Blood
Composition of Blood:
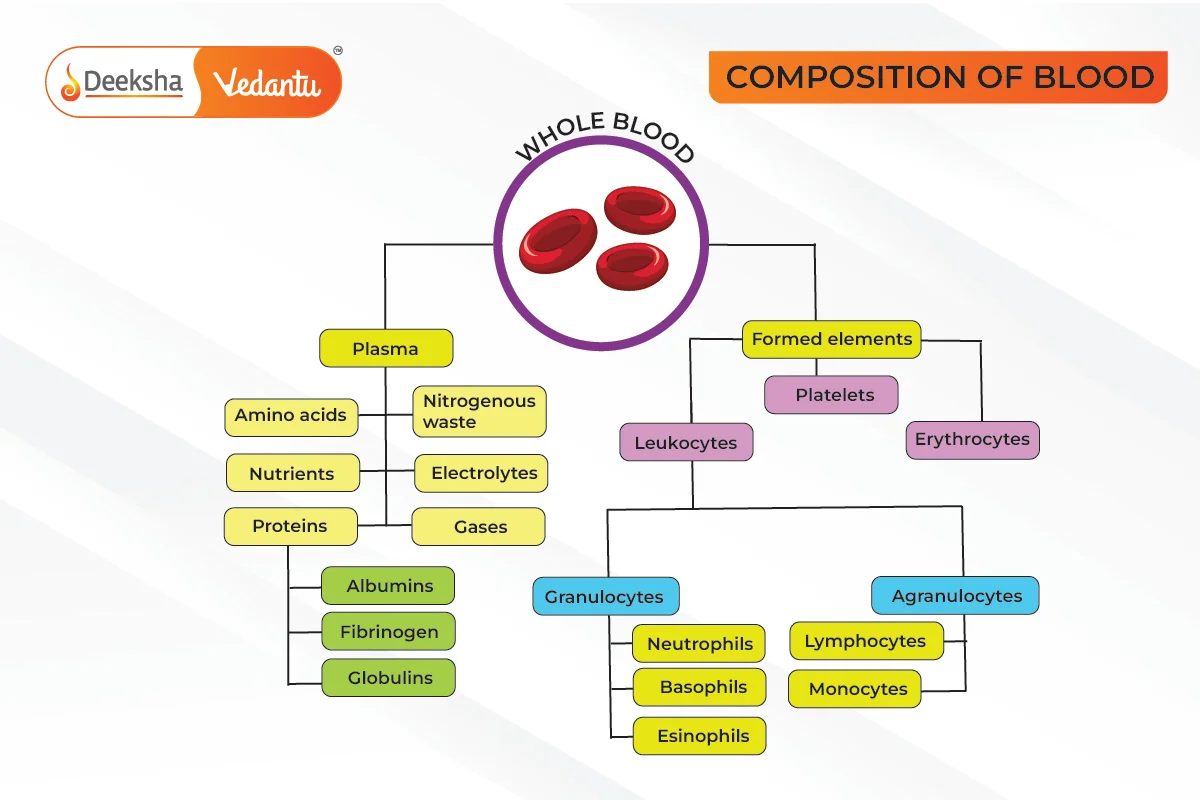
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of cells (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets).
- Plasma constitutes 55% of blood volume. It is a viscous fluid containing 90-92% water, 6-8% proteins (fibrinogens, albumins, globulins), amino acids, glucose, and electrolytes (Na+, Ca++, Cl–).
- Formed Elements include erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Erythrocytes (RBCs):
- Most abundant cells in blood.
- Formed in bone marrow, biconcave, anucleate.
- Lifespan of 120 days, destroyed in the spleen.
