What is Soil Pollution?
Soil pollution occurs when harmful chemicals, known as pollutants or contaminants, are present in the soil at high levels, posing risks to human health and the environment. In simple terms, it’s when human activities change the natural soil. For example, high levels of benzene in soil can lead to diseases like leukemia.

What is Soil Contamination?
Soil contains harmful compounds naturally, but at very low levels that aren’t dangerous. When these harmful substances increase enough to damage living organisms, the soil is considered contaminated. This usually happens due to human activities, such as overuse of pesticides, which can reduce soil fertility and increase soil acidity or alkalinity.
Types of Soil Pollution
- Agricultural Soil Pollution: Excessive use of pesticides and insecticides.
- Industrial Soil Pollution: Discharge of chemicals from mining and manufacturing.
- Solid Waste Pollution: Poor waste management and disposal.
- Urban Activities: Various urban activities also contribute to soil pollution.
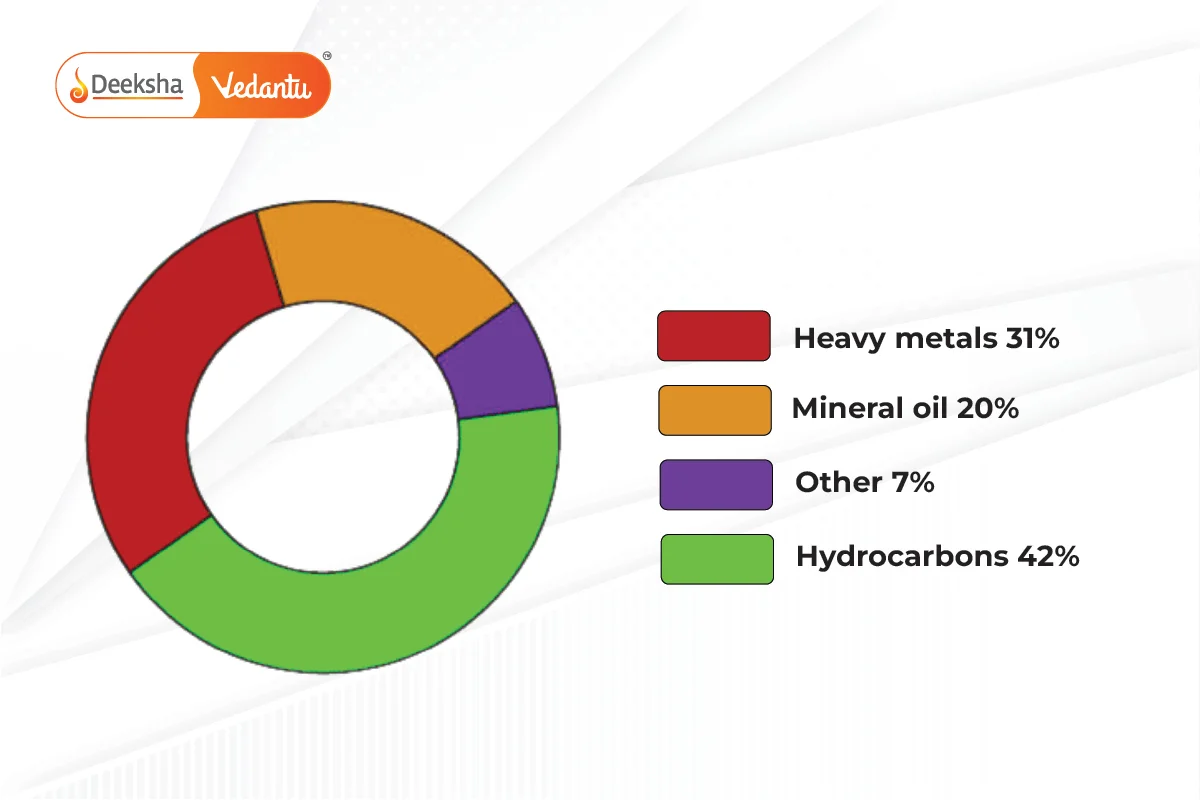
Causes of Soil Pollution
Industrial Pollution:
Industrial waste, including chemicals from mining and manufacturing, pollutes the soil. In India, increased mining and manufacturing activities lead to more soil degradation. Contaminated by-products are often disposed of improperly, remaining on the soil and making it unsuitable for use.
