The area of a triangle is the space inside its three sides in a two-dimensional plane. A triangle, having three sides and three vertices, encloses a specific region. The general formula for finding the area of a triangle is half the product of its base and height.
The term “area” refers to the space occupied within the boundary of a flat object or shape, measured in square units like square meters (m²). To compute the area of various shapes like squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles, there are specific formulas. This article focuses on the formulas for different types of triangles with example problems.
What is the Area of a Triangle?
The area of a triangle is the total space enclosed by its three sides. It is calculated as half of the base times height, or . This formula applies to all types of triangles, including scalene, isosceles, and equilateral. The base and height must be perpendicular to each other, and the area is measured in square units (m², cm²).
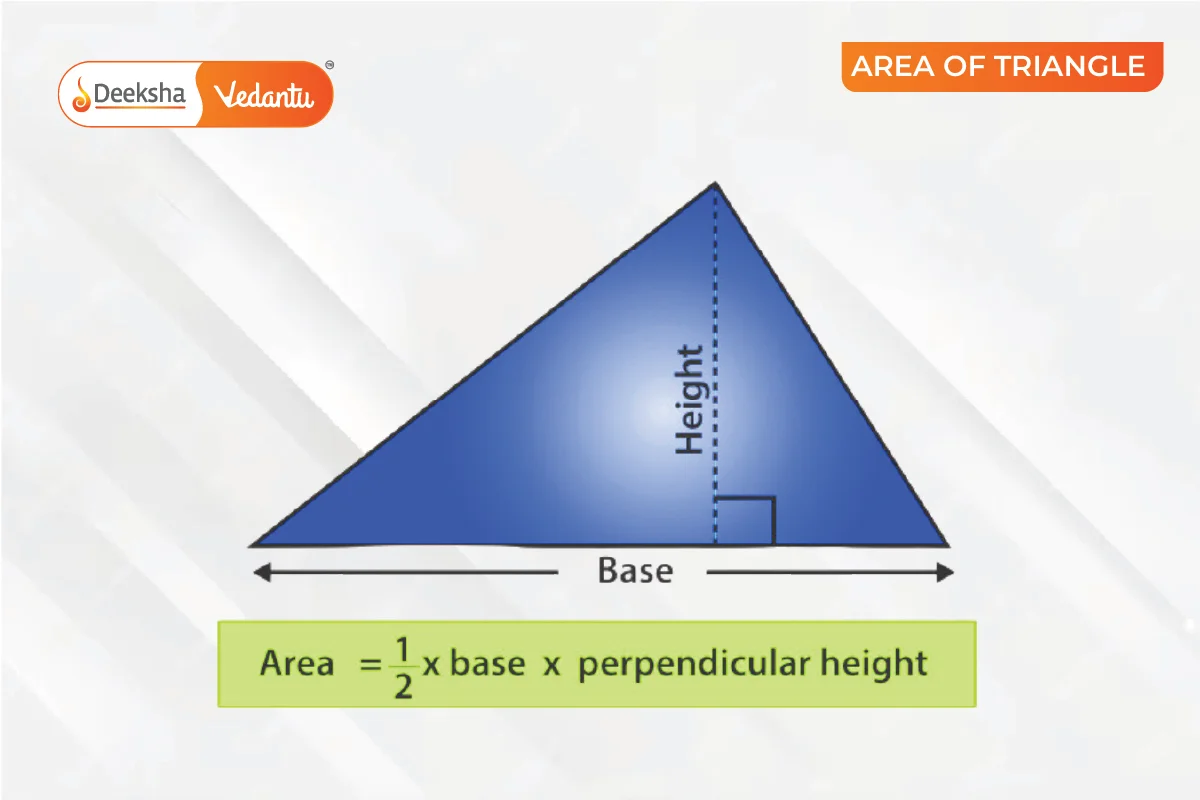
Example: What is the area of a triangle with a base of 3 cm and a height of 4 cm?
Using the formula:
Area of a Triangle,
=
=
=
Apart from this formula, Heron’s formula can calculate the area when the lengths of all three sides are known. Trigonometric functions help find the area when two sides and the included angle are known. This article will cover all these methods.
Area of a Triangle Formula
The area of a triangle is given by:
where b is the base, and h is the height of the triangle.
We will now see how to calculate the area using this formula for different types of triangles, including equilateral, right-angled, and isosceles triangles, and using Heron’s formula for a triangle with three sides.
Area of a Right-Angled Triangle
A right-angled triangle has one angle of 90°. The height is the length of the perpendicular side.