Leukocytes (WBCs):
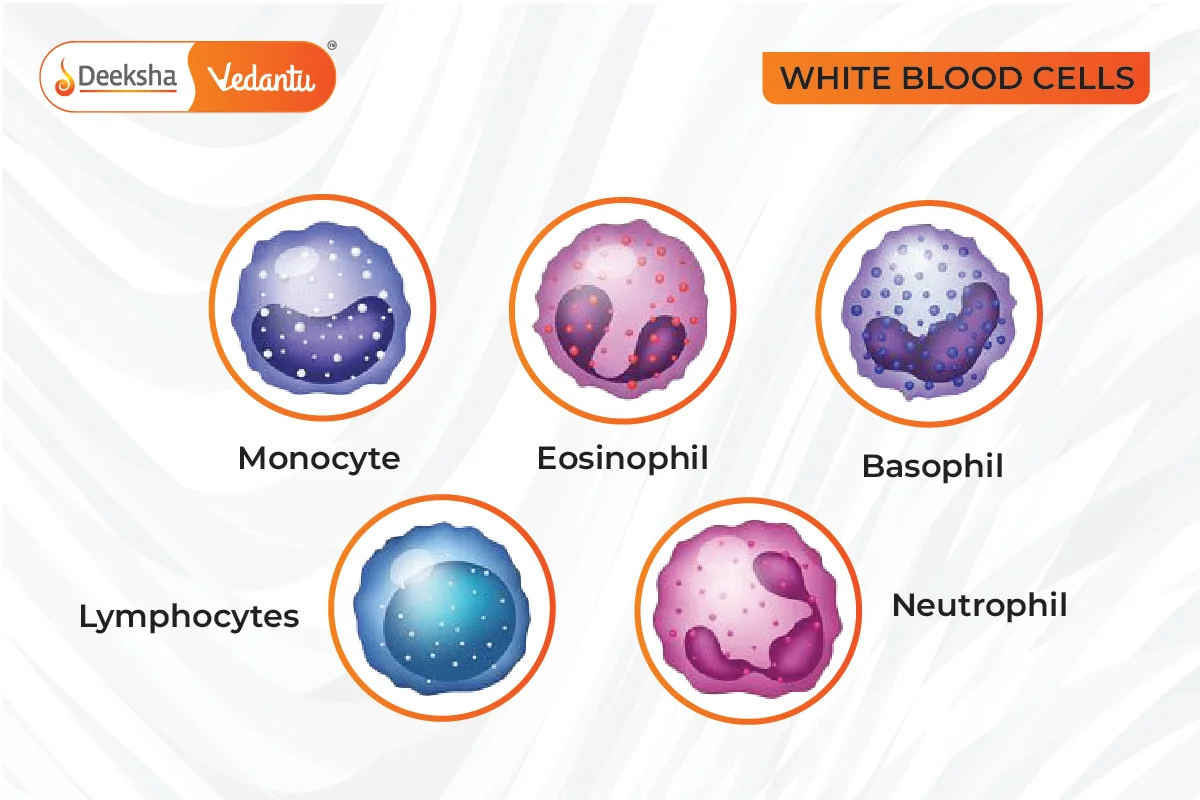
- Colorless due to the absence of hemoglobin.
- Life span of 3-4 days.
- Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils.
- Agranulocytes: Lymphocytes, Monocytes.
Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes):
- Formed from megakaryocytes in bone marrow.
- Involved in blood clotting.
