Cell division is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction. Multiple cell cycles transform a single cell into a multicellular organism.
Cell Cycle:
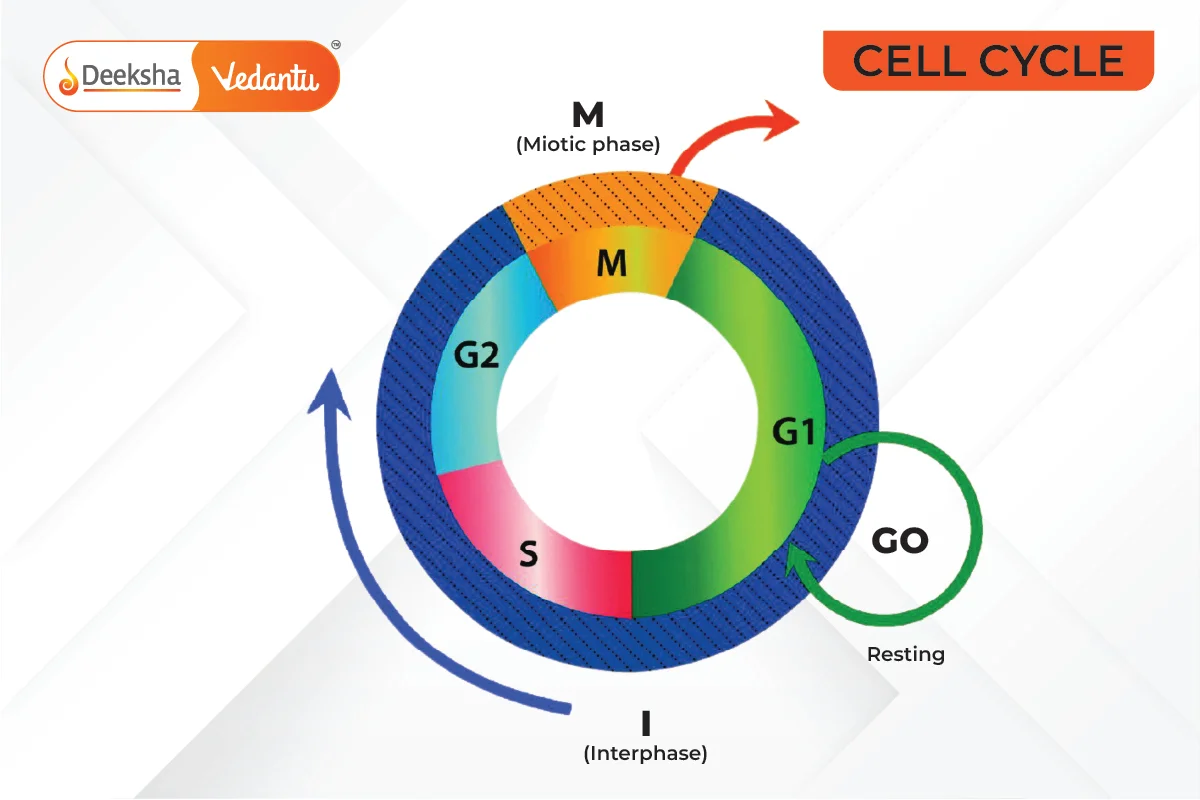
- The cell cycle consists of cell growth, DNA replication, and cell division.
- Events in a cell cycle are genetically controlled.
- Duration varies; human cell cycle averages 24 hours, while a yeast cell completes it in 90 minutes.
- The cell cycle is divided into Interphase and M phase.
Phases of the Cell Cycle:
- Interphase: Period of cell growth and DNA replication, constituting 95% of the cell cycle.
- G1 Phase (Gap 1): Interval between mitosis and DNA replication of the next cell cycle.
- S Phase (Synthesis): DNA replication occurs, doubling the DNA content, while chromosome number remains the same.
- G2 Phase (Gap 2): Cell grows and prepares for mitosis, with protein synthesis.
- G0 Phase: Inactive phase for cells that do not divide, such as heart cells.
- M Phase: Phase of mitosis (cell division), resulting in two daughter cells with the same chromosome number as the parent cell.