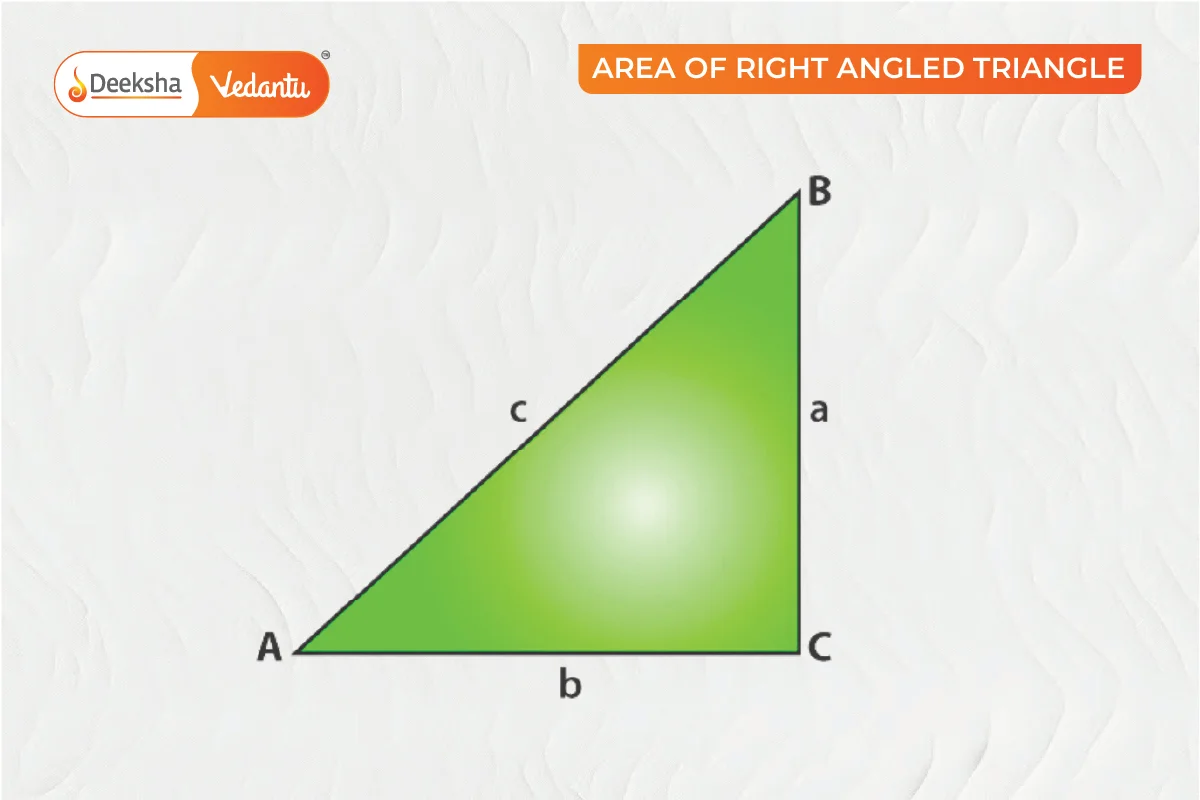
From the above figure:
Area of triangle
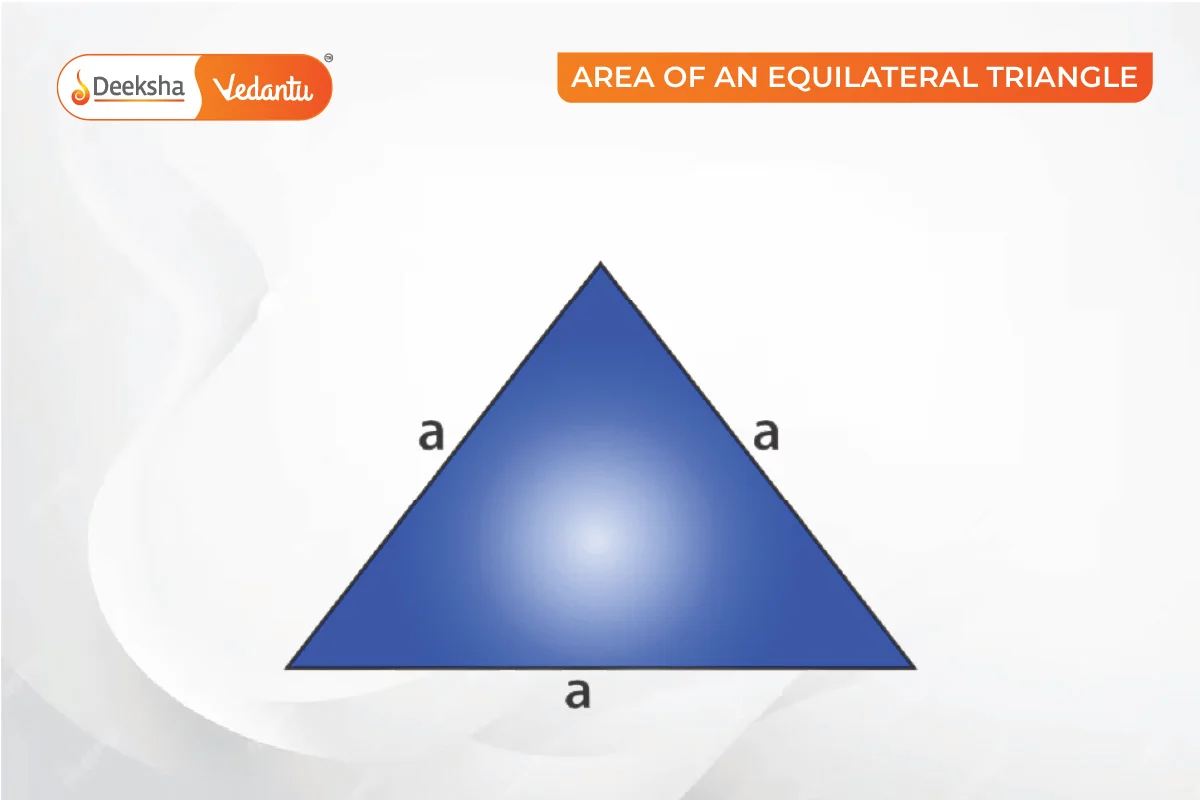
Area of an Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all sides equal. The perpendicular from the