Blood Groups
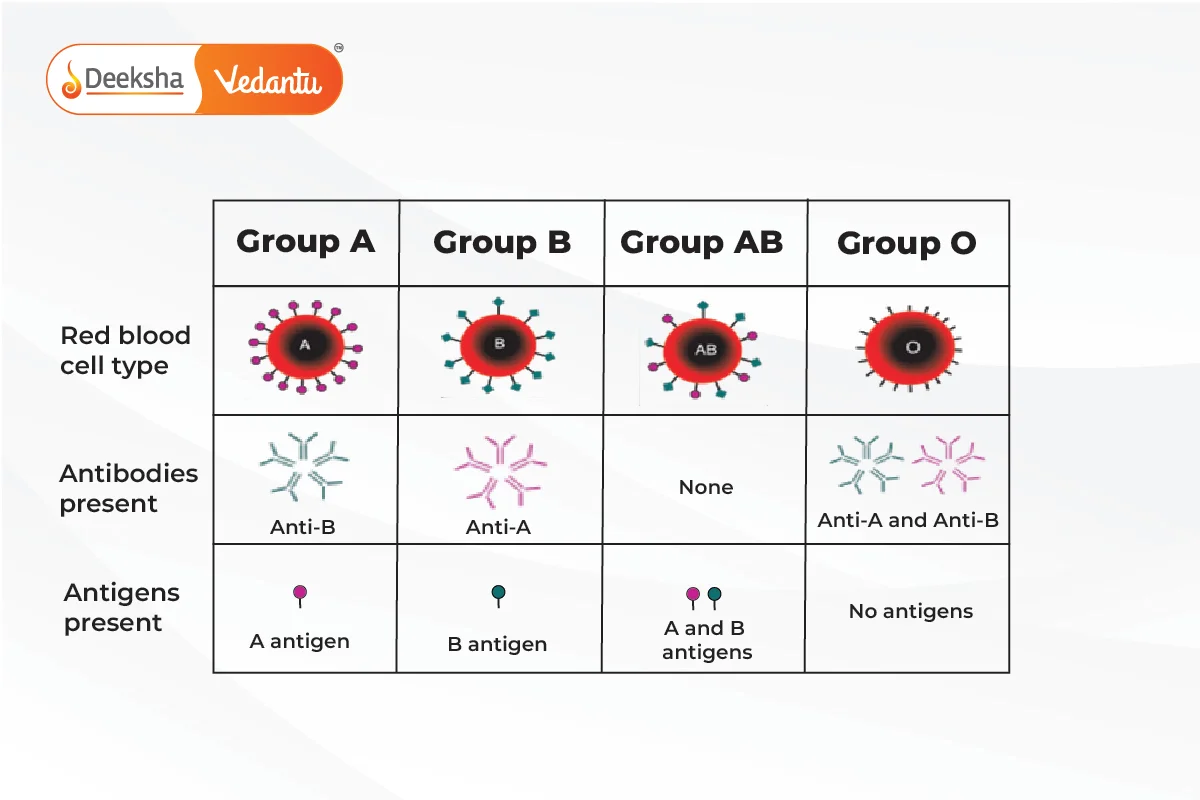
ABO Blood Group System:
- Four types: A, B, AB, O.
- Based on surface antigens on RBCs (A and B antigens).
- Blood Group A: Antigen A, Anti-B antibodies.
- Blood Group B: Antigen B, Anti-A antibodies.
- Blood Group AB: Antigens A and B, no antibodies (universal acceptor).
- Blood Group O: No antigens, Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies (universal donor).
Rh Grouping:
- Rh antigen present in 80% of people (Rh+).
- Erythroblastosis fetalis: Mother is Rh–, father is Rh+, fetus is Rh+. The condition can be managed by administering anti-Rh antibodies to the mother after the first childbirth.
Coagulation of Blood
- Blood clotting prevents excessive blood loss from injuries.
- Clot consists of fibrin, which traps blood cells.
- Clotting process:
- Inactive fibrinogen → Fibrin (by Thrombin).
- Prothrombin → Thrombin (by Thrombokinase).
- Ca++ is crucial in the coagulation process.
Lymph
- Lymph is a fluid connective tissue that drains interstitial fluid back to major veins.
- Contains lymphocytes, part of the immune system.
- Absorbs fats in the intestine through lacteals and transports them to blood.
Circulatory Pathways
Types:
- Open Circulatory System: Blood is in open cavities (sinuses), found in arthropods and molluscs.
- Closed Circulatory System: Blood circulates in vessels, found in annelids and chordates.