Mitosis
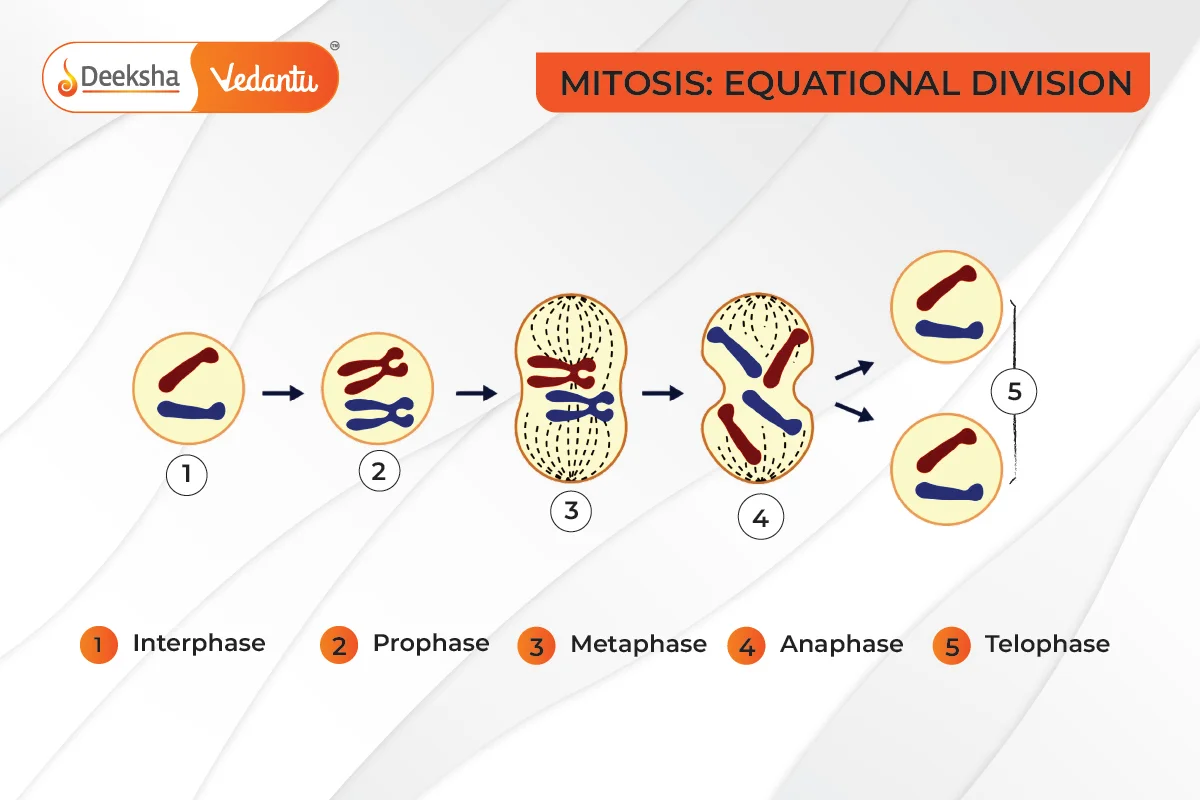
Key Points:
- Occurs mostly in diploid somatic cells of animals and both haploid and diploid cells in plants.
- Responsible for genetic continuity, growth, and repair.
- Involves four stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase, followed by Cytokinesis.
Stages of Mitosis:
- Prophase:
- Chromosomes condense and become visible.
- Mitotic apparatus forms, and nuclear components disappear.
- Metaphase:
- Chromosomes align at the cell equator.
- Chromatids attach to spindle fibres.
- Anaphase:
- Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
- Chromatids now become daughter chromosomes.
- Telophase:
- Chromosomes cluster at poles and decondense.
- Nuclear envelope and organelles reappear.
- Cytokinesis:
- Division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two daughter cells.
Meiosis
Key Points:
- Also known as reduction division, producing haploid gametes.
- Consists of two sequential divisions: Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
- Results in four haploid daughter cells.
Phases of Meiosis I:
- Prophase I:
- Extended stage with sub-stages: Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene, and Diakinesis.
- Homologous chromosomes pair and exchange genetic material.
- Metaphase I:
- Homologous chromosomes align at the equator.
- Anaphase I:
- Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles.
- Telophase I:
- Nuclear membranes reappear, forming two haploid cells.
Phases of Meiosis II:
- Prophase II:
- Nuclear envelope disappears.
- Metaphase II:
- Chromosomes align at the equator.
- Anaphase II:
- Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
- Telophase II:
- Nuclear membrane reappears, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
FAQs
Checkpoints in the cell cycle (G1, G2, and M checkpoints) ensure that the cell is ready to proceed to the next phase, preventing errors and ensuring proper cell division.
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I of meiosis, leading to genetic variation.
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through cleavage, while in plant cells, a cell plate forms to divide the cytoplasm.
Centromeres hold sister chromatids together and attach to spindle fibers, ensuring proper chromosome separation.
The stages of mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, followed by Cytokinesis.
Meiosis produces haploid gametes, ensuring genetic diversity and the correct chromosome number in offspring.
DNA replication occurs, doubling the DNA content while maintaining the same chromosome number.
Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse haploid cells.
The main phases are Interphase (G1, S, G2) and M Phase (Mitosis).
The cell cycle is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction. It ensures genetic continuity and the proper function of cells.
Related Topics
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Body Fluids and Circulation
- Euglena
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – The Living World
- Parenchyma Cells
- DNA Polymerases
- Types of Fermentation
- Plant Hormones
- Plasma Membrane Structure
- Connective Tissue
- What is Hemoglobin
- Epithelial Tissue
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Chromosome Structure
- Bryophytes
- Marchantia
- Difference between Ideal Solution and Non-ideal Solution










Get Social