Introduction
After learning graphical methods of vector addition and the resolution of vectors, NCERT introduces the analytical method of vector addition as a more powerful and precise approach. This method relies on resolving vectors into their rectangular components and then adding these components algebraically. Unlike graphical methods, which depend on accurate drawings and scale, the analytical approach is exact, systematic, and suitable for solving numerical problems.
For JEE aspirants, the analytical method is far more important than graphical methods because almost all examination problems require precise numerical answers. Whether dealing with displacement, velocity, acceleration, or force, vector addition using analytical techniques forms the backbone of problem-solving. At Deeksha Vedantu, students are trained to move seamlessly from graphical intuition to analytical execution, ensuring both conceptual clarity and calculation accuracy.
Need for Analytical Vector Addition
Graphical methods help visualise vector addition but suffer from limitations such as scale dependency, drawing errors, and lack of numerical accuracy. As the number of vectors increases or when exact values are required, graphical methods become impractical.
To overcome these limitations, vectors are added analytically using their components along coordinate axes. This method converts a two-dimensional vector problem into two independent one-dimensional problems.
In analytical vector addition:
- Each vector is first resolved into perpendicular components
- Components along the same direction are added algebraically
- The resultant vector is reconstructed from its resultant components
This approach is especially useful when dealing with multiple vectors, relative velocity, and motion in two dimensions, all of which are commonly tested in JEE.
Component Form of Vectors
Consider a vector of magnitude
making an angle
with the positive x-axis.
Its rectangular components along the coordinate axes are:
These components represent the projections of the vector along the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Thus, the vector can be written in component form as:
This component representation is fundamental to analytical vector addition and is repeatedly used in JEE-level problems.
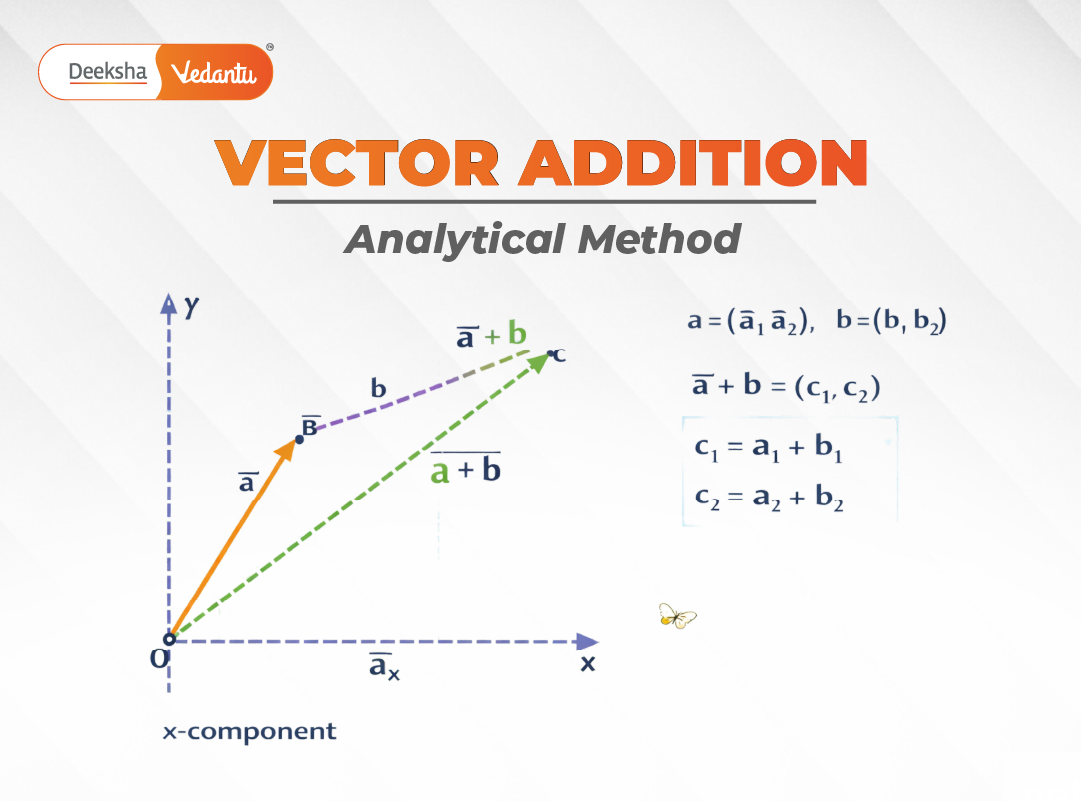
Addition of Two Vectors Using Analytical Method
Let two vectors and
act simultaneously in a plane.
