Hydrogen bonding is a fundamental intermolecular and intramolecular force described in NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 – Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure. It plays a crucial role in the structure, stability, and physical properties of various compounds. From the perspective of NEET and JEE, hydrogen bonding is highly significant as it explains boiling points, density of water, solubility of compounds, protein folding, and DNA structure.
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds but stronger than van der Waals forces. They form when hydrogen is bonded to a highly electronegative atom like nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F), and this hydrogen interacts with another electronegative atom.
What Is Hydrogen Bonding?
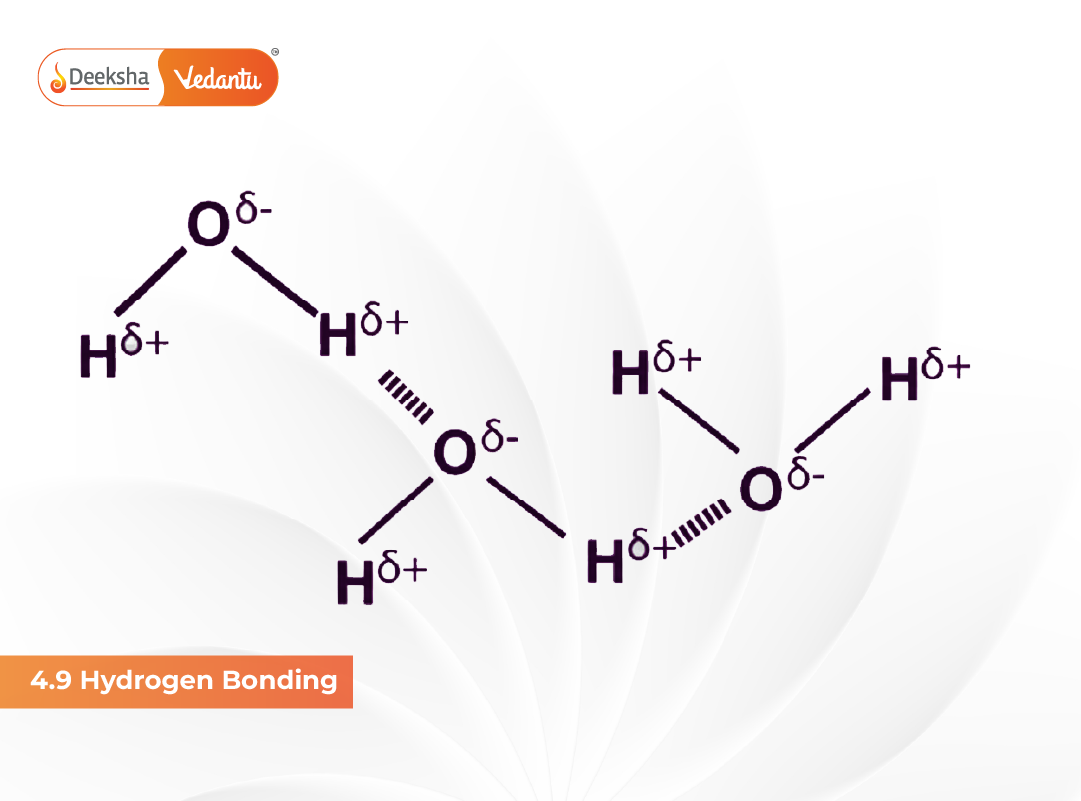
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. Due to high electronegativity, the bonded hydrogen becomes partially positively charged (δ⁺) and is strongly attracted to a lone pair of electrons on another electronegative atom of a neighboring molecule. This attractive force is known as hydrogen bonding. Although weaker than covalent bonds, it significantly influences physical and chemical properties such as boiling point, viscosity, solubility and molecular geometry.
Cause of Formation of Hydrogen Bond
When hydrogen is bonded to a strongly electronegative atom (F, O or N), the electron density is pulled towards the electronegative atom, leaving hydrogen electron-deficient. This creates a strong dipole and results in partial charges: hydrogen gets δ⁺ while the electronegative atom gets δ⁻. The hydrogen atom then interacts with lone pairs on nearby electronegative atoms, forming hydrogen bonds. The strength of this bond depends on electronegativity, atomic radius and availability of lone pairs.
Types of Hydrogen Bonding
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding – occurs between two separate molecules. This leads to higher boiling points, increased viscosity and higher solubility in polar solvents.
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonding – occurs within the same molecule. This often forms a ring structure and decreases solubility in water, e.g., o-nitrophenol.
Importance
Hydrogen bonding plays a critical role in determining physical, chemical, and biological properties of molecules. It explains why water has such unique characteristics, why ice floats, why proteins fold in a particular manner, and why certain compounds show higher boiling points. Understanding its importance allows students to connect theoretical chemistry with real-life applications.
Key Roles of Hydrogen Bonding
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding – Occurs between different molecules, leading to higher boiling points, greater viscosity, and better solubility in polar solvents. It is the reason water remains liquid at room temperature.
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonding – Occurs within the same molecule and forms a ring structure. This decreases solubility in water but affects molecular geometry. Examples include o-nitrophenol and salicylic acid.
Additional Points
- Hydrogen bonding helps stabilize DNA and proteins.
- It explains anomalies in physical properties of Group 16 hydrides.
