What is a Chemical Reaction?
A chemical reaction is a process where reactants undergo chemical changes to form products. An example is respiration, where we inhale oxygen that reacts with glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy:

Characteristics of a Chemical Reaction
Chemical reactions often exhibit one or more of the following characteristics:
Evolution of Gas:
- Some reactions produce gas. For example, when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid:
- Some reactions produce gas. For example, when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid:
Change in Colour:
- Some reactions cause a color change. For example, when lead nitrate reacts with potassium iodide:
- Colorless lead nitrate and potassium iodide form yellow lead iodide and colorless potassium nitrate.
- Some reactions cause a color change. For example, when lead nitrate reacts with potassium iodide:
Change in Temperature:
- Some reactions release or absorb heat, making them exothermic or endothermic.
Change in Energy:
- Reactions often involve energy changes, such as in combustion, where energy is released.
Formation of Precipitate:
- Some reactions produce an insoluble precipitate. For example, when barium chloride reacts with sodium sulfate:
- Some reactions produce an insoluble precipitate. For example, when barium chloride reacts with sodium sulfate:
Change in State:
- Some reactions change the state of substances. For example, ammonia gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form solid ammonium chloride:
- Some reactions change the state of substances. For example, ammonia gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form solid ammonium chloride:
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are many types of chemical reactions. Here are eight common types:
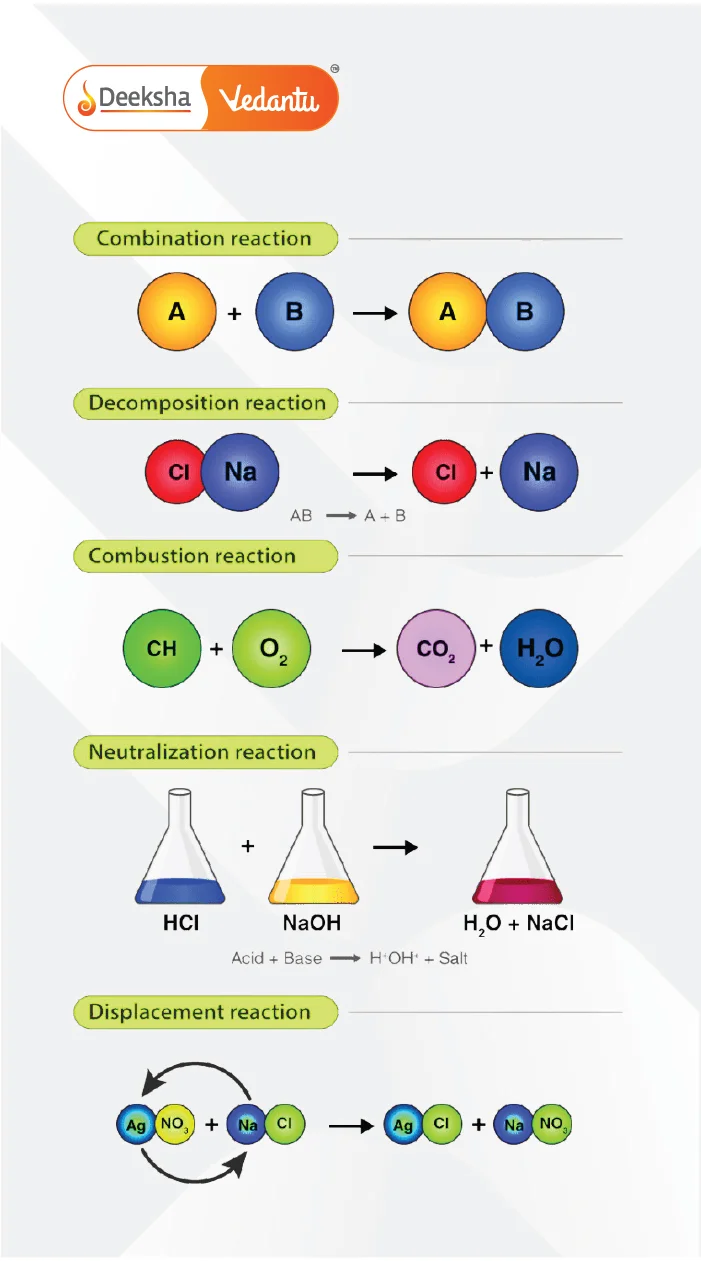
Decomposition Reaction:
- A compound breaks down into simpler substances. Example: Electrolysis of water:
- A compound breaks down into simpler substances. Example: Electrolysis of water:
Combination Reaction:
- Two or more substances combine to form a compound. Example: Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide:
- Two or more substances combine to form a compound. Example: Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide:
Combustion Reaction:
- An exothermic reaction where fuel reacts with oxygen to produce heat. Example: Burning methane:
- An exothermic reaction where fuel reacts with oxygen to produce heat. Example: Burning methane:
Neutralization Reaction:
- Acid reacts with base to form salt and water. Example: Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide:
- Acid reacts with base to form salt and water. Example: Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide:
Single Displacement Reaction:
- A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt. Example: Potassium reacts with magnesium chloride:
- A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt. Example: Potassium reacts with magnesium chloride:
Double Displacement Reaction:
- Two ionic compounds exchange ions to form new compounds. Example: Potassium nitrate reacts with aluminum chloride:
- Two ionic compounds exchange ions to form new compounds. Example: Potassium nitrate reacts with aluminum chloride:
Precipitation Reaction:
- Two soluble salts react to form an insoluble precipitate. Example: Silver nitrate reacts with potassium chloride:
- Two soluble salts react to form an insoluble precipitate. Example: Silver nitrate reacts with potassium chloride:
Redox Reaction:
- Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. Example: Copper oxide reacts with hydrogen:
- Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. Example: Copper oxide reacts with hydrogen:
List of Common Chemical Reactions
Here are some common chemical reactions:
- Electrolysis of Water:
- Rusting of Iron:
- Quicklime with Water:
- Photosynthesis:
(in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll)
- Respiration:
- Combustion of Hydrogen:
- Decomposition of FeSO4:
- Decomposition of Lead Nitrate:
- Displacement of Copper Sulfate by Iron:
FAQs
A reaction where oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. Example: Copper oxide reacting with hydrogen.
A reaction where two or more substances combine to form a compound. Example: Magnesium burning in oxygen.
A reaction where a compound breaks down into simpler substances. Example: Electrolysis of water.
A chemical reaction is a process where reactants undergo chemical changes to form products.
A chemical reaction is a process where reactants undergo chemical changes to form products.






Get Social