Definition of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms from different environments including land, sea, and deserts. It includes all the ecosystems and the ecological complexes they form.
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity refers to the rich variety of life on Earth, encompassing plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is essential for the sustainability of life and includes different organisms and their frequencies within an ecosystem. Biodiversity was first coined in 1985 and is crucial for both natural and artificial ecosystems.
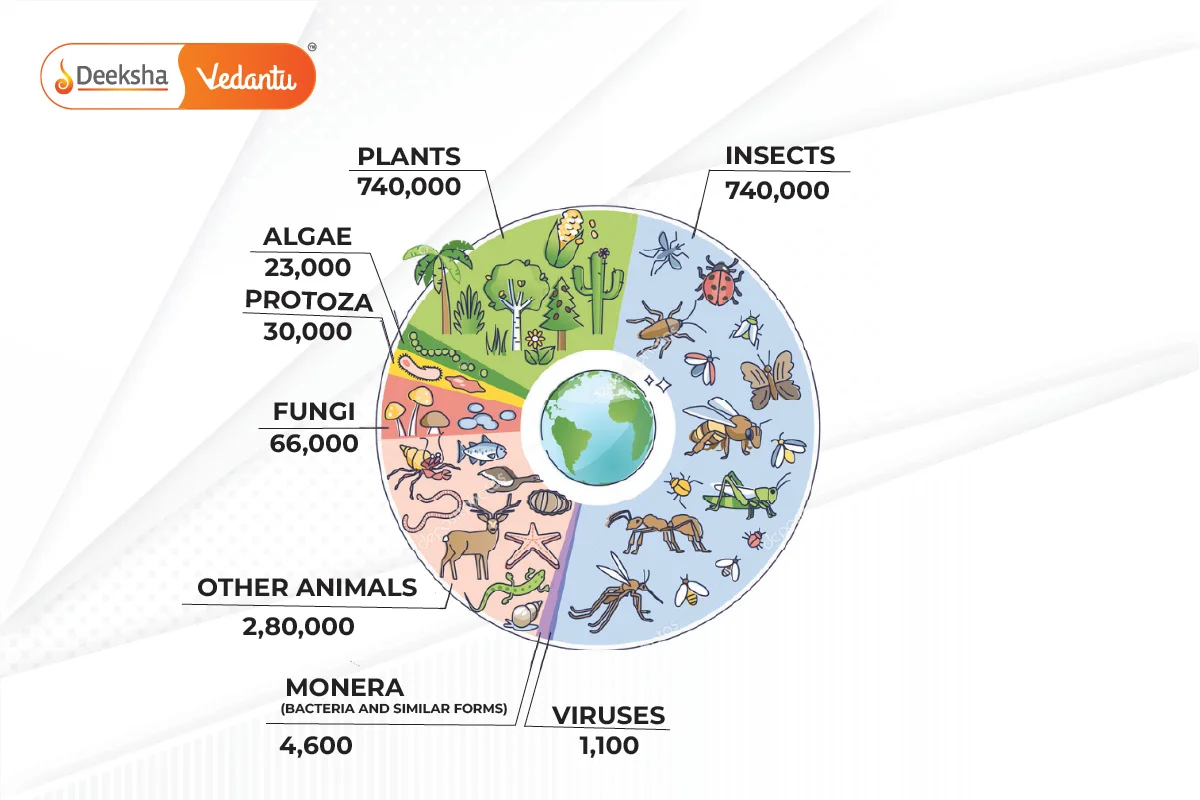
Types of Biodiversity
There are three main types of biodiversity:
- Genetic Biodiversity: Variations in the genetic makeup of organisms within a species.
- Species Biodiversity: Variety of species within a particular area.
- Ecological Biodiversity: Differences among ecosystems in a region, such as deserts, rainforests, and mangroves.
Species Diversity
This refers to the different types of species found in a particular area, from plants to microorganisms. Each species shows variability among its individuals.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity involves variations in the genetic composition within species, leading to differences among individuals. For example, different varieties of rice or wheat.
Ecological Diversity
Ecological diversity includes the variety of ecosystems, such as deserts, rainforests, and mangroves, and the interactions among species within these ecosystems.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is crucial for sustaining life on Earth for several reasons:
- Ecological Stability: Diverse ecosystems are more productive and resilient to environmental stress.
- Economic Importance: Biodiversity provides resources for food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and more.
- Ethical Importance: Every species has a right to exist, and preserving biodiversity maintains cultural and spiritual heritage.
Biodiversity in India
India is one of the most biodiverse countries, ranking ninth in plant species richness. It hosts two of the world’s 25 biodiversity hotspots and is the origin of many important crops. India has about 91,000 animal species and numerous domesticated plant species. Despite this richness, biodiversity is declining, prompting various conservation programs.
FAQs
Diverse ecosystems are more productive and resilient to environmental stress, supporting essential services for human survival.
Ecological diversity includes the variety of ecosystems in a region and the interactions among species within these ecosystems.
Genetic diversity involves the variations in the genetic makeup within species, leading to differences among individuals.
Species diversity refers to the different types of species found in a particular area. Each species shows variability among its individuals.
Biodiversity provides resources for food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and other products. It also supports tourism and recreational activities.
Biodiversity is essential for ecological stability, economic resources, and maintaining cultural and ethical values. It supports ecosystems that humans rely on for survival.
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including all plants, animals, and microorganisms, and the ecosystems they form.
Related Topics
- Human Heart
- Rainwater Harvesting
- How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Modes Of Reproduction Used By Single Organisms
- Plant Cell
- Global Warming
- Overview of Food Chain
- Sexual Reproduction
- Human Respiratory System
- Air Pollution Control
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- What Are Life Processes?
- Cell Organelles
- Control and Coordination
- Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance












Get Social