All living organisms obtain the energy required to perform cellular functions through respiration. While most animals respire aerobically (in the presence of oxygen), certain organisms like bacteria and yeast can generate energy anaerobically (in the absence of oxygen).
Fermentation – Definition
Fermentation is an enzyme-catalyzed metabolic process where organisms convert starch or sugar into alcohol or acid anaerobically, releasing energy. The scientific study of fermentation is known as “zymology”.
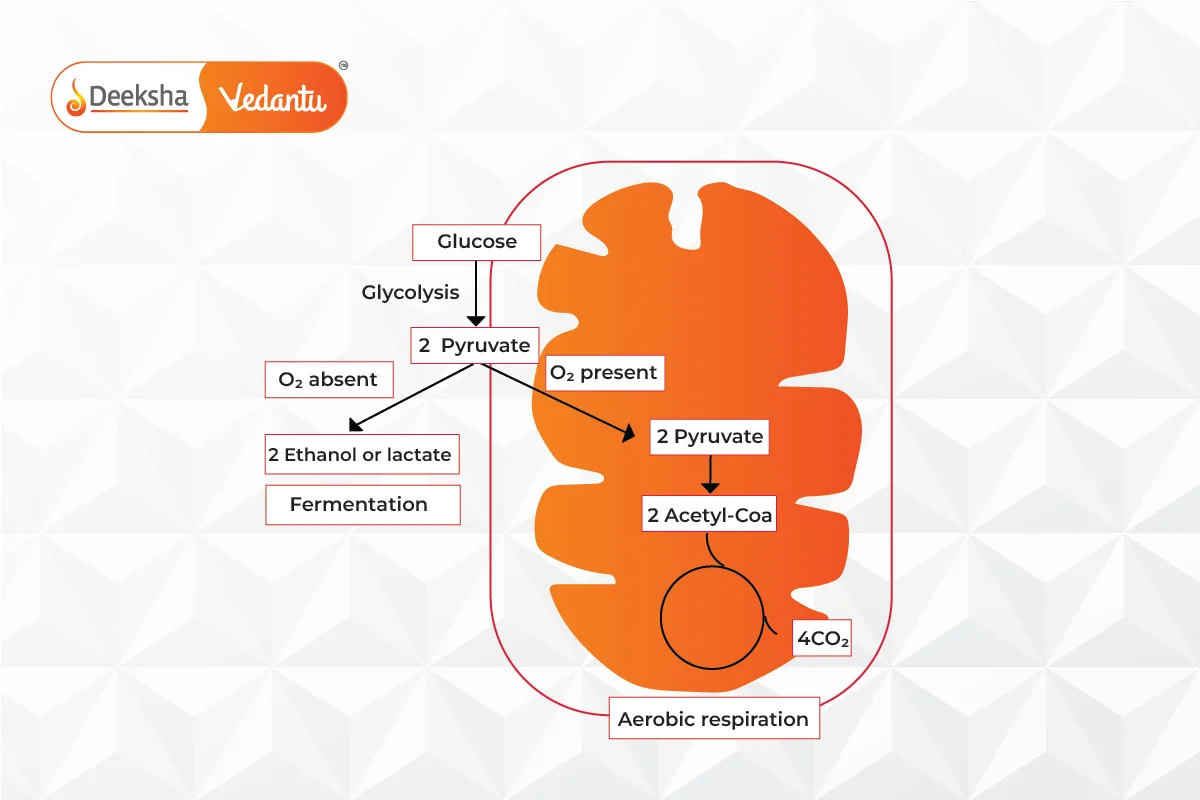
Process of Fermentation
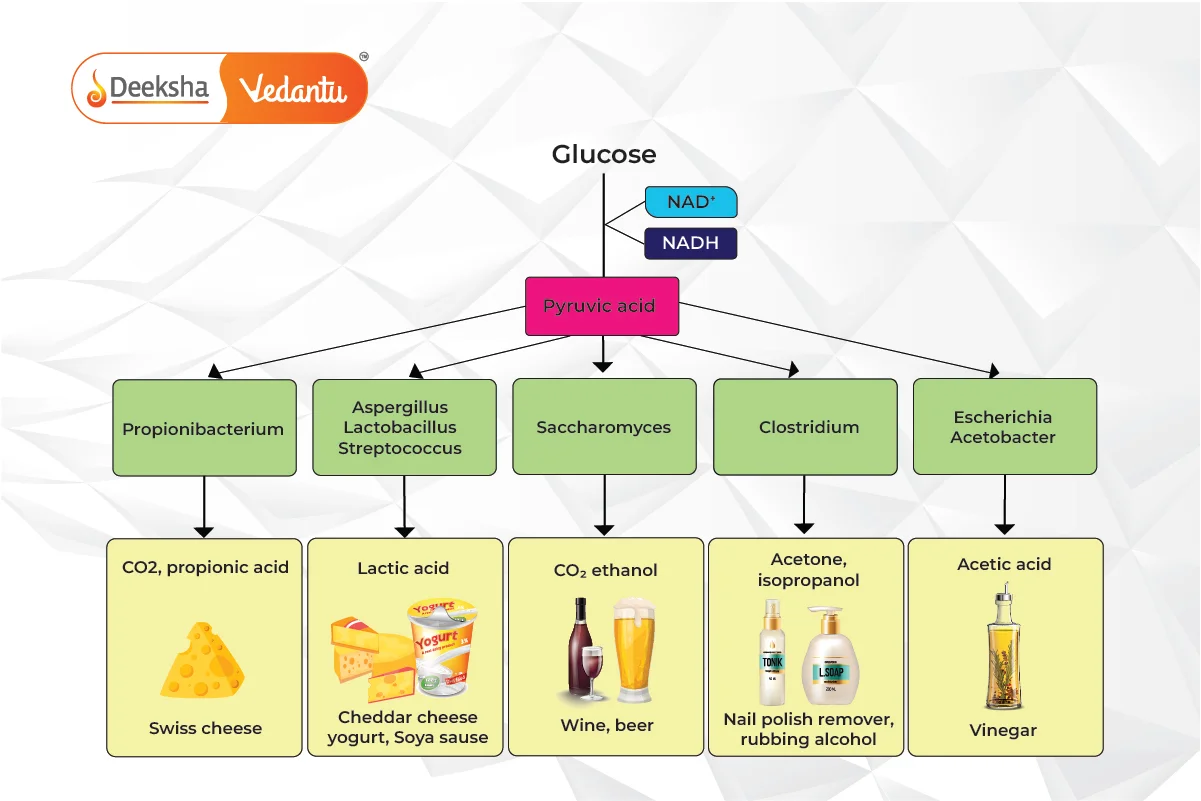
Fermentation is an anaerobic biochemical process. It begins similarly to cellular respiration with the formation of pyruvic acid through glycolysis, yielding a net gain of 2 ATP molecules. The pyruvate is then reduced to lactic acid, ethanol, or other products, regenerating NAD+ for use in glycolysis.