vertex to the base divides the base into two equal parts.
Area of an Isosceles Triangle
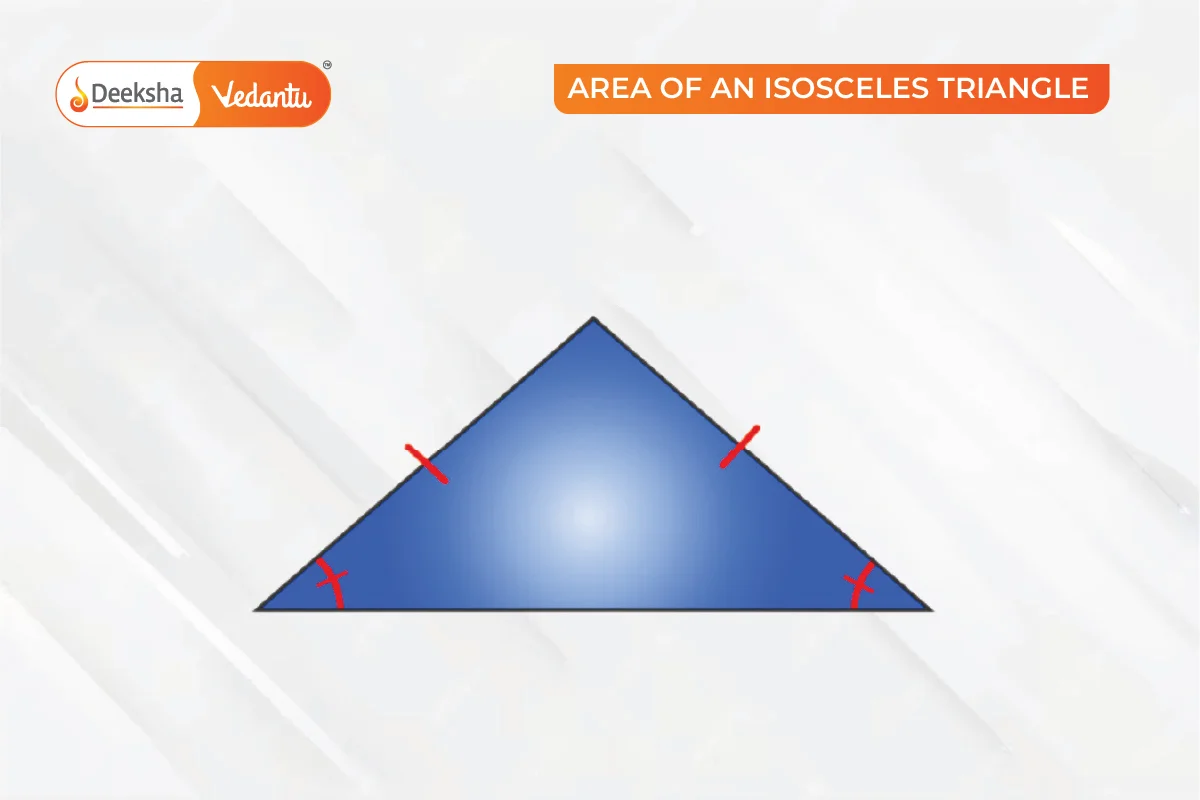
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides, and the angles opposite these sides are equal.