Human Circulatory System:
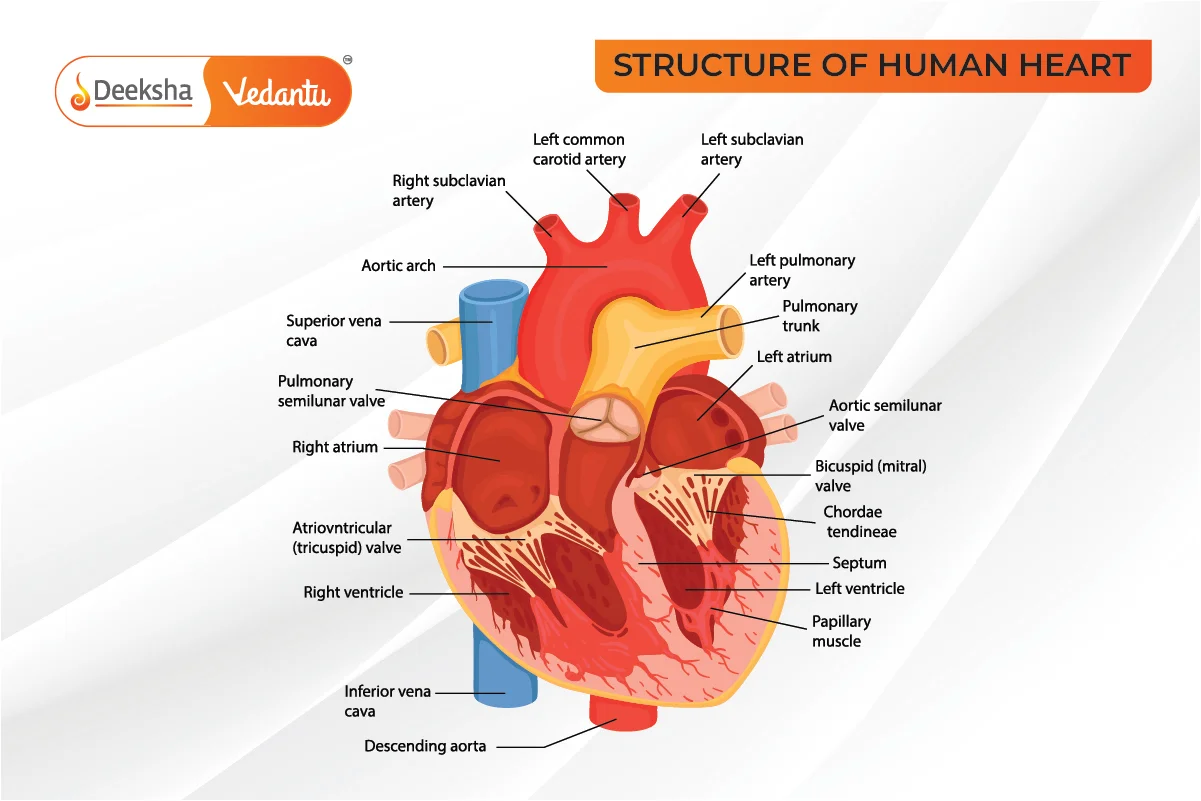
- Heart: Four-chambered, mesodermal origin, located between lungs in the thoracic cavity, protected by pericardium.
- Heart Structure:
- Valves: Bicuspid (mitral) between left atrium and ventricle; Tricuspid between right atrium and ventricle; Semilunar at openings of pulmonary artery and aorta.
- Nodal Tissue: SAN (pacemaker), AVN, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries; made of tunica intima, media, and externa.
