Introduction
After learning how vectors can be scaled by real numbers, NCERT introduces the addition and subtraction of vectors using graphical methods. Since vectors possess both magnitude and direction, their addition cannot be performed using ordinary algebra. Instead, specific geometric rules are followed to obtain the resultant vector.
For JEE aspirants, this section is extremely important because graphical understanding forms the conceptual base for analytical vector addition, resolution of vectors, relative velocity, and projectile motion. At Deeksha Vedantu, students are encouraged to visualise vector addition geometrically before moving to algebraic techniques.
Need for Graphical Addition of Vectors
Vectors represent physical quantities such as displacement, velocity, force, and acceleration. When multiple vectors act simultaneously, the combined effect is obtained by finding a single vector called the resultant vector.
Since direction plays a crucial role, vector addition must account for both magnitude and direction. Graphical methods provide a clear and intuitive way to understand how vectors combine in two dimensions.
Triangle Law of Vector Addition
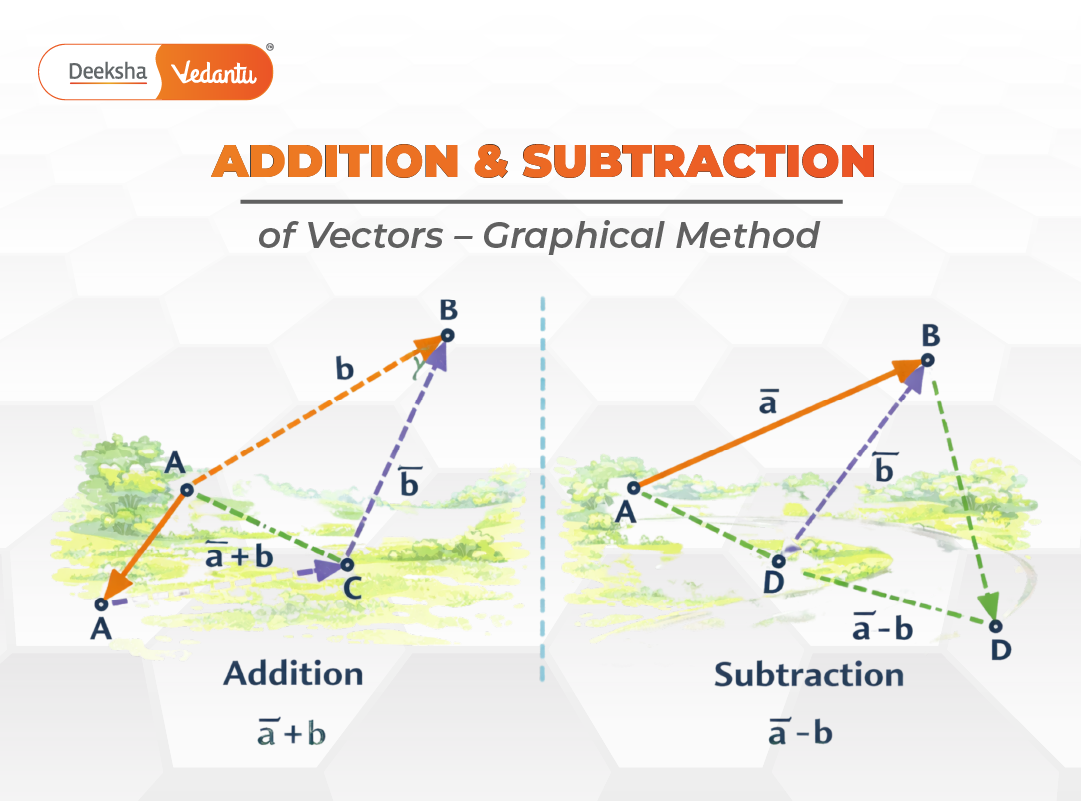
The triangle law of vector addition is one of the simplest graphical methods used to add two vectors.
Statement of Triangle Law
If two vectors are represented in magnitude and direction by two sides of a triangle taken in the same order, then the third side of the triangle taken in the opposite order represents their resultant.
Graphical Construction
To add two vectors A and B using the triangle law:
- Draw vector A
- From the head of vector A, draw vector B
- Join the tail of vector A to the head of vector B
The resulting vector obtained is the resultant R, represented as:
The direction of the resultant is from the tail of the first vector to the head of the second vector.
Physical Interpretation
The triangle law is useful in situations where two displacements or velocities occur successively. For example, when a person walks in one direction and then in another, the net displacement is obtained using this law.
Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
The parallelogram law is another graphical method commonly used for vector addition.
Statement of Parallelogram Law
If two vectors acting at a point are represented in magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram drawn from that point, then the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through that point represents the resultant vector.
Graphical Construction
To apply the parallelogram law:
- Draw vectors A and B from the same point
- Complete the parallelogram using A and B as adjacent sides
- Draw the diagonal starting from the common point
The diagonal represents the resultant vector:
Significance
The parallelogram law is especially useful when two vectors act simultaneously from the same point, such as forces acting on a body.
Properties of Vector Addition (Graphical)
From graphical construction, the following properties of vector addition are observed:
- Vector addition is commutative:
- Vector addition is associative:
These properties are important in simplifying vector expressions in JEE problems.
Subtraction of Vectors – Graphical Method
Vector subtraction is defined as the addition of a vector with the negative of another vector.
Mathematically:
Graphical Method of Vector Subtraction
To subtract vector B from vector A:
- Reverse the direction of vector B to obtain −B
- Add vector A and −B using the triangle law
The resultant vector gives the difference between the two vectors.
Physical Meaning
Vector subtraction is commonly used to find relative displacement, relative velocity, and change in momentum. This concept is frequently tested in JEE through relative motion problems.
Limitations of Graphical Method
Although graphical methods provide clear visual understanding, they have certain limitations:
- Accuracy depends on the scale of drawing
- Not suitable for precise numerical calculations
- Becomes difficult when many vectors are involved
Due to these limitations, NCERT later introduces analytical methods of vector addition.
Importance for JEE Preparation
Understanding graphical vector addition is crucial because:
- It builds intuition for vector behaviour
- Helps avoid sign and direction errors
- Forms the base for analytical vector addition and resolution
- Essential for topics like projectile motion and relative velocity
At Deeksha Vedantu, emphasis is placed on conceptual clarity through diagrams before introducing formula-based approaches.
FAQs
Q1. What is the triangle law of vector addition?
It states that if two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle taken in order, the third side represents their resultant.
Q2. What is the parallelogram law of vector addition?
It states that the diagonal of a parallelogram formed by two vectors represents their resultant.
Q3. How is vector subtraction performed graphically?
Vector subtraction is performed by adding the negative of the vector to be subtracted.
Q4. Why are graphical methods important?
They help in visualising vector addition and understanding direction clearly.
Q5. Why are graphical methods not used for exact calculations?
Because drawing-based methods depend on scale and may introduce errors.
Conclusion
Section 3.4 Addition and Subtraction of Vectors using graphical methods provides the geometric foundation of vector algebra. For JEE aspirants, mastering this section ensures strong conceptual understanding of how vectors combine in two dimensions. A clear visual approach, as emphasised at Deeksha Vedantu, prepares students for analytical methods and advanced mechanics problems that follow.





Get Social