Area of Triangle with Three Sides (Heron’s Formula)
To find the area of a triangle with three different side lengths, use Heron’s formula:
- Calculate the semi-perimeter,
- Use the semi-perimeter in Heron’s formula:
Area of a Triangle Given Two Sides and the Included Angle (SAS)
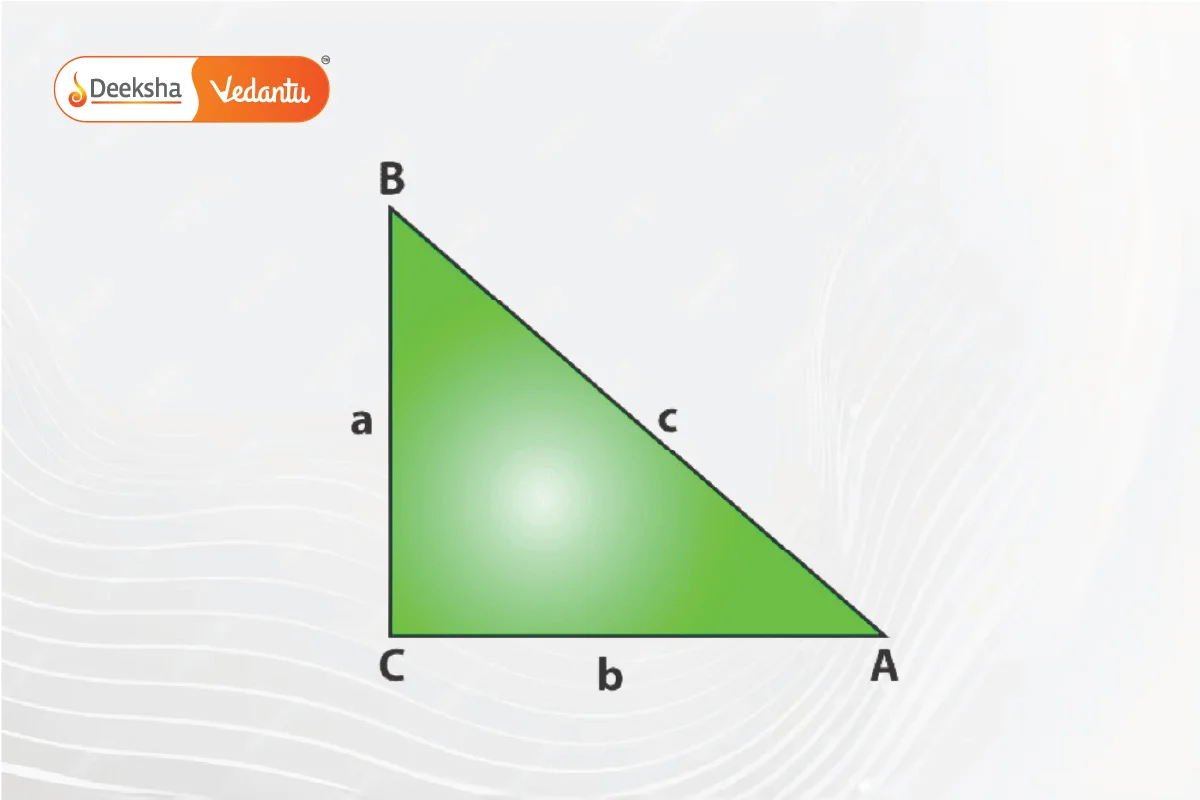
If two sides and the included angle are known, the area is calculated as:
Example: In ΔABC, if A=30°, b=2 and c=4:
FAQs
The area of a triangle is measured in square units, such as square meters (m²) or square centimeters (cm²).
If two sides and the included angle are known, the area can be found using ½ b c sinA, where A is the included angle, and b and c are the sides.
Heron’s formula calculates the area of a triangle when the lengths of all three sides are known. It is , where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle.
Yes, the formula applies to all types of triangles, including scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles.
The basic formula to find the area of a triangle is
Related Topics
- Revisiting Irrational Numbers
- Introduction to Arithmetic Progressions
- The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
- Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
- Sets
- Introduction To Coordinate Geometry
- Solution of a Quadratic Equation by Factorisation
- Rational Numbers
- Real Numbers
- Some applications Of Trigonometry
- Ordinal Numbers
- Tangent to a Circle
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Maths FAQs
- Percentage












Get Social