Introduction
Newton’s Third Law of Motion completes the logical structure of classical mechanics by explaining how forces originate due to interactions between bodies. While Newton’s First Law describes motion in the absence of net force and the Second Law quantifies the effect of force on motion, the Third Law explains why forces exist in the first place.
This law reveals that forces never act in isolation. Every force arises as a result of mutual interaction between two bodies. From simple everyday activities like walking and jumping to complex physical systems such as rockets and recoil mechanisms, Newton’s Third Law governs all interactions. For JEE aspirants, a clear understanding of this law is essential because many conceptual errors in mechanics stem from confusion about action–reaction force pairs. At Deeksha Vedantu, this law is treated as a cornerstone concept for analysing interacting systems accurately.
Statement of Newton’s Third Law
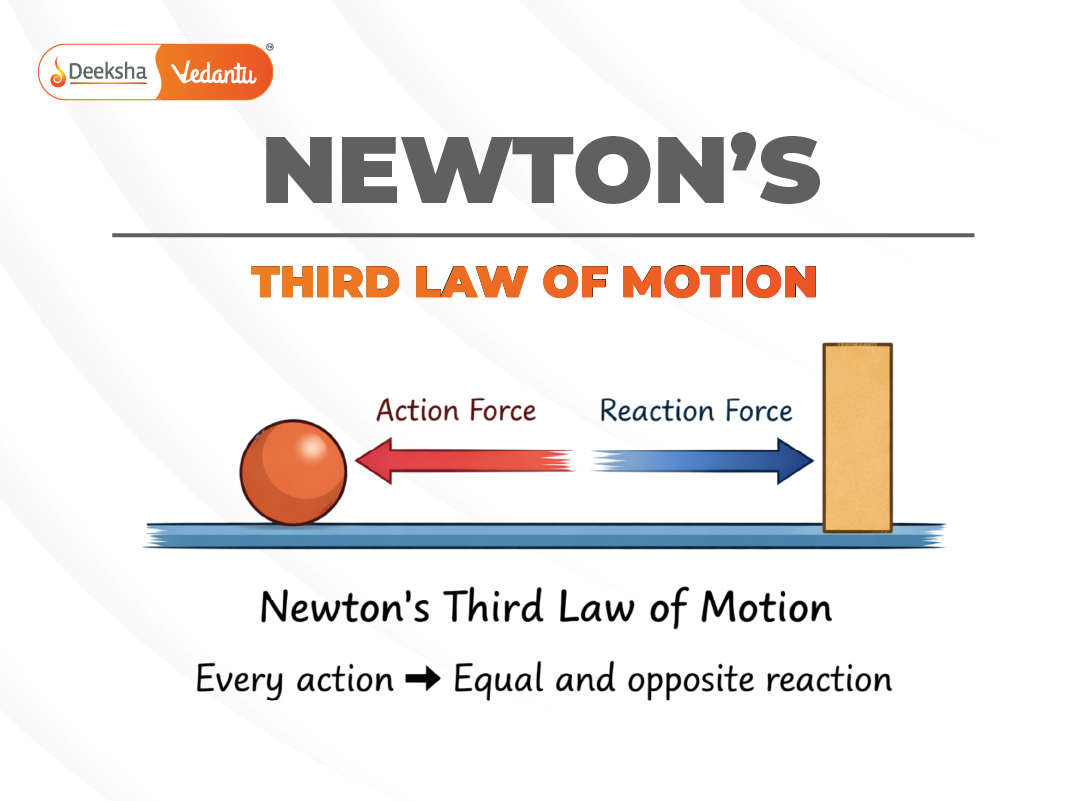
Newton’s Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
In physical terms, this means that whenever one body exerts a force on another body, the second body simultaneously exerts a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction on the first body. These two forces arise together due to interaction and cannot exist independently.
Meaning of Action–Reaction Force Pairs
According to Newton’s Third Law:
- Forces always occur in pairs
- The two forces act on different interacting bodies
- The forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- The forces act simultaneously and along the same line
Because action and reaction forces act on different bodies, they never cancel each other. This idea is central to correctly applying Newton’s laws in mechanics problems.
