Atomic Mass of Elements From 1 to 30
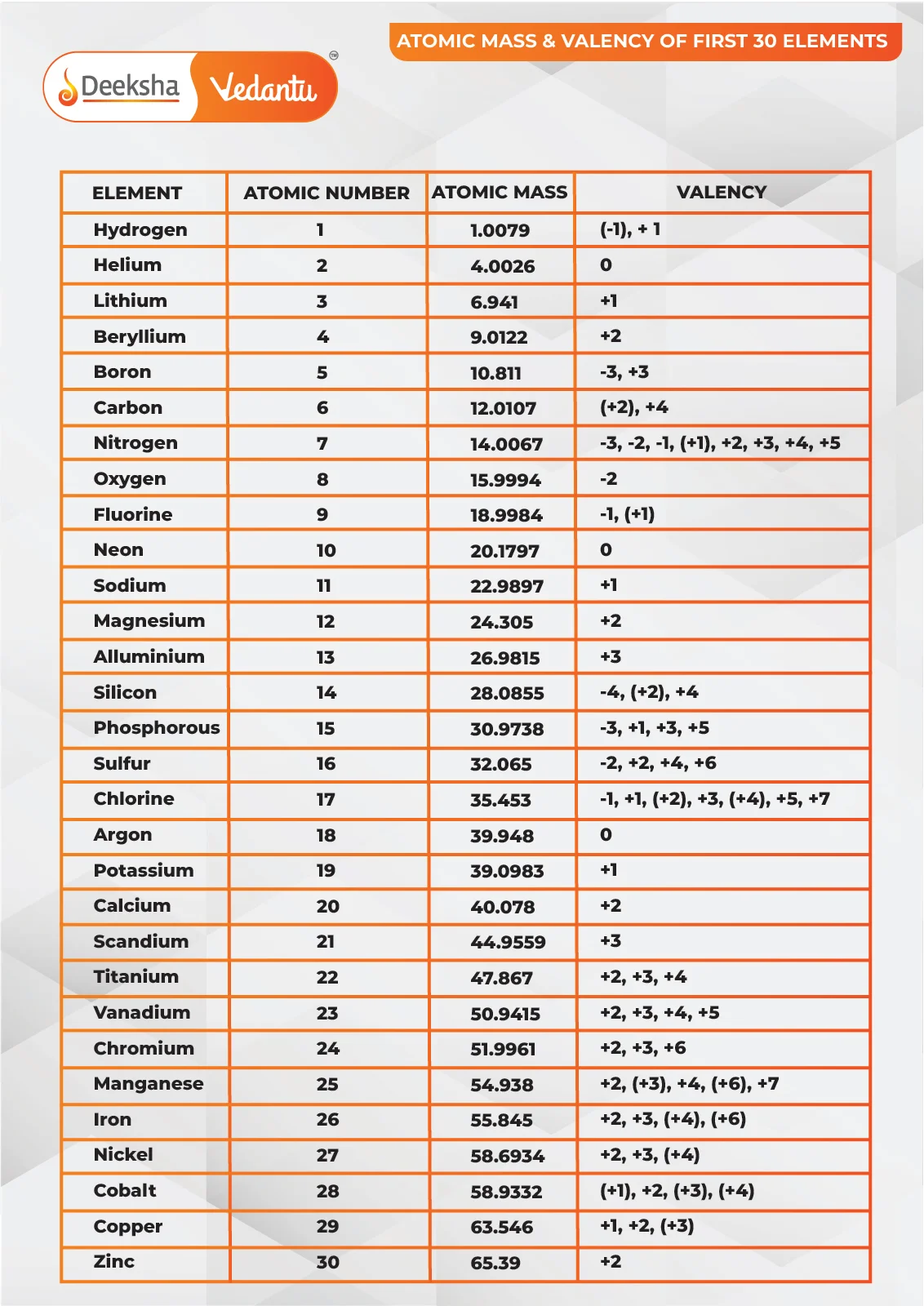
Here is a table of the first 30 elements, along with their atomic masses:
| Atomic Number | Element | Atomic Mass |
| 1 | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | Helium | 4.0026 |
| 3 | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Beryllium | 9.0122 |
| 5 | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | Fluorine | 18.998 |
| 10 | Neon | 20.18 |
| 11 | Sodium | 22.99 |
| 12 | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Aluminium | 26.982 |
| 14 | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | Phosphorus | 30.974 |
| 16 | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | Potassium | 39.098 |
| 20 | Calcium | 40.078 |
| 21 | Scandium | 44.956 |
| 22 | Titanium | 47.867 |
| 23 | Vanadium | 50.942 |
| 24 | Chromium | 51.996 |
| 25 | Manganese | 54.938 |
| 26 | Iron | 55.845 |
| 27 | Cobalt | 58.933 |
| 28 | Nickel | 58.693 |
| 29 | Copper | 63.546 |
| 30 | Zinc | 65.38 |
Difference Between Atomic Number and Atomic Mass
Atomic Number:
- The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- It is denoted by the letter ‘Z’.
- The atomic number defines the identity of an element.
- It determines the element’s position in the periodic table.
- For example, the atomic number of hydrogen is 1, meaning it has one proton.
Atomic Mass:
- The atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an element’s isotopes, measured in atomic mass units (amu).
- It is denoted by the letter ‘A’.
- Atomic mass considers both protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- It can vary slightly due to the presence of different isotopes.
- For example, the atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12.01 amu.
Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Mass Calculation
Isotopes:
- Isotopes are variants of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
- For example, carbon has isotopes like carbon-12 and carbon-13.
- Isotopes have nearly identical chemical properties but different atomic masses.
Calculating Atomic Mass:
- Atomic mass is the weighted average of all isotopes of an element.
- It considers the mass and natural abundance of each isotope.
Example: Neon Isotopes
- Neon has three isotopes: neon-20, neon-21, and neon-22.
- Their respective abundances are 90.48%, 0.27%, and 9.25%.
- The atomic mass is calculated as follows:
- 0.9048×19.992=18.09 amu
- 0.0027×20.994=0.057 amu
- 0.0925×21.991=2.03 amu
- The average atomic mass of neon is 18.09+0.057+2.03=20.18 amu.
Importance of Atomic Mass in Chemistry
- Atomic mass helps determine the molar mass of elements and compounds.
- It is essential for calculating stoichiometric relationships in chemical reactions.
- For example, knowing the atomic mass of iron (55.85 amu) helps in determining that one mole of iron weighs 55.85 grams.
- This concept is vital in determining the amounts of substances required or produced in chemical reactions.
Understanding atomic number and atomic mass is fundamental in the study of chemistry. They provide critical information about the properties of elements and how they interact in chemical reactions. This knowledge is crucial for scientific research, industrial applications, and educational purposes.
FAQs
The atomic mass in amu is numerically equivalent to the mass in grams of one mole of atoms of an element. For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu, so one mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 grams.
The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is an average based on natural isotope abundances and generally does not change. However, variations can occur in different samples due to isotopic enrichment or depletion.
Different isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons, which results in different atomic masses. For instance, carbon-12 has six neutrons, while carbon-13 has seven neutrons.
The atomic mass unit (amu) is a standard unit of mass that quantifies the mass of atoms and subatomic particles. 1 amu is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Atomic mass is usually not a whole number because it is a weighted average of all the isotopes of an element, each with a different mass and natural abundance.
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus and defines the element. The atomic mass includes the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, representing the element’s isotopic composition.
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of that element, measured in atomic mass units (amu). It accounts for both the mass and the relative abundance of each isotope.







Get Social