Introduction
After understanding scalar and vector quantities in the previous section, NCERT introduces the concept of multiplying vectors by real numbers. This operation is fundamental to vector algebra and is frequently used while describing physical quantities such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration in motion analysis.
For JEE aspirants, this concept is essential because scaling vectors is used in resolving vectors, reversing directions, and interpreting physical quantities correctly. At Deeksha Vedantu, this topic is taught as a natural continuation of scalar–vector distinction, ensuring students build strong conceptual clarity before moving to vector addition and resolution.
Meaning of Multiplication of a Vector by a Real Number
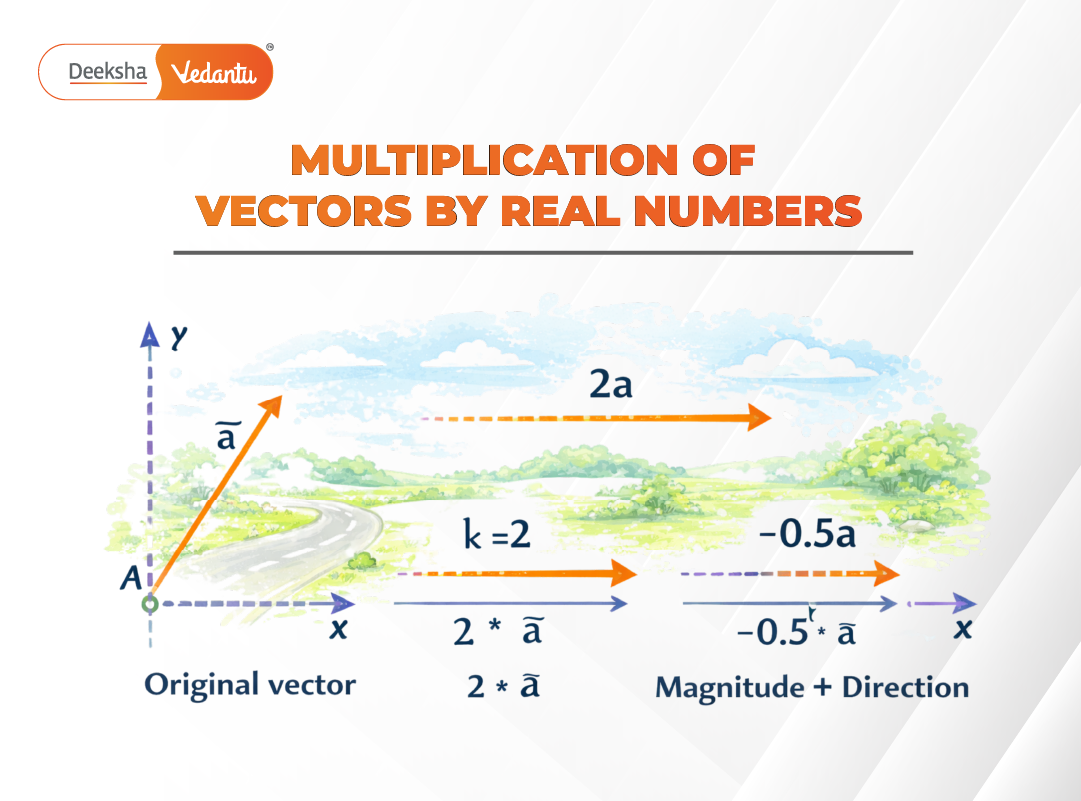
When a vector is multiplied by a real number, the result is another vector.
If a vector is multiplied by a real number
, the new vector is written as:
This operation changes the magnitude of the vector and may also change its direction depending on the sign of the real number.
Effect on Magnitude of a Vector
The magnitude of the new vector obtained after multiplication is:
This implies:
- If
, the magnitude of the vector increases
- If
, the magnitude of the vector decreases
- If
, the resulting vector becomes a zero vector
Understanding how magnitude changes is crucial while analysing velocity and acceleration vectors in JEE problems.
Effect on Direction of a Vector
The direction of the vector after multiplication depends on the sign of the real number.
Multiplication by a Positive Real Number
If , the direction of the vector remains unchanged.
For example:
has the same direction as
but twice the magnitude.
Multiplication by a Negative Real Number
If , the direction of the vector is reversed.
For example:
has the same magnitude as
but points in the opposite direction.
This idea is extremely important in JEE when interpreting direction changes in displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
Graphical Interpretation
Graphically, multiplying a vector by a real number changes the length and/or direction of the arrow representing the vector.
- A positive real number changes only the length of the vector
- A negative real number reverses the direction of the vector
This visual understanding helps avoid sign-related errors in vector-based problems.
Special Cases
Multiplication by Zero
When a vector is multiplied by zero:
- The result is a zero vector
- Magnitude becomes zero
- Direction is undefined
Multiplication by One
When a vector is multiplied by one:
The vector remains unchanged.
Multiplication by Minus One
When a vector is multiplied by minus one:
- Magnitude remains the same
- Direction is reversed
Physical Significance in Motion in a Plane
Multiplication of vectors by real numbers is used extensively in motion analysis to:
- Scale displacement and velocity vectors
- Represent acceleration direction using sign conventions
- Resolve vectors along coordinate axes
For example, acceleration due to gravity is represented along the vertical direction using a negative sign to indicate downward direction. Such representations directly depend on scalar multiplication of vectors.
At Deeksha Vedantu, students are trained to attach physical meaning to signs and coefficients in vector equations rather than treating them as mere mathematical symbols.
Common Conceptual Errors (JEE Perspective)
Some common mistakes include:
- Assuming multiplication always changes direction
- Ignoring the effect of negative real numbers
- Confusing scalar multiplication with vector addition
Avoiding these errors is critical for accurate problem-solving in JEE-level physics.
FAQs
Q1. What happens when a vector is multiplied by a real number?
The magnitude of the vector changes according to the real number, and the direction may remain the same or reverse depending on the sign.
Q2. Does multiplication by a positive real number change direction?
No, multiplication by a positive real number does not change the direction of the vector.
Q3. What is the effect of multiplying a vector by a negative real number?
The magnitude changes proportionally, and the direction of the vector is reversed.
Q4. What is the result of multiplying a vector by zero?
The result is a zero vector with zero magnitude.
Q5. Why is this concept important for JEE?
Because scalar multiplication of vectors is used repeatedly in resolving vectors, interpreting motion, and applying sign conventions in physics problems.
Conclusion
Section 3.3 Multiplication of Vectors by Real Numbers explains how vectors change when scaled by numerical factors. For JEE aspirants, mastering this concept is essential for understanding vector algebra and motion analysis. A clear conceptual approach, as emphasised at Deeksha Vedantu, ensures accuracy and confidence before advancing to more complex vector operations.





Get Social