Nature of Action and Reaction Forces
Action and reaction forces have several important characteristics:
- They are of the same nature (both contact forces or both non-contact forces)
- They act along the same line of interaction
- They arise due to direct or indirect contact between bodies
- They exist only as long as the interaction continues
For example, when a book is placed on a table, the book exerts a downward force on the table due to its weight, and the table exerts an equal upward force on the book. These forces act on different bodies and are equal and opposite.
Why Action and Reaction Forces Do Not Cancel
A very common misconception among students is that action and reaction forces cancel each other. This is incorrect because cancellation of forces can occur only when equal and opposite forces act on the same body.
Action–reaction forces act on different bodies and therefore cannot cancel. Each force must be considered separately while analysing the motion of each body using free body diagrams. Understanding this distinction is crucial for solving JEE problems correctly.
Role of Newton’s Third Law in Producing Motion
Newton’s Third Law explains how motion is produced through interaction. A body cannot change its state of motion on its own; it must interact with another body.
Some important examples include:
- Walking: the foot pushes the ground backward, and the ground pushes the person forward
- Swimming: the swimmer pushes water backward, and water pushes the swimmer forward
- Rocket motion: gases are expelled backward, producing a forward force on the rocket
In each case, motion occurs due to interaction forces described by Newton’s Third Law.
Newton’s Third Law and Free Body Diagrams
Free Body Diagrams (FBDs) play a crucial role in applying Newton’s Third Law correctly. An FBD represents only the forces acting on the body under consideration.
While drawing FBDs:
- Include all forces acting on the chosen body
- Exclude reaction forces exerted by the body on other objects
- Clearly identify interacting bodies
At Deeksha Vedantu, students are trained to separate force pairs across different bodies, which significantly reduces conceptual errors in multi-body systems.
Applications of Newton’s Third Law
Newton’s Third Law is applicable in a wide variety of physical situations:
- Recoil of a gun when a bullet is fired
- Rocket and jet propulsion systems
- Interaction between tyres and road while driving
- Tension forces in strings and cables
- Normal reaction forces between surfaces in contact
In all these cases, motion and force transmission are possible only because of interaction between bodies.
Newton’s Third Law in Multi-Body Systems
In systems involving multiple bodies, Newton’s Third Law helps identify internal forces between interacting objects. While internal action–reaction forces cancel when analysing the entire system, they play a crucial role when analysing individual bodies.
This idea is particularly important in JEE problems involving blocks connected by strings, pulleys, or contact surfaces.
Importance of Newton’s Third Law for JEE
Newton’s Third Law is important for JEE because:
- It explains the origin and nature of forces
- It helps draw correct free body diagrams
- It prevents incorrect cancellation of forces
- It is essential for analysing interacting and constrained systems
At Deeksha Vedantu, students are encouraged to always identify interacting pairs before applying equations, leading to more systematic problem-solving.
Common Conceptual Errors (JEE Perspective)
Students often make errors such as:
- Assuming action and reaction forces act on the same body
- Cancelling action–reaction forces incorrectly
- Including reaction forces in free body diagrams
- Failing to identify the correct interacting bodies
Awareness of these errors helps improve accuracy in mechanics problems.
FAQs
Q1. What does Newton’s Third Law of Motion state?
It states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Q2. Do action and reaction forces cancel each other?
No, because they act on different bodies.
Q3. Are action and reaction forces always equal?
Yes, they are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Q4. How does Newton’s Third Law help in drawing FBDs?
It helps identify which forces act on a body and which forces are reactions exerted by it.
Q5. Why is Newton’s Third Law important for JEE preparation?
Because it is essential for analysing interacting systems and avoiding force-pair misconceptions.
Conclusion
Newton’s Third Law of Motion reveals the interactive nature of forces and completes the conceptual framework of classical mechanics. By understanding that forces always arise in equal and opposite pairs acting on different bodies, students gain clarity in analysing real-world motion and complex mechanical systems. For JEE aspirants, mastering this law is essential for accurate force analysis and confident problem-solving. A concept-driven approach, as emphasised at Deeksha Vedantu, ensures strong fundamentals and long-term success in mechanics.





Get Social