Agricultural Activities:
Long-term use of pesticides and insecticides can pollute soil. These chemicals, not naturally occurring, degrade soil quality and fertility. Plants absorb these chemicals, which later pollute the soil when they decompose.
Pesticides:
Pesticides are used to kill pests like weeds, insects, and fungi. Types include:
- Herbicides: Kill weeds.
- Insecticides: Kill insects.
- Fungicides: Kill fungi.
When pesticides spread unintentionally, they cause soil and water pollution, posing health risks like nervous system disorders and cancer.
Waste Disposal:
Improper disposal of plastics, batteries, and human waste causes soil pollution. Harmful chemicals from these wastes can leach into the soil.
Acid Rain:
Pollutants in the air mix with rain and fall to the ground, dissolving essential soil nutrients and altering soil structure, making it unsuitable for agriculture.
Heavy Metals:
High concentrations of heavy metals like lead and mercury in soil are toxic to humans.
Nuclear Waste:
Leads to soil degradation.
Oil Spills:
Oil leaks during storage or transport deteriorate soil quality and can contaminate groundwater.
Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution affects humans, plants, and animals. Crops grown in polluted soil absorb toxins, reducing agricultural output. Consuming these crops can cause chronic diseases. Children are especially vulnerable as they play in contaminated soil.
Effects on Human Health:
Living or working in contaminated soil can cause respiratory and skin diseases, headaches, nausea, and more.
Effects on Plants:
Plants struggle to adapt to polluted soil, leading to soil erosion and reduced fertility. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides lower soil quality, making it unsuitable for agriculture and local vegetation.
Effects on the Ecosystem:
Soil pollution disrupts habitats for microorganisms, birds, and insects, leading to their gradual decline.
Solutions to Soil Pollution
Reduce Chemical Fertilizers:
Excessive use of chemical fertilizers can poison the soil and alter its pH balance.
Promote Reforestation and Afforestation:
Reforesting deforested areas helps prevent soil erosion, a major source of soil pollution.
Recycle and Reuse Products:
These actions reduce waste output and soil pollution. Plastics are a major waste component buried in landfills.
Use Natural Manure:
Natural manure is safe and restores essential nutrients to the soil, improving its health without harmful by-products.
By understanding the importance of soil and addressing pollution, we can work towards healthier ecosystems and environments.
FAQs
Soil contamination occurs when harmful substances reach high concentrations. It can be due to human activities like industrial waste disposal, agricultural chemicals, improper waste management, or natural processes.
Industrial pollution contributes by discharging waste into the soil, including chemicals from mining and manufacturing. These wastes can stay on the soil surface for long periods, degrading its quality and fertility.
Agricultural activities contribute through the excessive use of pesticides and insecticides. These chemicals can degrade soil quality, reduce fertility, and become pollutants when they seep into the soil and water.
Pesticides are substances used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. While they target pests, they can unintentionally spread into the environment, causing soil and water pollution and posing health risks to humans.
Improper disposal of plastics, batteries, and other solid wastes leads to soil pollution. Harmful chemicals from these wastes can leach into the soil, making it toxic.
Acid rain occurs when pollutants in the air mix with rain and fall to the ground. It can dissolve essential soil nutrients and alter soil structure, making it unsuitable for agriculture.
Soil pollution is the presence of toxic chemicals in the soil at concentrations high enough to pose a risk to human health and the ecosystem. It is often caused by human activities that alter the natural soil composition.






Get Social