Definition of Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is a region in the Earth’s stratosphere with high concentrations of ozone that protect the Earth from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation.
What is the Ozone Layer?
The ozone layer is located in the lower part of the Earth’s atmosphere and absorbs about 97-99% of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. Without it, many people would suffer from skin diseases and weakened immune systems. However, there is a hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica, mainly caused by chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
Ozone Layer Depletion
Ozone layer depletion is the thinning of the ozone layer due to chemicals containing bromine or chlorine from industrial and other human activities.
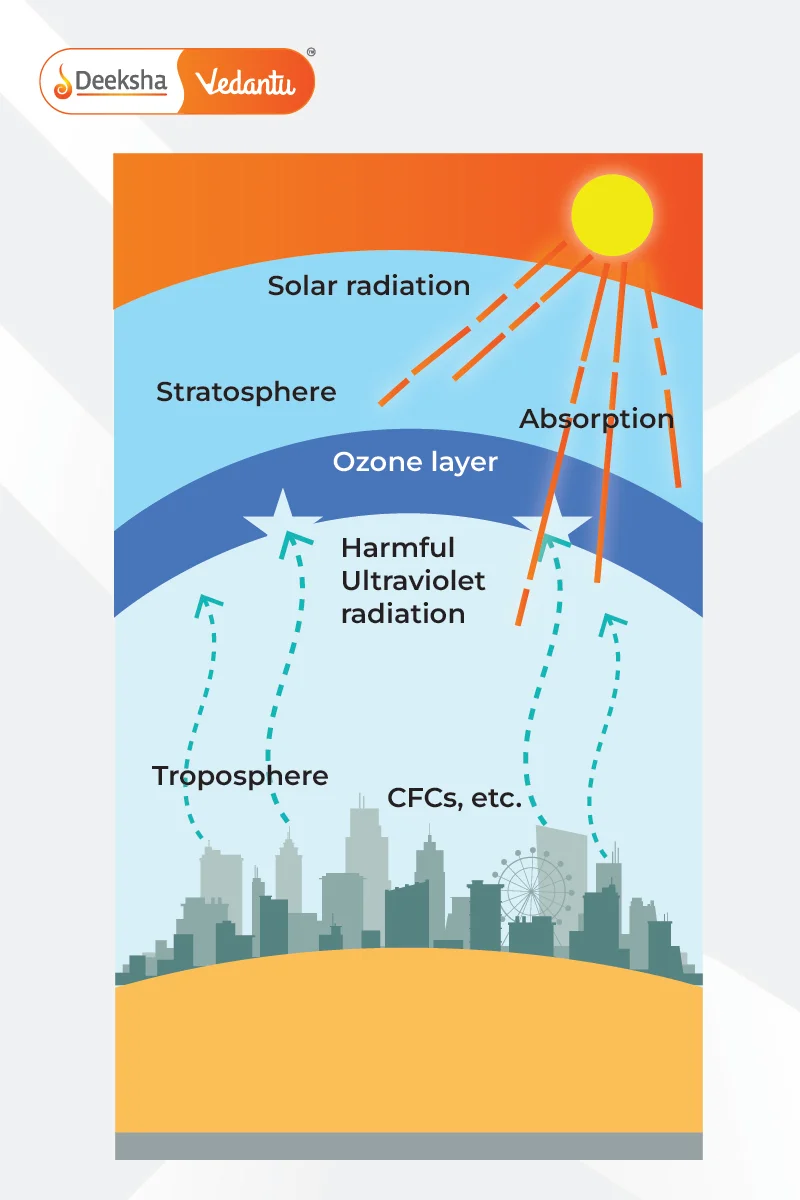
What is Ozone Layer Depletion?
Ozone layer depletion occurs when chlorine and bromine atoms in the atmosphere break down ozone molecules. One chlorine atom can destroy 100,000 ozone molecules, and these chemicals are released by compounds known as Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS).
