Carbohydrates are organic compounds found in living tissues and foods such as starch, cellulose, and sugars. They break down in the body to release energy and have the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen as water, which is 2:1.
What are Carbohydrates?
The general formula for carbohydrates is Cn(H2O)n, which applies to simple sugars composed of equal amounts of carbon and water. Initially, carbohydrates were named for their empirical formula CH2O. Nowadays, carbohydrates are classified based on their structures as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Examples include cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
General Formula of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have the general formula Cx(H2O)y, reflecting their initial identification as “hydrates of carbon.”
Definition in Chemistry
Chemically, carbohydrates are defined as “optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or compounds that produce these units upon hydrolysis.”
Carbohydrates in Science
The term carbohydrate, or hydrates of carbon, comes from their basic formula where carbon is combined with hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as water. They are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, their simple derivatives, or polymers.
Carbohydrate Structure
Historically, carbohydrates were identified by the formula Cn(H2O)m. Today, they are considered as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, their related molecules, or their oligomers or polymers. The terms “monosaccharide,” “disaccharide,” and “polysaccharide” refer to carbohydrates with one, two, and many monosaccharide units, respectively.
Types of Carbohydrates
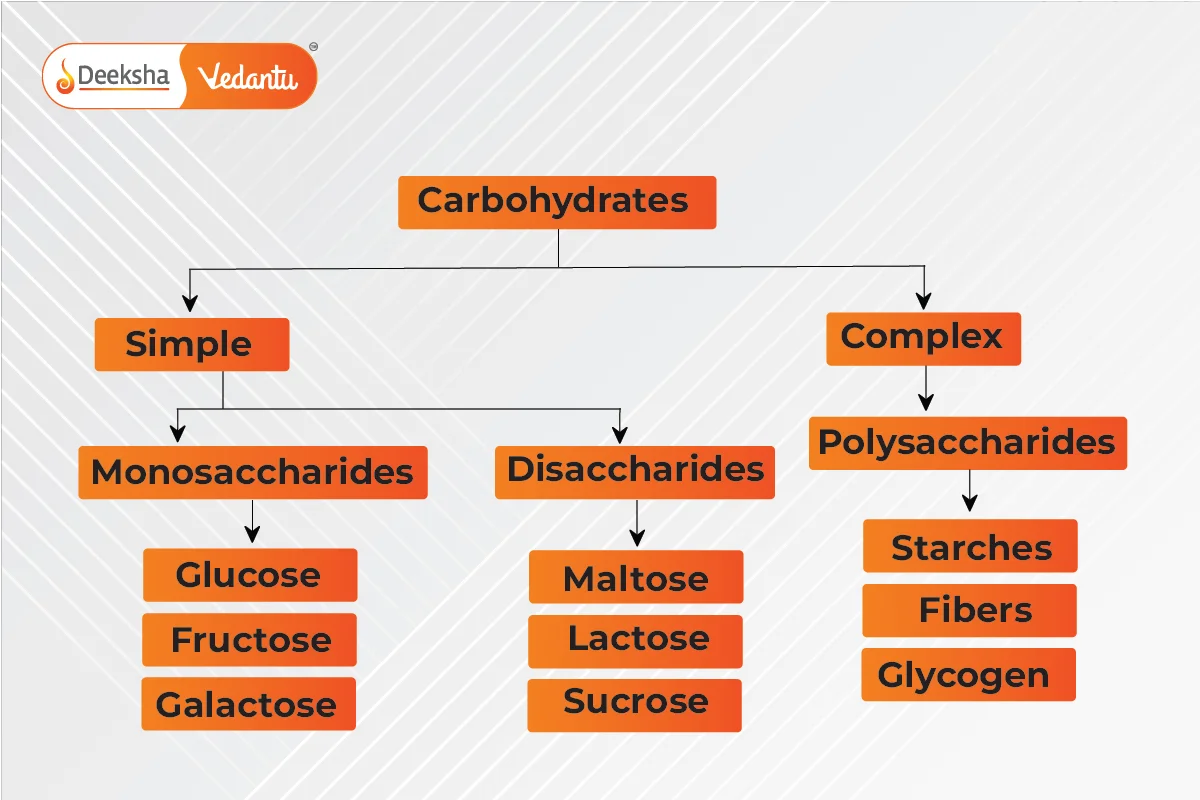
- Simple Carbohydrates: Found in sweets, fruits, and milk, they are quickly digested and include monosaccharides and disaccharides.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Provide long-lasting energy and are found in grains and vegetables. They include polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides: Single-unit carbohydrates, cannot be broken down further; examples include glucose. Disaccharides: Yield two monosaccharides upon hydrolysis; examples include sucrose and lactose. Polysaccharides: Long chains of monosaccharides; examples include starch and cellulose.