Cardiac Cycle
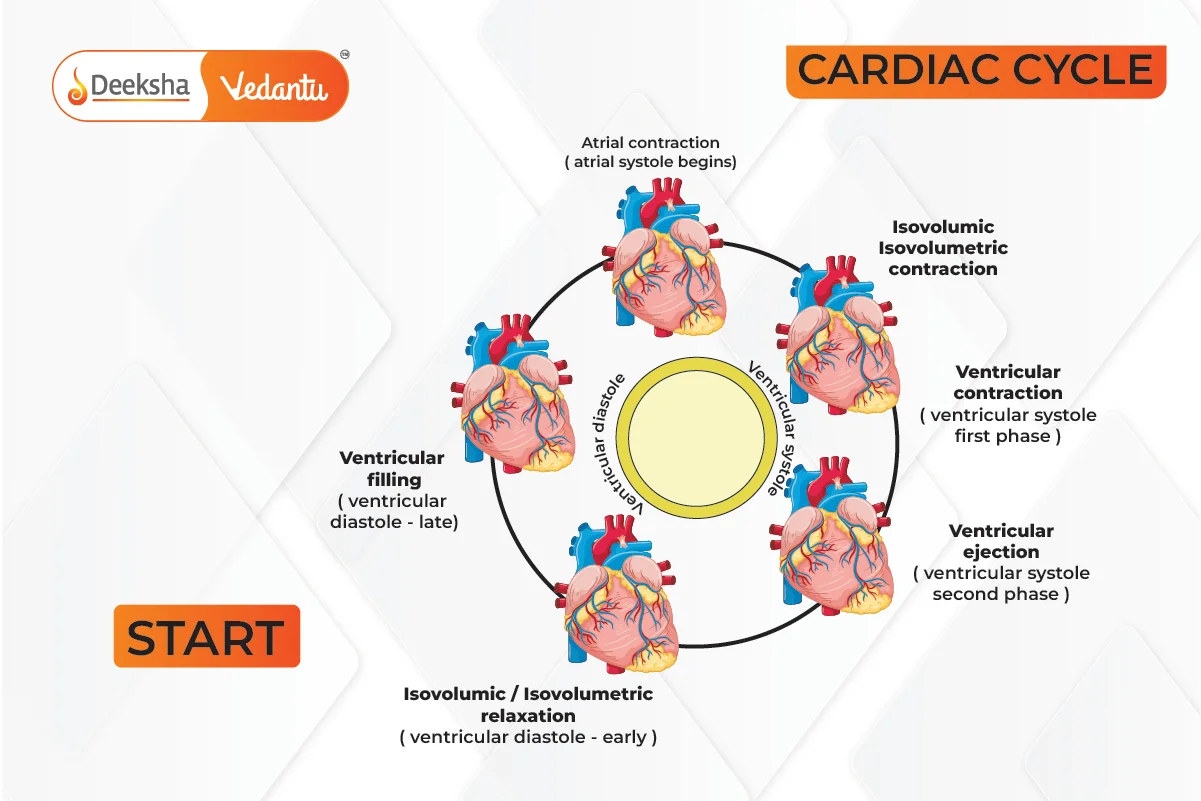
- Joint Diastole: All four chambers relaxed.
- Atrial Systole: SAN initiates contraction.
- Ventricular Systole: AVN transfers action potential, ventricles contract.
- Ventricular Diastole: Semilunar valves close.
- Stroke Volume: Blood pumped by each ventricle per cycle (~70 ml).
- Cardiac Output: Total blood output per minute (~5 L).
Heart Sounds:
- Lub: Closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valves during ventricular systole.