Step 1: Resolve the Vectors
Each vector is resolved into its rectangular components:
This step ensures that the contribution of each vector along the x and y directions is clearly identified.
Step 2: Add Corresponding Components
Components along the same axis are added algebraically:
This step is crucial, as adding magnitudes directly without resolving components is a common mistake made by students.
Step 3: Write the Resultant Vector
The resultant vector is expressed using its components:
This vector represents the combined effect of vectors A and B.
Magnitude of the Resultant Vector
The magnitude of the resultant vector is obtained using Pythagoras' theorem, since the x and y components are perpendicular:
This formula is extensively used in JEE problems involving displacement, velocity, force, and acceleration vectors.
Direction of the Resultant Vector
The direction of the resultant vector is given by the angle it makes with the positive x-axis:
While calculating the direction, it is essential to identify the correct quadrant using the signs of and
. Many JEE errors occur due to incorrect quadrant selection.
Extension to Multiple Vectors
The analytical method can be easily extended to the addition of more than two vectors.
When several vectors act together:
- Resolve each vector into x and y components
- Add all x-components algebraically
- Add all y-components algebraically
- Calculate the resultant magnitude and direction using standard formulas
This method is widely applied in relative velocity problems, motion of boats and swimmers, and systems involving multiple forces.
Physical Significance in Motion in a Plane
In motion analysis, analytical vector addition is used to:
- Determine net displacement when motion occurs in different directions
- Combine velocity vectors to study resultant motion
- Add acceleration vectors acting simultaneously
For example, in relative velocity problems, velocities of different objects are added or subtracted analytically using component-wise methods. In projectile motion, velocity components at different instants are analysed using the same approach.
At Deeksha Vedantu, students are encouraged to follow a fixed, step-by-step analytical structure, which helps reduce calculation errors and improves speed during exams.
Advantages of Analytical Method
The analytical method of vector addition offers several clear advantages:
- Provides exact and reliable numerical results
- Eliminates errors arising from scale or drawing inaccuracies
- Handles complex situations involving many vectors efficiently
- Essential for competitive examinations like JEE
Due to these advantages, the analytical method is preferred over graphical methods for all exam-oriented vector problems.
Common Conceptual Errors (JEE Perspective)
Despite its systematic nature, students often make errors such as:
- Forgetting to resolve vectors before adding
- Adding vector magnitudes instead of components
- Making sign mistakes while adding components
- Ignoring quadrant rules while finding direction
Regular practice and strong conceptual understanding help avoid these mistakes.
FAQs
Q1. What is the analytical method of vector addition?
It is a method in which vectors are resolved into rectangular components and added algebraically to obtain the resultant vector.
Q2. Why is the analytical method preferred over the graphical method?
Because it provides exact numerical results and is suitable for complex, exam-oriented problems.
Q3. How is the magnitude of the resultant vector calculated?
By using the relation .
Q4. How is the direction of the resultant vector determined?
By calculating the angle using and identifying the correct quadrant.
Q5. Why is this method important for JEE preparation?
Because most JEE problems involving vectors require precise numerical solutions using component-wise analysis.
Conclusion
Section 3.6 Vector Addition – Analytical Method introduces the most reliable and precise technique for adding vectors in two dimensions. For JEE aspirants, mastering this method is essential because it is used extensively in projectile motion, relative velocity, circular motion, and force analysis. A structured and concept-driven approach, as emphasised at Deeksha Vedantu, ensures speed, accuracy, and confidence while solving vector-based problems in competitive examinations.





Get Social