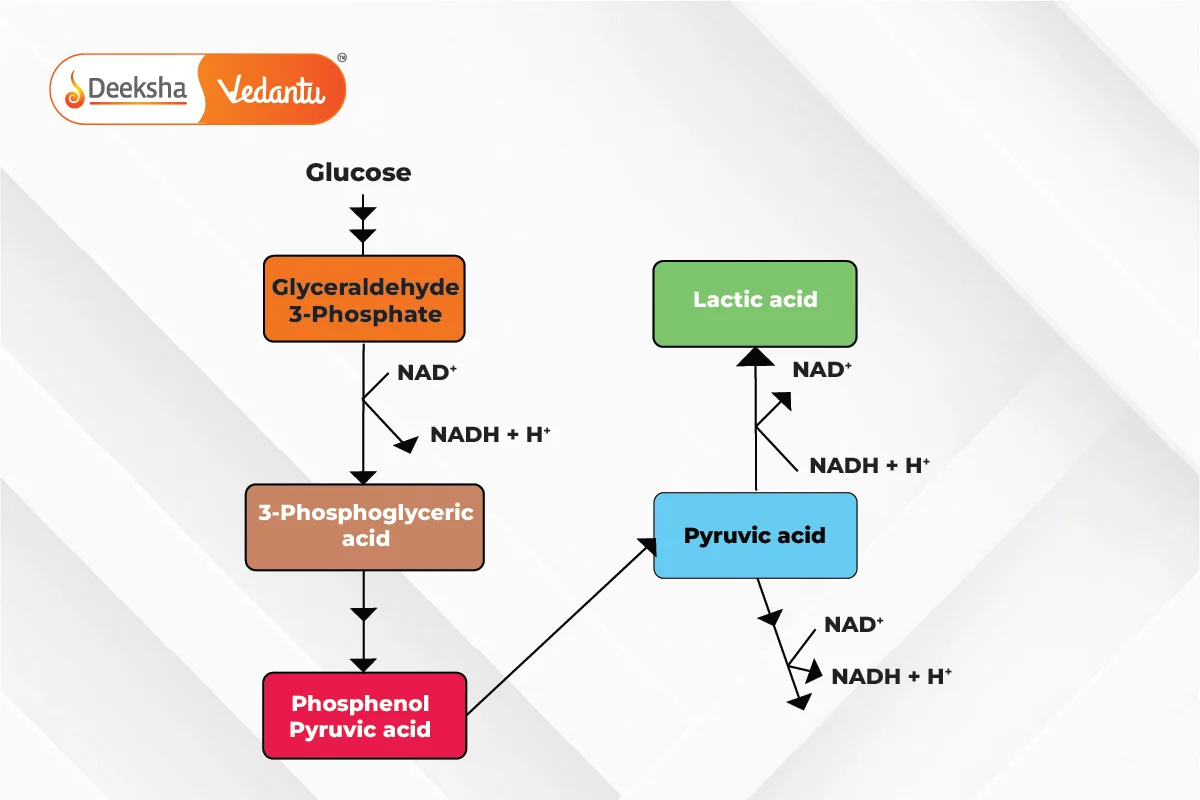
Fermentation Process Overview:
- Glycolysis produces pyruvic acid and ATP.
- Pyruvate is reduced to form various end products (e.g., lactic acid, ethanol).
- NAD+ is regenerated for glycolysis.
Types of Fermentation
Fermentation can be classified based on the end products formed:
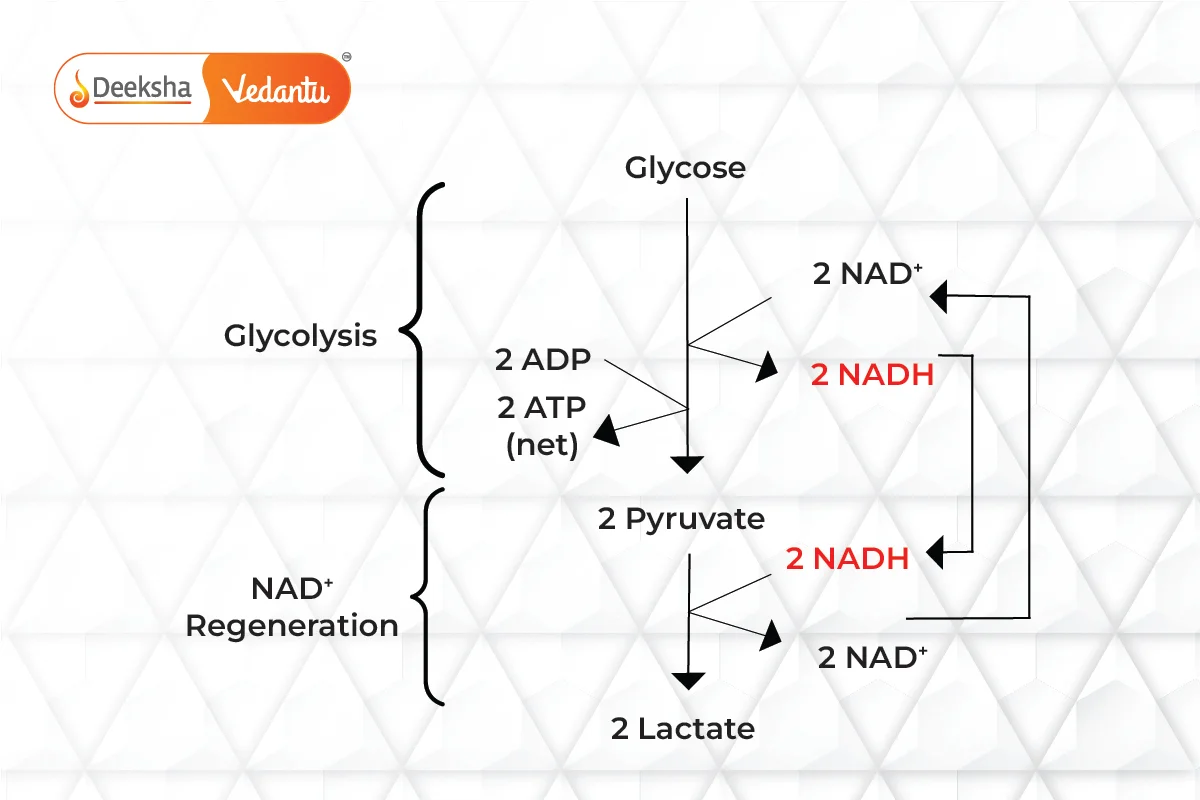
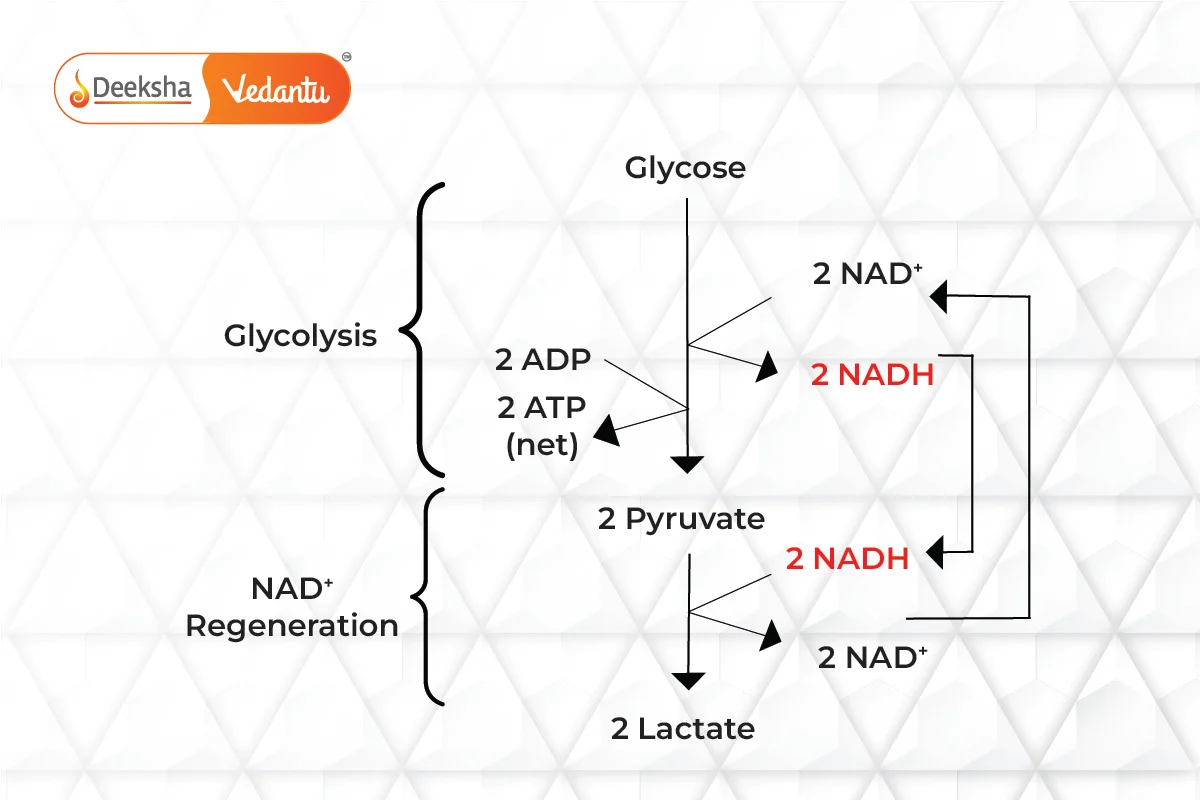
Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Process: Pyruvate from glycolysis is reduced to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase, regenerating NAD+ from NADH.
