A triangle is one of the most fundamental shapes in geometry, forming the basis of numerous mathematical concepts and real-world applications. It is a polygon with three sides, three vertices, and three angles, with the sum of its interior angles always equal to .
Triangles are widely classified based on their sides and angles.
Classification of Triangles
By Sides
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal, and each angle measures
.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal, and the angles opposite these sides are also equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides and angles are unequal.
By Angles
- Acute Triangle: All angles are less than
.
- Right Triangle: One angle measures exactly
.
- Obtuse Triangle: One angle is greater than
.
Similarity of Triangles
Two triangles are similar if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in proportion. This is a cornerstone of geometry, used extensively in solving problems related to height, distance, and measurement.
Criteria for Similarity
- AA (Angle-Angle) Criterion: If two angles of one triangle are equal to two angles of another triangle, the triangles are similar.
- SSS (Side-Side-Side) Criterion: If the corresponding sides of two triangles are in proportion, the triangles are similar.
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side) Criterion: If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are in proportion, the triangles are similar.
Example
Problem: In and
,
,
, and
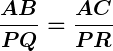
.
Solution:
By the AA criterion:
Additionally, 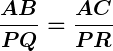
Important Theorems on Triangles
- Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales' Theorem):
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle, intersecting the other two sides, it divides those sides in the same ratio:
- Pythagoras Theorem:
In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides:
Example Using Pythagoras Theorem
Problem: In a right-angled triangle, the lengths of two sides are and
. Find the hypotenuse.
Solution:
Using the formula:
Substituting the values:
Answer:
Applications of Similarity in Triangles
- Measuring Heights and Distances:
Triangle similarity is used in indirect measurement techniques, such as calculating the height of a building using shadows. - Map Scaling:
Similar triangles are used in maps and scale models to represent real-world distances.
Practice Problems
- Problem: In
,
, and
. Find
.
Solution:
Using the Basic Proportionality Theorem:
- Problem: In a triangle, the sides are
. Show whether the triangle is right-angled.
Solution:
Using Pythagoras Theorem:
Substituting the values:
The triangle satisfies Pythagoras Theorem, so it is a right-angled triangle.
FAQs
To prove similarity, use the AA, SSS, or SAS criterion:
.
.
.
Similar triangles are used in:
- Indirect measurement techniques (e.g., finding heights of buildings).
- Map scaling and architectural designs.
In a right-angled triangle, one angle measures , and the Pythagoras Theorem holds:
.
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always .





Get Social