed by Robert Hooke in 1665. He named them cells because they looked like small rooms in a honeycomb.
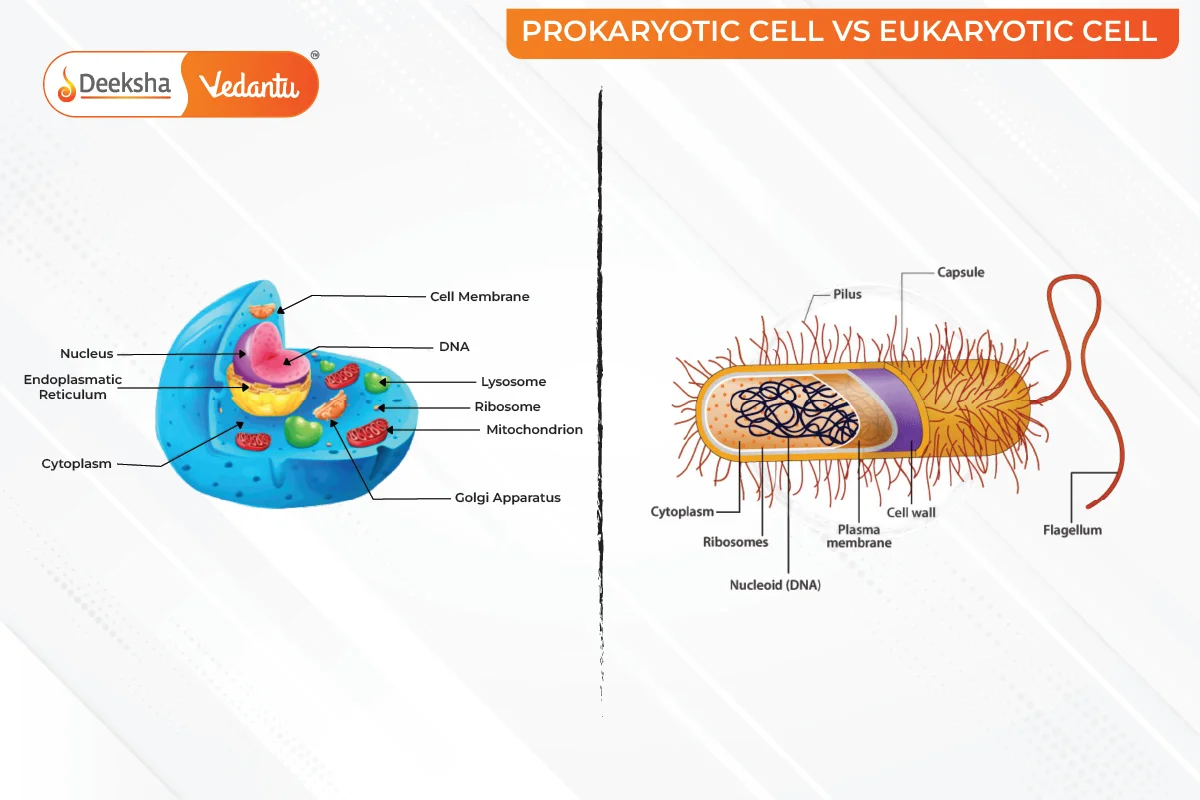
Prokaryotic Cells
- Definition: Prokaryotes are ancient and simple cells without a nucleus. The term comes from Greek words meaning “before nuclei.”
- History: Prokaryotes appeared around 3.5 billion years ago and thrived in the early Earth environment.
- Structure: Prokaryotic cells are small and simple. They lack membrane-bound organelles like a nucleus. They reproduce by binary fission.
- Features:
- Capsule: A protective coat around the cell.
- Pilus: Hair-like structures that help the cell attach to surfaces.
- Cell Wall: Provides strength and rigidity.
- Cytoplasm: Gel-like substance inside the cell.
- Plasma Membrane: Separates the cell from its environment.
- Ribosomes: Small structures for protein synthesis.
- Mesosomes: Assist in cellular respiration.
- Plasmids: Small, circular DNA molecules.
- Flagella: Help with movement.
- Examples: Bacteria and archaea.
Eukaryotic Cells
- Definition: Eukaryotes are more complex cells with a nucleus. The term means "true nuclei" in Greek.
- Structure: Eukaryotic cells are larger and have membrane-bound organelles.
- Features:
- Cell Wall: Supports and protects the cell membrane (in plants).
- Plasma Membrane: Controls entry and exit of substances.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls cell activities.
- Nucleolus: Helps in protein synthesis.
- Mitochondria: Produce energy for the cell.
- Chloroplasts: Site of photosynthesis in plant cells.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transports materials within the cell.
- Other Organelles: Include ribosomes, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, cytoplasm, chromosomes, vacuoles, and centrosomes.
- Examples: Plant cells, animal cells, and unicellular organisms with a nucleus.
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Feature | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Type of Cell | Always unicellular | Unicellular and multicellular |
| Cell Size | 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm in diameter | 10 μm – 100 μm in diameter |
| Cell Wall | Usually present; chemically complex | When present, chemically simple |
| Nucleus | Absent, nucleoid region instead | Present |
| Ribosomes | Smaller, spherical | Larger, linear |
| DNA Arrangement | Circular | Linear |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present, no organelles | Present, with organelles |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Plasmids | Present | Rarely found |
| Lysosomes | Absent | Present |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis |
| Flagella | Smaller | Larger |
| Reproduction | Asexual | Both asexual and sexual |
| Example | Bacteria and Archaea | Plants and Animals |
FAQs
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies are found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells.
The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell.
Eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually through processes like mitosis and meiosis.
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, a form of asexual reproduction.
The main difference is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both.
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They include plants, animals, and other unicellular organisms with a nucleus.
Prokaryotic cells are simple, ancient cells without a nucleus. They include bacteria and archaea.












Get Social