Plant Cell Definition
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that perform specific functions.
What is a Plant Cell?
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several ways from other eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells. They have a nucleus and similar organelles but also have a unique structure called a cell wall outside the cell membrane.
Plant Cell Diagram
Plant cells are rectangular and generally larger than animal cells. They perform different functions and have some distinct features when observed under a microscope.
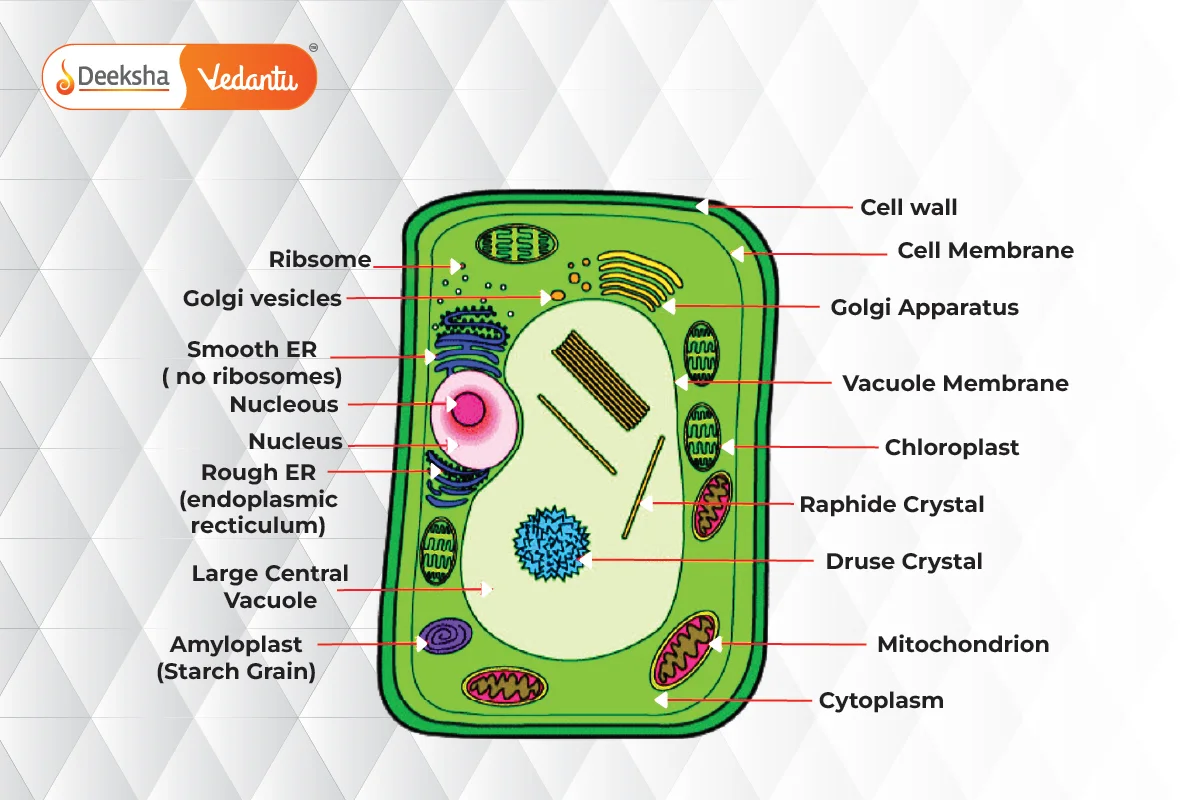
Plant Cell Structure
Plant cells have various components called organelles that perform different functions. These organelles include:
Cell Wall
- Rigid layer made of cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose.
- Provides structural support and protection.
- Involves three layers: primary, secondary, and middle lamella.
Cell Membrane
- Semi-permeable membrane within the cell wall.
- Regulates entry and exit of substances.
- Keeps toxins out and transports nutrients and minerals.
Nucleus
- Membrane-bound structure that stores DNA.
- Controls cell division, metabolism, and growth.
Plastids
- Membrane-bound organelles with their own DNA.
- Important for storing starch and photosynthesis.
- Types include leucoplasts, chloroplasts, and chromoplasts.
Central Vacuole
- Occupies about 30% of the cell’s volume.
- Stores substances and maintains turgor pressure.
Golgi Apparatus
- Distributes synthesized macromolecules within the cell.
Ribosomes
- Sites of protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
- Double-membraned organelles that produce energy.
- Known as the “powerhouse of the cell.”
Lysosome
- Contains digestive enzymes for waste disposal.
- In plants, vacuoles perform a similar role.
Plant Cell Types
Plant cells specialize to perform specific functions, such as nutrient and water transportation or food storage. Types include:
Collenchyma Cells
- Provide support to plants, especially in areas of growth.
Sclerenchyma Cells
- More rigid and provide support.
Parenchyma Cells
- Involved in gas exchange, food production, and storage.
Xylem Cells
- Transport water and minerals from roots to other parts.
Phloem Cells
- Transport food from leaves to other parts.
Plant Cell Functions
Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. The main function is photosynthesis, occurring in chloroplasts, where sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are used to produce food and energy (ATP). Some cells help transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
FAQs
Types include leucoplasts (storage), chloroplasts (photosynthesis), and chromoplasts (pigment storage).
Xylem cells transport water and minerals from the roots, while phloem cells transport food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
The central vacuole stores substances and helps maintain turgor pressure against the cell wall.
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis, where plants produce food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the plant cell.
Main components include the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, plastids, central vacuole, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes.
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a nucleus and specialized organelles, distinct from animal cells by the presence of a cell wall.










Get Social