A compound microscope is a crucial tool in scientific research and education, providing detailed magnification of small specimens. Let’s delve into the specifics of this instrument, its working principle, parts, advantages, disadvantages, and various applications.
What is a Compound Microscope?
A compound microscope is a type of optical microscope that uses two sets of lenses to achieve high resolution and magnification, producing a 2-dimensional image of the sample. The term “compound” refers to the use of more than one lens in the microscope. Unlike simple microscopes, which use only one lens, compound microscopes provide greater magnification and detail.
Diagram of Compound Microscope
Working Principle of Compound Microscope
A compound microscope magnifies objects using a complex lens system. It consists of two primary lenses:
- Objective Lens: Placed close to the object being examined, it forms a real image.
- Eyepiece (Ocular Lens): Magnifies the real image formed by the objective lens to produce a virtual image for viewing.
Light passes through the transparent object, and the objective lens creates a magnified real image. The eyepiece then further magnifies this real image, making it visible as a virtual image. This mechanism, where light passes directly through the lenses to the eye, is why it is also called a bright-field microscope.
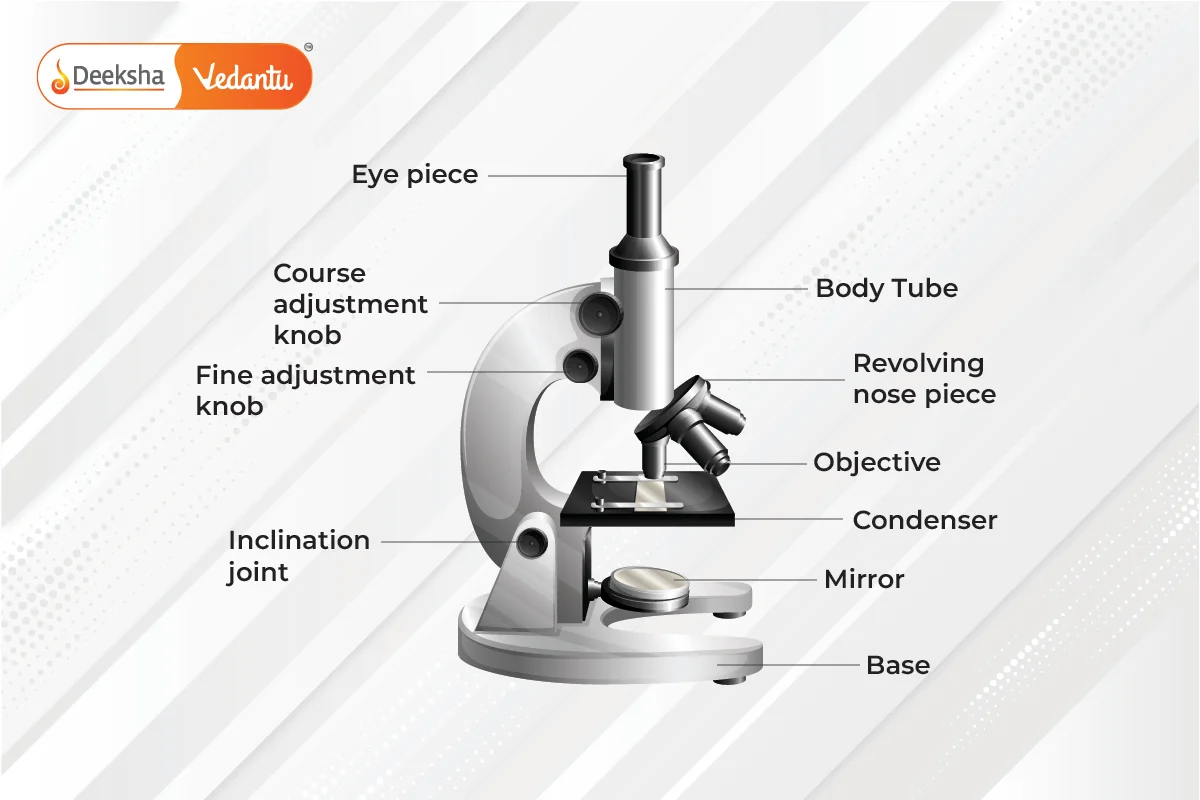
Parts of Compound Microscope
The parts of a compound microscope can be categorized into non-optical and optical components.
Non-Optical Parts
- Base: The supportive structure of the microscope, typically U or horseshoe-shaped.
- Pillar: Connects the base to the arm.
- Arm: Supports the stage and body tube, connecting them to the base.
- Inclination Joint: Allows the microscope to be tilted for comfortable viewing.
- Stage: A platform where slides are placed, often with clips or a mechanical stage to hold the slides.
- Body Tube: Holds the objective and ocular lenses at opposite ends, providing a pathway for light.
- Draw Tube: Holds the ocular lens and is attached to the body tube.
- Rack and Pinion: Used for focusing by moving the body tube or stage.
- Adjustment Screws: Fine and coarse adjustments for precise focusing.
- Automatic Stop: Prevents the body tube from descending too far, protecting the lenses.
Optical Parts
- Diaphragm: Controls the amount of light passing through the specimen.
- Condenser: Focuses light onto the specimen.
- Reflector: A mirror directing light through the condenser; may be plane or concave.
- Objective Lenses: Typically include low power, high power, and oil immersion lenses, forming a real image.
- Ocular Lens: Also known as the eyepiece, magnifies the real image to form a virtual image. Common magnifications are 5X, 10X, 15X, and 20X.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Compound Microscope
Advantages:
- Provides detailed magnification of specimens.
- Has built-in light sources for better visibility.
- User-friendly and easy to handle.
Disadvantages:
- Magnification is limited to a certain extent; beyond this, the sample cannot be viewed clearly.
Uses of Compound Microscope
- Pathology Labs: Identifying diseases.
- Forensic Labs: Detecting human fingerprints.
- Metal Detection: Identifying the presence of metals.
- Microbiology: Studying bacteria and viruses.
- Educational Institutions: Academic purposes in schools and universities.
FAQs
Used in pathology labs for disease identification, forensic labs for fingerprint detection, microbiology for studying bacteria and viruses, and in educational institutions for academic purposes.
It offers detailed magnification, built-in light sources, and ease of use.
The main parts include the base, arm, stage, body tube, objective lenses, eyepiece, diaphragm, condenser, and reflector.
It uses an objective lens to form a real image of the specimen and an eyepiece to magnify this image into a virtual one, viewed by the observer.
A compound microscope is an optical device with high resolution that uses two sets of lenses to magnify specimens, providing a 2-dimensional image.
Related Topics
- Atmospheric Refraction
- Kirchhoff’s Law
- Electric Potential And Potential Difference
- Laws of Motion
- Magnetic Field And Field Lines
- P-N Junction
- Projectile Motion
- Human Eye – Structure and Functioning
- Magnetic Field Due To A Current – Carrying Conductor
- Refraction Of Light
- Mirrors
- Electric Power
- Factors On Which The Resistance Of A Conductor Depends
- Difference between AC and DC
- Velocity












Get Social