Examples of Carbohydrates
Common sources of carbohydrates include dairy products (yogurt, milk), fruits (whole fruit and fruit juice), grains (cereal, bread), legumes (beans), and starchy vegetables (corn, potatoes).
Carbohydrate Structure Details
- Glucose: An important monosaccharide, can be derived from sucrose or starch. It forms a ring structure in solution and is a primary energy source.
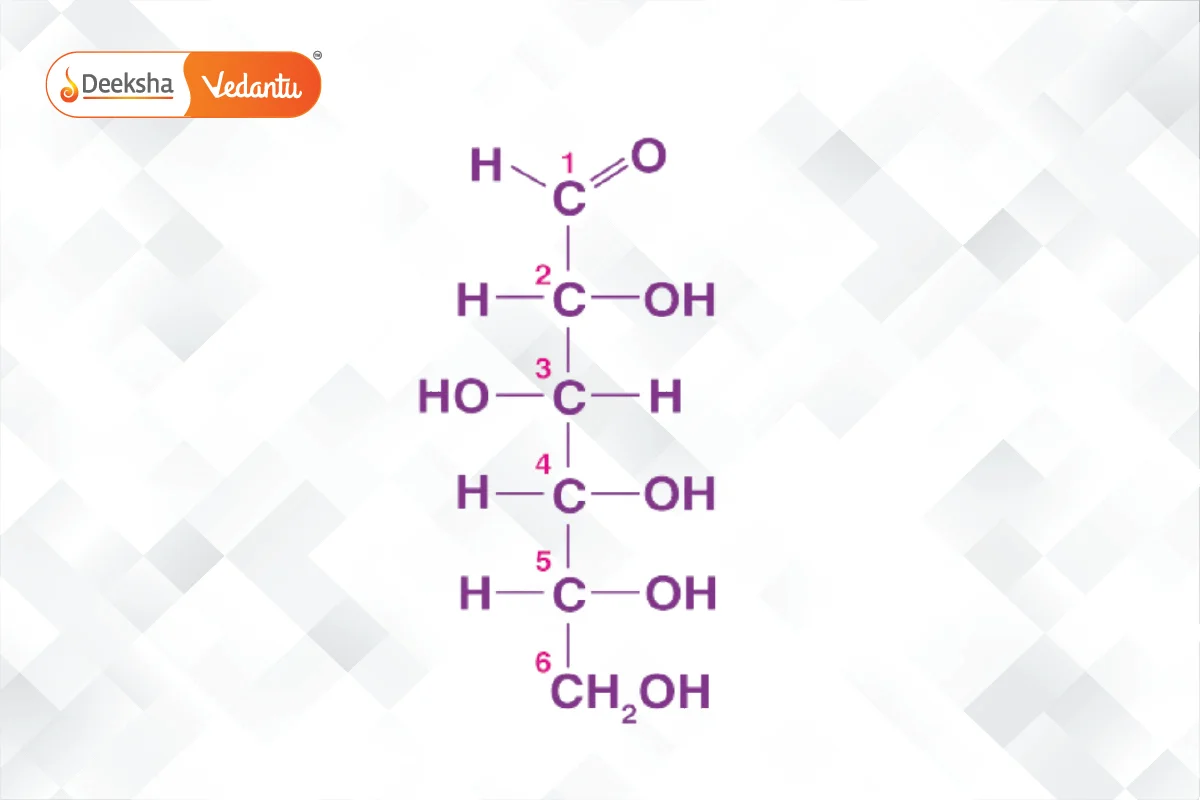
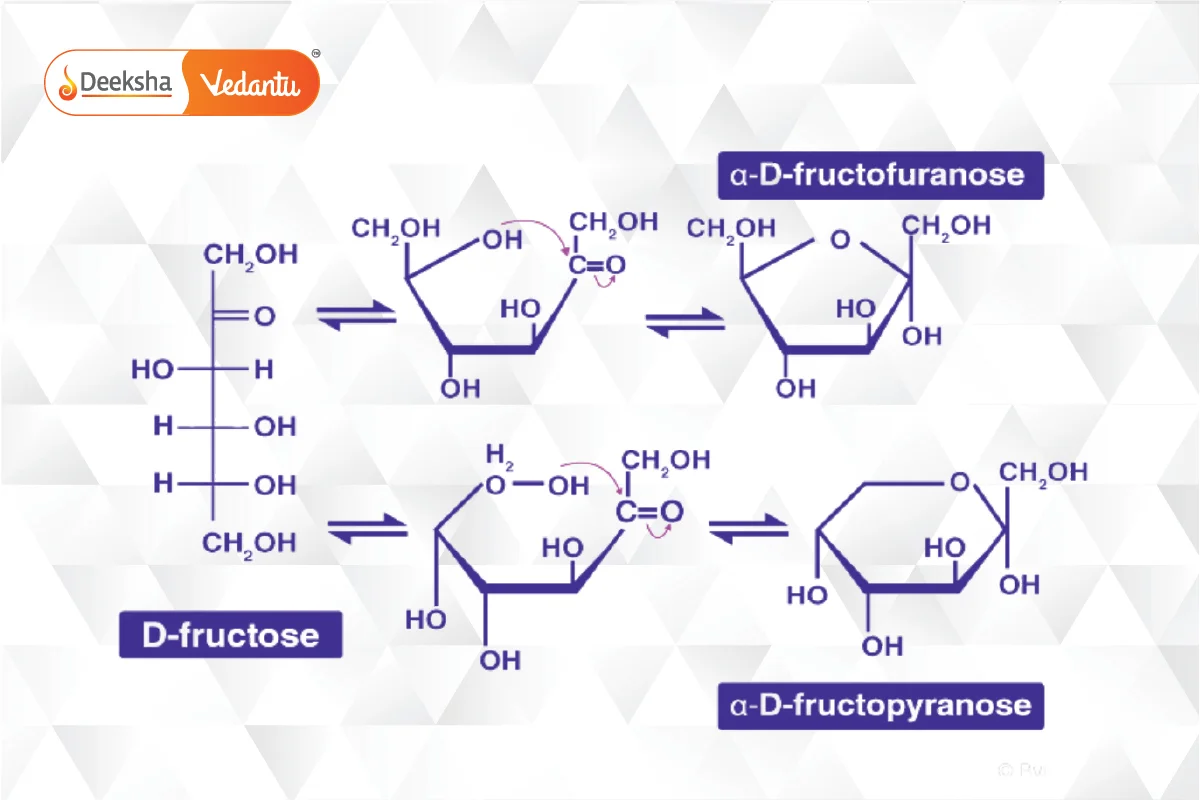
- Fructose: A key ketohexose, similar to glucose but with a ketone group. It also forms a ring structure called furanose.
Historical Context
By the 19th century, carbohydrates like sucrose, cellulose, starch, glucose, fructose, mannose, and lactose were well-known. Emil Fischer’s work in the late 1800s helped advance the understanding of carbohydrates.
Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an essential part of the diet, found in foods like potatoes, maize, milk, popcorn, and bread.
FAQs
Carbohydrates break down to release energy, providing fuel for various bodily functions and activities.
Common sources include potatoes, maize, milk, popcorn, and bread.
Types include monosaccharides (single unit), disaccharides (two units), and polysaccharides (many units).
Carbohydrates are classified based on their structures into simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starch, cellulose).
The general formula is Cx(H2O)y, originally thought to be hydrates of carbon.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds found in living tissues and foods, breaking down to release energy. They include sugars, starch, and cellulose.
Related Topics
- Chemistry FAQs
- Atomic Mass of Elements
- Hybridization
- What Do All Acids And All Bases Have In Common?
- Versatile Nature Of Carbon
- Electronic Configuration of First 30 Elements
- Rutherford’s Model of Atoms and its Limitations
- Isomerism
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Bohr’s Model Of Atom
- Modern Periodic Table
- How Strong Are Acid Or Base Solutions?
- Understanding the Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
- Soaps And Detergents
- Protein Structure And Levels of Protein








Get Social