- Dub: Closure of semilunar valves during ventricular diastole.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
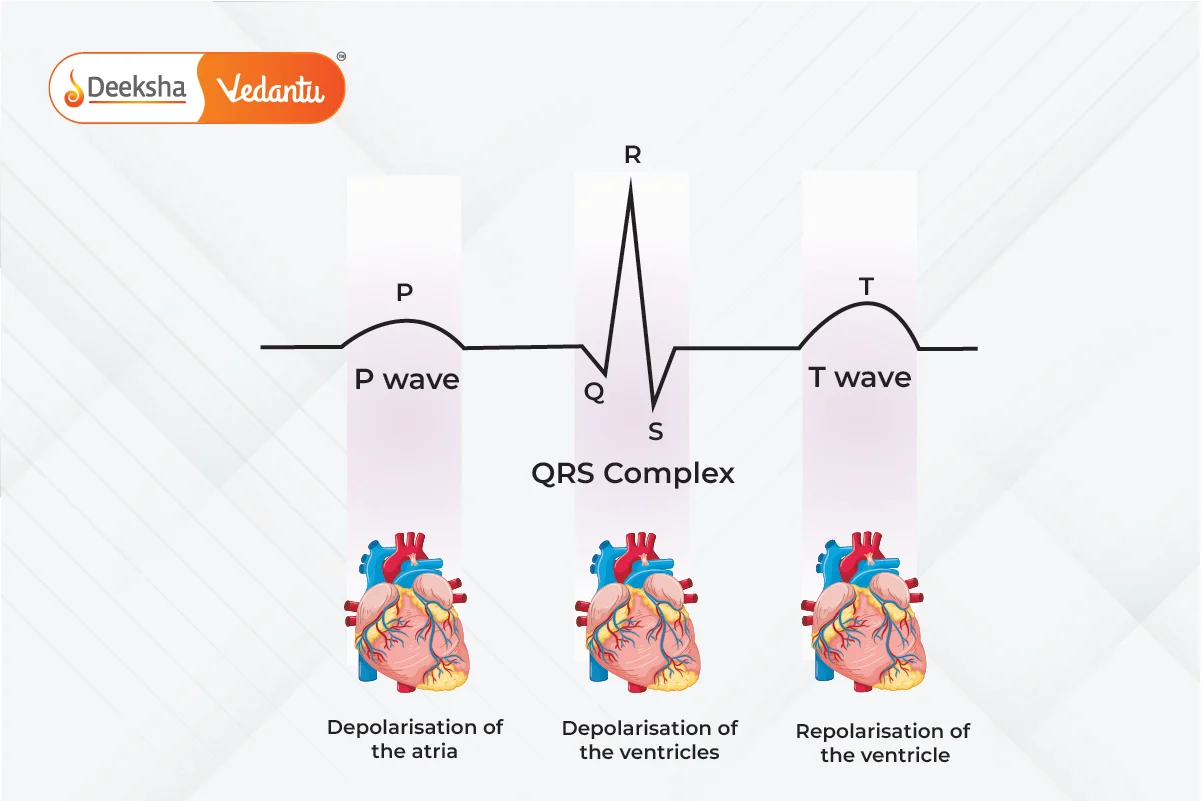
- P Wave: Atrial depolarization.
- QRS Complex: Ventricular depolarization.
- T Wave: Ventricular repolarization.
- Measures heart rate and detects abnormalities.
Double Circulation
- Pulmonary Circulation: Deoxygenated blood to lungs via pulmonary artery; oxygenated blood to left atrium via pulmonary vein.
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygenated blood from left ventricle to body; deoxygenated blood returns to right atrium.
Hepatic Portal System: Connects liver and digestive tract, transporting nutrients.
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
- Myogenic Heart: Activity regulated by nodal tissue.
- ANS Regulation: Sympathetic (increases rate) and parasympathetic (decreases rate) neural signals from medulla oblongata.
Disorders of the Circulatory System
- Hypertension: High blood pressure (>140/90 mm Hg).
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing of arteries due to plaque.
- Angina: Chest pain due to insufficient oxygen to heart muscles.
- Heart Failure: Inability to pump sufficient blood.
- Coronary Thrombosis: Clot in coronary artery leading to heart attack.
FAQs
Pulmonary circulation involves the exchange of gases in the lungs, while systemic circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the body and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Hypertension is caused by factors like genetics, lifestyle, stress, and underlying health conditions.
An ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart used to detect heart conditions.
The heart’s activity is regulated by the sinoatrial node (pacemaker) and the autonomic nervous system.
The Rh factor determines compatibility for blood transfusions; mismatched Rh factors can lead to immune reactions.
Oxygen is primarily transported by hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Blood consists of plasma (fluid part) and formed elements (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets).
Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Related Topics
- Plasma Membrane Structure
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – The Living World
- Parenchyma Cells
- Krebs Cycle
- Types of Fermentation
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Paramecium
- What is Hemoglobin
- Difference between Ideal Solution and Non-ideal Solution
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Chromosome Structure
- Bryophytes
- Epithelial Tissue
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- NEET Biology Weightage
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Anatomy of Flowering Plants











Get Social