Unit VI of Class 12 NCERT Biology, titled Reproduction, explores the biological process by which organisms perpetuate their lineage. This unit lays the foundation for understanding reproductive mechanisms in plants, animals, and humans. It includes three detailed chapters:
- Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organisms
- Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Chapter 3: Human Reproduction
Let’s dive into each chapter with a detailed explanation, examples, and learning insights.
Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organisms
This chapter provides a basic understanding of how living organisms reproduce, either asexually or sexually. It highlights reproduction as a fundamental characteristic of life and explains how it varies across unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Key Concepts:
- Asexual Reproduction: Binary fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation.
- Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring that are genetically distinct.
- Reproductive Cycles: Oestrus and menstrual cycles are discussed with respect to animals.
- Lifespan and Death: All organisms have a defined lifespan, and reproduction ensures the continuity of species.
Examples:
- Amoeba and yeast show asexual reproduction.
- Hydra reproduces via budding.
- Higher animals and humans reproduce sexually.
Practice MCQs:
- Which of the following organisms reproduces by binary fission?
A. Hydra
B. Yeast
C. Amoeba
D. Planaria
Answer: C - What is the term for the reproductive phase in the life of an organism?
A. Senescence
B. Juvenile phase
C. Reproductive phase
D. Vegetative phase
Answer: C
Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
This chapter dives deep into the complex process of sexual reproduction in angiosperms. It covers flower structure, pollination, fertilization, seed formation, and fruit development.
Key Concepts:
- Flower Structure: Details of androecium (male part) and gynoecium (female part).
- Pollination: Types include autogamy, geitonogamy, and xenogamy.
- Fertilization: Double fertilization mechanism unique to angiosperms.
- Seed and Fruit Formation: Endosperm formation, development of seed coat and pericarp.
- Apomixis and Polyembryony: Important topics for NEET and board exams.
Examples:
- Pollination by wind (anemophily): Maize
- Pollination by insects (entomophily): Rose, sunflower
Practice MCQs:
- Double fertilization is a characteristic feature of which group of plants?
A. Gymnosperms
B. Angiosperms
C. Bryophytes
D. Pteridophytes
Answer: B - Which of the following represents the correct sequence of events in reproduction in flowering plants?
A. Pollination → Fertilization → Embryo → Seed
B. Fertilization → Pollination → Embryo → Seed
C. Embryo → Pollination → Fertilization → Seed
D. Seed → Embryo → Fertilization → Pollination
Answer: A
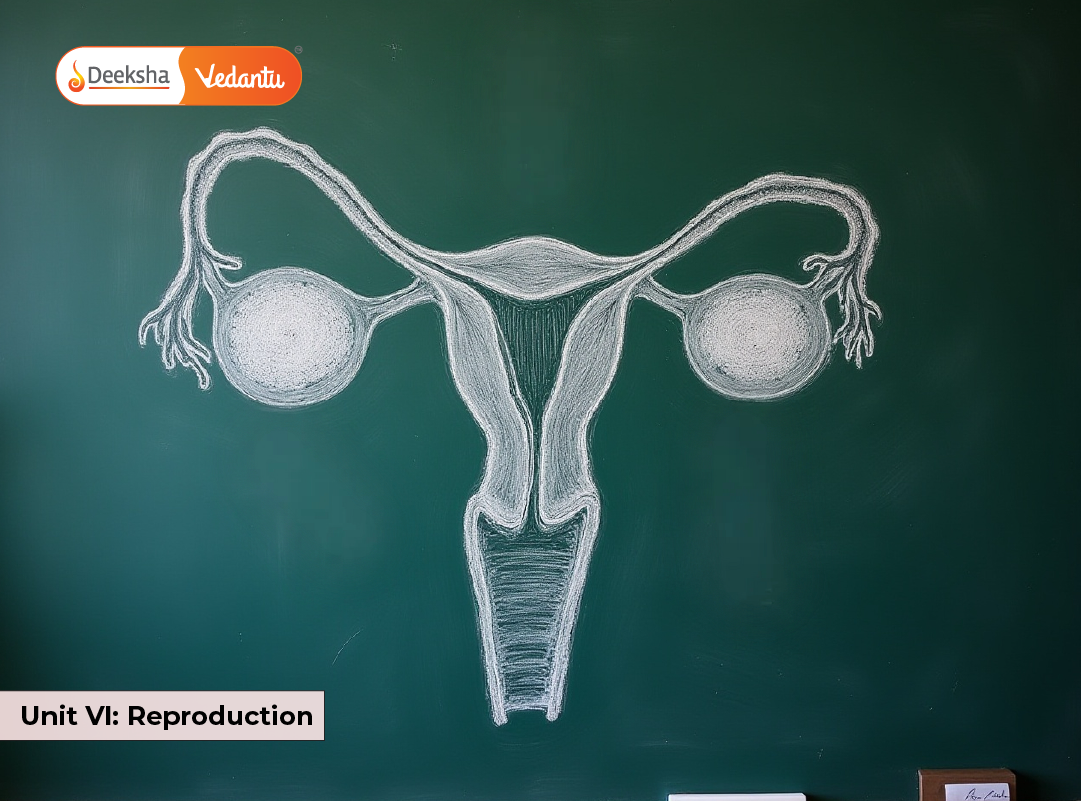
Chapter 3: Human Reproduction
This chapter introduces the structure and function of the male and female reproductive systems, followed by the process of gametogenesis, fertilization, and development of the embryo.
Key Concepts:
- Reproductive Organs: Male (testes, vas deferens) and female (ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes).
- Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis and oogenesis processes.
- Fertilization and Implantation: Fertilization usually occurs in the ampulla region of the fallopian tube.
- Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal regulation and phases.
- Pregnancy and Embryonic Development: Placenta formation, parturition, and lactation.
Examples:
- Estrogen and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle.
- LH surge triggers ovulation in females.
Practice MCQs:
- Where does fertilization typically occur in humans?
A. Uterus
B. Ovary
C. Fallopian tube
D. Cervix
Answer: C - Which hormone is responsible for milk ejection from the mammary glands?
A. Estrogen
B. Oxytocin
C. Progesterone
D. Prolactin
Answer: B
FAQs
What is the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and no gamete formation, while sexual reproduction requires two parents and gamete fusion.
Why is double fertilization important in flowering plants?
Double fertilization leads to the formation of both the embryo and the endosperm, ensuring the nourishment of the developing embryo.
What triggers ovulation in females?
The surge in Luteinizing Hormone (LH) during the menstrual cycle triggers ovulation.
Are these chapters important for NEET?
Absolutely. All three chapters—especially Human Reproduction and Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants—are frequently tested in NEET and other competitive exams.
What is apomixis?
Apomixis is a type of asexual reproduction where seeds are formed without fertilization. It is useful in maintaining hybrid vigor.
How is gametogenesis different in males and females?
Spermatogenesis in males produces four functional sperm cells, whereas oogenesis in females results in one ovum and three polar bodies.
Why is understanding the menstrual cycle important?
It helps in understanding fertility patterns, reproductive health, and hormonal regulation.
Conclusion
Unit VI of NCERT Class 12 Biology – Reproduction – is a cornerstone for understanding how life continues and evolves. From simple asexual processes in lower organisms to the complex reproductive mechanisms in flowering plants and humans, these chapters build a comprehensive understanding of the biological continuity of life. Mastering this unit not only prepares students for board exams but also equips them with essential knowledge for competitive exams like NEET. Regular revision, practice with MCQs, and conceptual clarity will ensure a strong grasp over this vital unit.





Get Social