Introduction
After understanding graphical methods of vector addition and subtraction, NCERT introduces resolution of vectors as a powerful analytical technique to simplify vector problems. Resolution of vectors involves breaking a single vector into two or more component vectors along specified directions, most commonly along mutually perpendicular axes. This method allows complex two-dimensional situations to be handled using simple one-dimensional principles.
For JEE aspirants, this section is extremely important because almost all numerical problems in two-dimensional motion rely on resolving vectors into components. Whether it is projectile motion, relative velocity, or motion under gravity, vector resolution forms the starting point of analysis. At Deeksha Vedantu, vector resolution is taught as the key tool that converts complex two-dimensional problems into simpler, systematic one-dimensional analyses.
Meaning of Resolution of Vectors
Resolution of a vector means expressing a given vector as the sum of two or more vectors acting along chosen directions. These component vectors together produce the same physical effect as the original vector.
If a vector is acting in a plane, it can always be resolved into two perpendicular components, usually along the x-axis and y-axis. This choice of perpendicular directions is convenient because motion along one axis does not affect motion along the other.
Mathematically, if a vector is resolved along two perpendicular directions, its components are written as:
This expression shows that the original vector can be reconstructed completely by adding its components.
Rectangular Components of a Vector
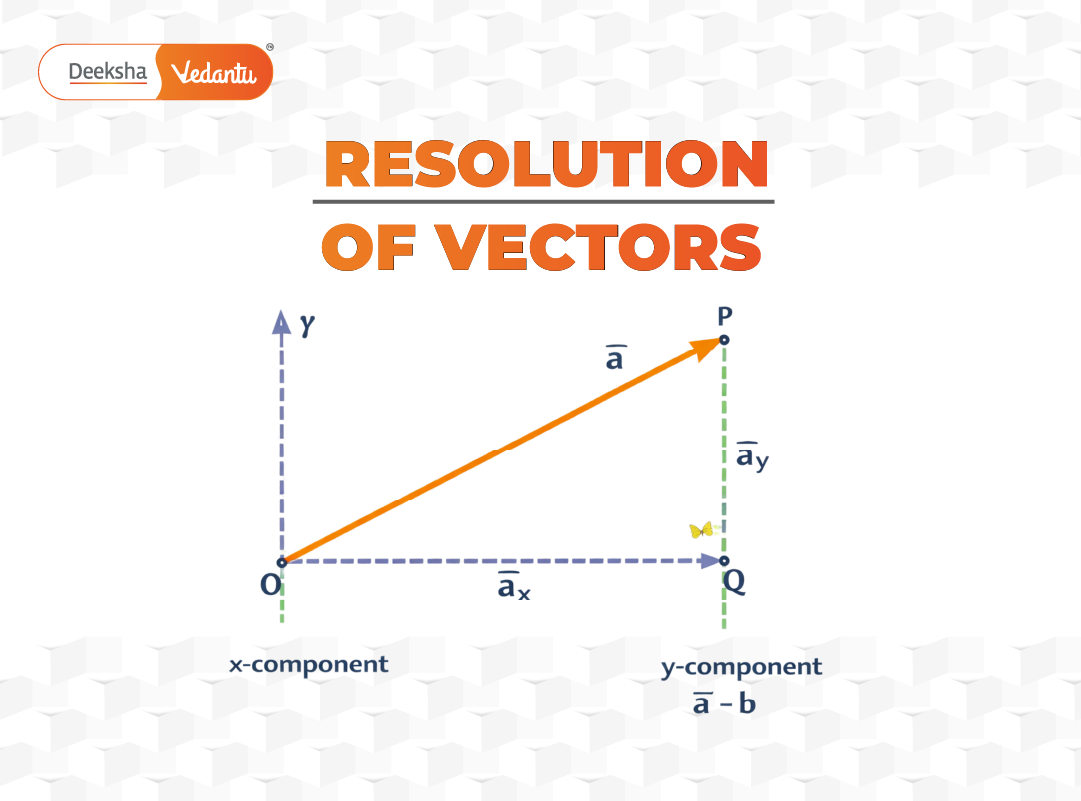
The most common method of resolution discussed in NCERT is resolution into rectangular components. These components are taken along mutually perpendicular coordinate axes, typically the horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis).