- It governs many chemical reactions in biochemistry and medicine.
Importance for NEET & JEE
- Explains physical properties and molecular interactions.
- Crucial in biomolecules, protein structure, DNA replication.
- Often tested in questions related to boiling point order, solubility, and molecular geometry.
- Concept-based and application-oriented questions are frequently asked in both NEET and JEE examinations.
- Explains physical properties
- Important for biomolecules
- Frequently asked in exams
Detailed Explanation (Based on NCERT)
The hydrogen bond acts as a bridge between two atoms. It is weaker than a covalent bond but plays a major role in determining molecular structure and physical properties.
Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Occurs between different molecules like water and alcohols.
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Occurs within the same molecule like o-nitrophenol.
Competitive Exam Perspective (NEET & JEE)
- Frequently asked in biomolecules and physical chemistry
- Concept-based questions are common
Practice Questions (NEET & JEE)
MCQs
- Which atom must hydrogen be bonded to for hydrogen bonding to occur?
a) C b) P c) F d) S
Answer: c - Which molecule shows intramolecular hydrogen bonding?
a) Water b) Ethanol c) o-nitrophenol d) HF
Answer: c - Hydrogen bonding is strongest in:
a) Solid state b) Gas state c) Liquid state
Answer: a
Assertion-Reason Questions
Assertion: Hydrogen bonding affects boiling point of water.
Reason: Hydrogen bonding increases intermolecular attraction.
Answer: Both assertion and reason are true, reason explains assertion.
Numerical (JEE Level)
Calculate number of hydrogen bonds formed by one water molecule.
Answer: Two hydrogen bonds can be formed (one per hydrogen).
Real-Life Applications of Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is not just a theoretical topic — it plays a crucial role in real-world chemical, biological and physical processes. Understanding these helps students in NEET and JEE when questions are framed beyond textbook definitions.
Water – The Anomalous Liquid
The high boiling point, high heat capacity, high surface tension and lower density of ice are all due to hydrogen bonding. Without hydrogen bonding, water would boil at much lower temperatures, making life on Earth impossible.
DNA Double Helix Structure
Hydrogen bonds between nucleotide base pairs hold the two strands of DNA together:
- Adenine (A) forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C) forms three hydrogen bonds with Guanine (G)
This bonding maintains stability but allows DNA replication when bonds break temporarily.
Protein Folding
The secondary structure of proteins (α-helix and β-pleated sheets) is stabilized by hydrogen bonding, which plays a major role in the biological activity of enzymes and hormones.
Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids
Alcohols have higher boiling points than alkanes due to hydrogen bonding between –OH groups. Carboxylic acids exist as dimers due to strong hydrogen bonding between molecules.
NEET & JEE Important Points to Memorize
- Hydrogen bond strength: F > O > N
- Ice is less dense than water because it forms an open hexagonal lattice
- Molecules with intramolecular hydrogen bonding are less soluble in water
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases viscosity and boiling point
- Hydrogen bonding occurs only when hydrogen is attached to F, O, or N
Trick to Remember:
“FON makes H bond.”
(F = Fluorine, O = Oxygen, N = Nitrogen)
Hydrogen Bonding vs Van der Waals vs Covalent Bond
| Type of Bond | Relative Strength | Nature | Example |
| Covalent bond | Strongest | True bond | H–O in water |
| Hydrogen bond | Intermediate | Intermolecular | Water, HF |
| van der Waals force | Weakest | Temporary attraction | Noble gases |
Additional Practice Questions
NEET Level
- Which of the following has the highest boiling point due to hydrogen bonding?
a) H₂S b) H₂O c) HCl d) NH₃
Answer: b - Intramolecular hydrogen bonding causes:
a) Higher solubility b) Lower solubility
c) Low viscosity d) High boiling point
Answer: b - In which biological molecule does hydrogen bonding play a crucial role?
a) Fats b) Proteins c) Hydrocarbons
Answer: b
JEE Main Level – Numerical
The boiling point of ethanol is 78°C while ethane boils at −89°C. Explain briefly using hydrogen bonding concept.
Answer: Ethanol forms strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds while ethane does not; hence ethanol has a higher boiling point.
Assertion-Reason
Assertion: Carboxylic acids form dimers in vapour state.
Reason: They undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Answer: Both assertion and reason are correct; reason explains assertion.
Competitive Exam Weightage
| Exam | Expected Marks | Type of Questions |
| NEET | 1–2 | MCQs & reasoning |
| JEE Main | 2–4 | Concept & numerical |
| JEE Advanced | 4–6 | Assertion-reason + application |
FAQs
Q1: Which atoms form hydrogen bonds?
Only F, O, and N can form hydrogen bonds with hydrogen.
Q2: Why does ice float on water?
Due to hydrogen bonding, ice has an open lattice structure making it less dense than water.
Q3: Is hydrogen bond weaker than covalent bond?
Yes, hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds but stronger than van der Waals forces.
Conclusion
Hydrogen bonding plays a vital role in chemistry and biology, influencing structure and properties of many compounds. For NEET and JEE aspirants, mastering this topic ensures strong conceptual clarity. At Deeksha Vedantu, students learn hydrogen bonding with diagrams, NCERT alignment and exam-focused problem solving for better results.






Get Social