Introduction to the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, stretching from the longest wavelengths (radio waves) to the shortest (gamma rays). This spectrum is fundamental to understanding both the physical universe and numerous technologies.
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
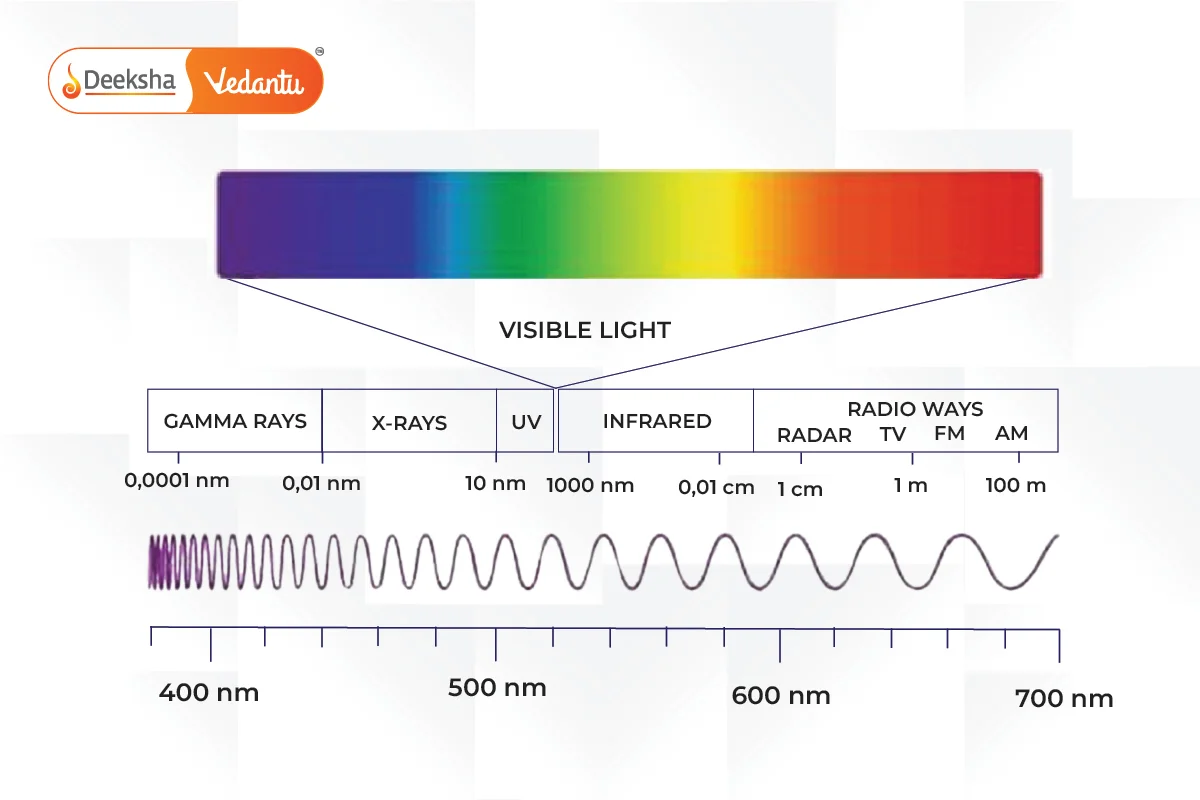
The electromagnetic spectrum represents a continuous range of electromagnetic waves sorted by frequency and wavelength. From less than one hertz to more than 10^25 Hz, these waves cover wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to fractions of the size of an atomic nucleus. In a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, but they differ greatly in their wavelengths and frequencies.
Components of the Electromagnetic Spectrum:
- Radio Waves:
- Frequency Range: Less than
- Applications: Used in broadcasting for television, radio, and mobile communications.
- Frequency Range: Less than
- Microwaves:
- Frequency Range:
- Applications: Cooking, satellite communications, and radar technology.
- Frequency Range:
- Infrared Radiation:
- Frequency Range:
- Applications: Night vision equipment, remote controls, and thermal imaging.
- Frequency Range:
- Visible Light:
- Frequency Range: Approximately
- Applications: Enables vision, used in lighting and photography.
- Frequency Range: Approximately
- Ultraviolet Light:
- Frequency Range:
- Applications: Sterilization, fluorescent lighting, and detecting forgeries.
- Frequency Range:
- X-Rays:
- Frequency Range:
- Applications: Medical imaging, airport security, and crystallography.
- Frequency Range:
- Gamma Rays:
- Frequency Range:
- Applications: Cancer treatment, sterilizing medical equipment, and astronomical observation.
- Frequency Range:
Significance of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is crucial for various fields, from scientific research to practical applications in medicine, communications, and astronomy. Understanding different types of electromagnetic waves allows scientists and engineers to harness them for a myriad of uses, impacting many aspects of modern life and expanding our understanding of the universe.
Applications Across the Spectrum:
- Radio Waves: Enable long-distance communication and data transmission.
- Microwaves: Critical for cooking and radar.
- Infrared: Essential for thermal sensing and night vision.
- Visible Light: The basis of human vision and photography.
- Ultraviolet: Used in sanitation and forensic science.
- X-Rays: Vital for medical diagnostics and security.
- Gamma Rays: Important in cancer treatment and radioactive tracing.
Understanding through Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy, the study of how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation, is a powerful method used in chemistry, physics, and astronomy. It allows scientists to identify materials and understand their properties by the way they emit or absorb different frequencies of electromagnetic waves.
Formulas for the Electromagnetic Radiation
The frequency (), speed (
), energy (
), and wavelength (
) of electromagnetic waves are related as
Where,
is the speed of light in a vacuum
is Planck’s constant.
Exploration of Light-Matter Interaction
When light interacts with matter, it can be absorbed, emitted, or scattered. Studying these interactions, scientists can deduce the physical properties of substances at molecular or even atomic levels. Spectroscopy reveals unique fingerprints of elements and compounds, manifested in their emission or absorption spectra.
FAQs
Some electromagnetic waves, like ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays, can be harmful due to their high energy, which can cause damage to biological tissues.
The electromagnetic spectrum is essential for understanding fundamental physical processes and is used extensively in scientific research, from astronomy to molecular chemistry.
Different types of electromagnetic waves are used in everyday technology; for example, microwaves in cooking, X-rays in medical diagnostics, and radio waves in communications.
Electromagnetic waves vary in wavelength and frequency, with radio waves having the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, and gamma rays having the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a classification of all electromagnetic waves by their respective wavelengths and frequencies, encompassing types from radio waves to gamma rays.









Get Social