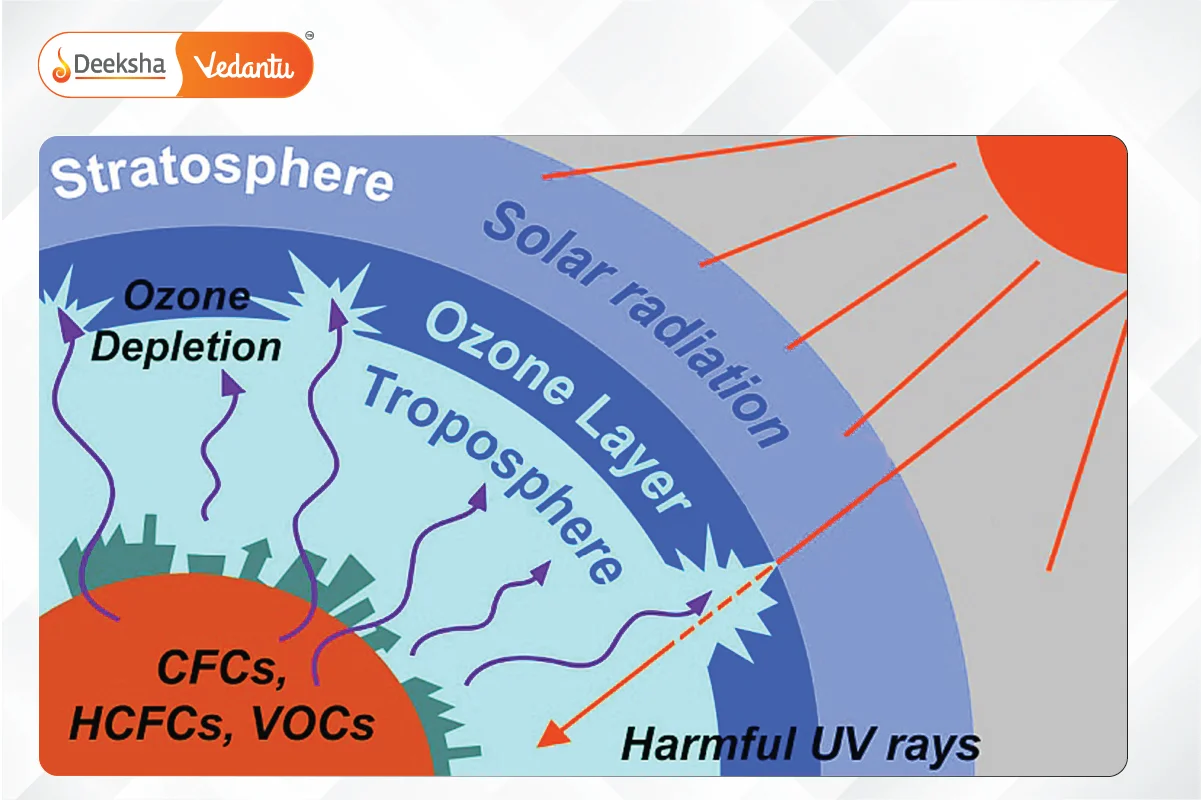
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): Found in solvents, aerosols, refrigerators, and air conditioners.
- Unregulated Rocket Launches: These cause more ozone depletion than CFCs.
- Nitrogenous Compounds: Such as NO2, NO, and N2O.
- Natural Causes: Including volcanic eruptions and stratospheric winds.
Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Human Health: Increased exposure to UV radiation can lead to skin diseases, cancer, sunburns, cataracts, premature aging, and weakened immune systems.
- Animals: UV radiation can cause skin and eye cancer in animals.
- Environment: UV radiation can harm plant growth, flowering, and photosynthesis.
- Marine Life: UV radiation affects planktons, which are crucial in the aquatic food chain.
Solutions to Ozone Layer Depletion
- Avoid Using ODS: Reduce the use of CFCs and replace halon-based fire extinguishers.
- Minimize Vehicle Use: Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using vehicles less.
- Use Eco-friendly Cleaning Products: Avoid products that release chlorine and bromine.
- Prohibit Nitrous Oxide Use: Government actions to reduce nitrous oxide emissions and public awareness about its harmful effects.
FAQs
UV radiation affects planktons, crucial organisms in the aquatic food chain, potentially disrupting marine ecosystems.
Higher UV radiation can harm plant growth, reduce photosynthesis, and affect forest ecosystems.
Increased UV radiation can cause skin and eye cancer in animals and disrupt their natural habitats.
Depletion of the ozone layer increases UV radiation exposure, leading to higher risks of skin diseases, cancer, sunburns, cataracts, premature aging, and weakened immune systems.
Ozone layer depletion is primarily caused by chemicals containing bromine and chlorine, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), used in aerosols, refrigerants, and industrial processes.
The ozone layer absorbs most of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing it from reaching the Earth’s surface and protecting living organisms from its harmful effects.
The ozone layer is a region in the Earth’s stratosphere with high concentrations of ozone that protect the Earth from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Related Topics
- Heredity Traits
- Do Organisms Create Exact Copies of Themselves?
- Human Digestive System
- Animals – Nervous System
- Enzymes
- Nutrition
- Neurons
- Plant Cell
- Kingdom Fungi
- Cell Organelles
- How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Mitosis
- Overview of Food Chain
- How Do Our Activities Affect The Environment?
- Modes Of Reproduction Used By Single Organisms










Get Social