- Example: Lactobacillus bacteria ferment milk to produce curd. During intense exercise, muscles produce lactic acid, causing fatigue.
Alcohol Fermentation
- Process: Pyruvic acid is converted to acetaldehyde and CO2, then acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol, regenerating NAD+.
- Applications: Used in the production of wine, beer, and biofuels. Yeast and some bacteria perform this fermentation.
Acetic Acid Fermentation
- Process:
- Anaerobic fermentation of sugar to ethyl alcohol by yeast.
- Aerobic oxidation of ethyl alcohol to acetic acid by Acetobacter bacteria.
- Example: Production of vinegar.
- Diagram:
- Process:
Butyric Acid Fermentation
- Process: Carried out by obligate anaerobic bacteria (e.g., Clostridium). Pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA and then reduced to butyric acid, yielding higher energy (3 ATP).
- Applications: Occurs in retting of jute, rancid butter, tobacco processing, and leather tanning. Butyric acid is also produced in the human colon from dietary fiber.
- Diagram:
Advantages of Fermentation
Fermentation is versatile and suitable for various environments, making it one of the oldest and most widespread metabolic processes. It is used in many industries to produce a variety of products:
Advantages of Fermentation
Fermentation is versatile and suitable for various environments, making it one of the oldest and most widespread metabolic processes. It is used in many industries to produce a variety of products:
Fermentation Products:
- Wine
- Beer
- Biofuels
- Yogurt
- Pickles
- Bread
- Sour foods (lactic acid)
- Certain antibiotics and vitamins
Benefits of Fermented Foods:
- Improves digestion and maintains intestinal bacteria.
- Exhibits anti-cancer properties.
- Enhances the immune system.
- Reduces lactose intolerance.
Industrial Uses:
- Methane production in sewage treatment plants and freshwater sediments.
FAQs
The main types are lactic acid fermentation, alcohol fermentation, acetic acid fermentation, and butyric acid fermentation.
No, fermentation is an anaerobic process and occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Butyric acid fermentation, carried out by Clostridium bacteria, produces butyric acid, which is essential for colon health and energy.
Fermented foods improve digestion by maintaining healthy intestinal bacteria and enhancing the immune system.
Fermentation is used to produce wine, beer, biofuels, yogurt, pickles, bread, certain antibiotics, and vitamins.
Yeast converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde and CO2, and then to ethanol, regenerating NAD+ in the process.
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is reduced to lactic acid, regenerating NAD+ for glycolysis.
Fermentation is an enzyme-catalyzed metabolic process where organisms convert sugars or starches into alcohol or acid anaerobically, releasing energy.
Related Topics
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Body Fluids and Circulation
- Paramecium
- Plasmid
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Chromosome Structure
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Marchantia
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Connective Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
- Important Notes For NEET Biology – Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Krebs Cycle
- DNA Polymerases
- Protozoa
- Nostoc











Get Social