Resolution Along Coordinate Axes
Consider a vector making an angle
with the positive x-axis. By dropping perpendiculars from the tip of the vector onto the axes, the vector can be split into horizontal and vertical components.
Its components along the x-axis and y-axis are:
These components represent the projections of the vector along the respective axes. The choice of sine or cosine depends on the angle the vector makes with the reference axis, which is a frequent source of confusion in JEE problems.
Vector Form of Components
The component vectors can be written in vector form as:
Thus, the vector can be expressed compactly as:
This form is widely used in JEE problems because it allows direct substitution into equations of motion and simplifies vector addition algebraically.
Physical Significance of Vector Resolution
Resolution of vectors allows independent analysis of motion along perpendicular directions. This independence is a fundamental principle of mechanics and is repeatedly used in NCERT examples.
In motion in a plane:
- Horizontal and vertical motions are independent of each other
- Acceleration due to gravity acts only along the vertical direction
- Velocities, displacements, and accelerations can be analysed separately along each axis
Because of this independence, equations of motion can be applied separately along the x and y directions, greatly simplifying problem-solving.
Resolution in Motion Analysis
In practical motion problems, resolution of vectors is used at multiple stages:
- Displacement vectors are resolved to determine net displacement in each direction
- Velocity vectors are resolved to analyse speed components along different axes
- Acceleration vectors are resolved to apply kinematic equations independently
For example, in projectile motion, the initial velocity vector is resolved into horizontal and vertical components. The horizontal component remains constant, while the vertical component changes due to gravity. This entire analysis is based on vector resolution.
At Deeksha Vedantu, students are trained to visualise component vectors clearly using diagrams before substituting values into equations. This approach reduces sign errors and improves conceptual clarity.
Advantages of Resolving Vectors
Resolution of vectors offers several advantages in physics problem-solving:
- Simplifies vector addition and subtraction by reducing them to scalar operations
- Converts two-dimensional problems into manageable one-dimensional ones
- Makes application of equations of motion straightforward and systematic
- Reduces dependence on approximate graphical methods
Due to these advantages, resolution of vectors is the preferred method for numerical problem solving in JEE examinations.
Common Conceptual Errors (JEE Perspective)
Despite its importance, students often commit errors while resolving vectors, such as:
- Interchanging sine and cosine components incorrectly
- Choosing the wrong reference angle
- Ignoring sign conventions for components in different quadrants
- Confusing vector magnitude with individual vector components
Being mindful of these errors and practising systematic resolution helps improve accuracy and speed in JEE-level questions.
FAQs
Q1. What is meant by resolution of vectors?
Resolution of vectors means breaking a single vector into two or more components along specified directions such that their combined effect equals the original vector.
Q2. Why are vectors usually resolved into perpendicular components?
Because perpendicular components act independently, making motion analysis simpler and more systematic.
Q3. How are rectangular components of a vector calculated?
By multiplying the magnitude of the vector with cosine and sine of the angle it makes with the reference axis.
Q4. Why is vector resolution important for JEE preparation?
Because most JEE problems involving two-dimensional motion rely on analysing motion component-wise.
Q5. Is vector resolution limited only to kinematics?
No, vector resolution is used throughout physics, including force analysis, equilibrium, and field-related topics.
Conclusion
Section 3.5 Resolution of Vectors introduces the most important analytical tool for handling vectors in two dimensions. For JEE aspirants, mastering this section is essential because it forms the base for projectile motion, relative velocity, and advanced mechanics problems. A strong conceptual understanding, as emphasised at Deeksha Vedantu, ensures speed, accuracy, and confidence while solving vector-based questions in competitive examinations.





Get Social