Introduction to Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are a crucial part of algebra, forming the foundation for solving complex problems across various disciplines. Let's dive into what quadratic equations are, explore their methods of solution, and review real-life applications.
What is a Quadratic Equation?
A quadratic equation is any equation that can be expressed as:
Where:
are constants (
).
is the variable.
Standard Form of Quadratic Equations
The standard form of a quadratic equation is:
Key components:
: The quadratic term.
: The linear term.
: The constant term.
Example:
Convert into standard form:
Rearrange terms: .
Multiply by :
.
Methods to Solve Quadratic Equations
1. Factorization
This involves expressing the quadratic equation as a product of two binomials.
Example: Solve .
Steps:
- Factorize:
.
- Solve:
,
.
Answer: .
2. Completing the Square
This technique transforms the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial.
Example: Solve .
Steps:
- Rewrite:
.
- Add
:
.
- Factorize:
.
- Solve:
.
,
.
Answer: .
3. Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is:
Example: Solve .
Steps:
- Identify
.
- Discriminant:
.
- Apply formula:
.
Solutions: .
4. Graphical Method
In this method, the equation is plotted as a parabola. The roots are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis.
Example: For :
- Plot
.
- Intersection points:
.
Answer: .
Nature of Roots
The discriminant () determines the type of roots:
: Two distinct real roots.
: One repeated root.
: Complex roots.
Example: Solve .
- Discriminant:
.
- Complex roots:
.
Answer: .
Applications of Quadratic Equations
- Projectile Motion: Calculating the path of an object in free fall.
- Geometry: Finding dimensions or areas of geometric shapes.
- Optimization: Maximizing profits or minimizing costs in economics.
Example:
A rectangle's area is 24 m². If the length is 2 m more than the width, find the dimensions.
- Let width =
. Length =
.
- Area:
.
- Solve
:
.
(positive value).
Answer: Width = 4 m, Length = 6 m.
Sample Questions with Answers
- Solve
.
Answer:.
- Find the nature of roots for
.
Answer:, one repeated root (
).
- Solve using the quadratic formula:
.
Answer:.
FAQs
Quadratic equations are used in physics, geometry, economics, engineering, and optimization problems.
The discriminant () determines if roots are real, repeated, or complex.
Factorization, completing the square, quadratic formula, and graphical method.
A polynomial equation of degree two, expressed as , where
.



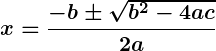
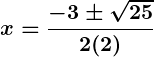
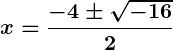


Get Social