What is Euglena?
Euglena is a type of euglenoid, a unicellular microorganism with a flexible body that exhibits characteristics of both plants and animals. They have plastids and can perform photosynthesis in light, but they also move around using their flagellum in the dark in search of food. There are around 1000 species of Euglena found in various environments, including freshwater, saltwater, marshes, and moist soil.
Euglena Classification
Euglena is a genus of euglenoids. The classification of Euglena is contentious, as they can be placed in either the phylum Euglenozoa or the phylum Euglenophyta due to the presence of chlorophyll. However, since not all species of Euglena contain chloroplasts, they are more commonly placed in the phylum Euglenozoa.
Classification:
- Domain: Eukaryota
- Phylum: Euglenozoa
- Class: Euglenophyceae
- Order: Euglenales
- Family: Euglenaceae
- Genus: Euglena
Euglena Structure with Diagram and Characteristics
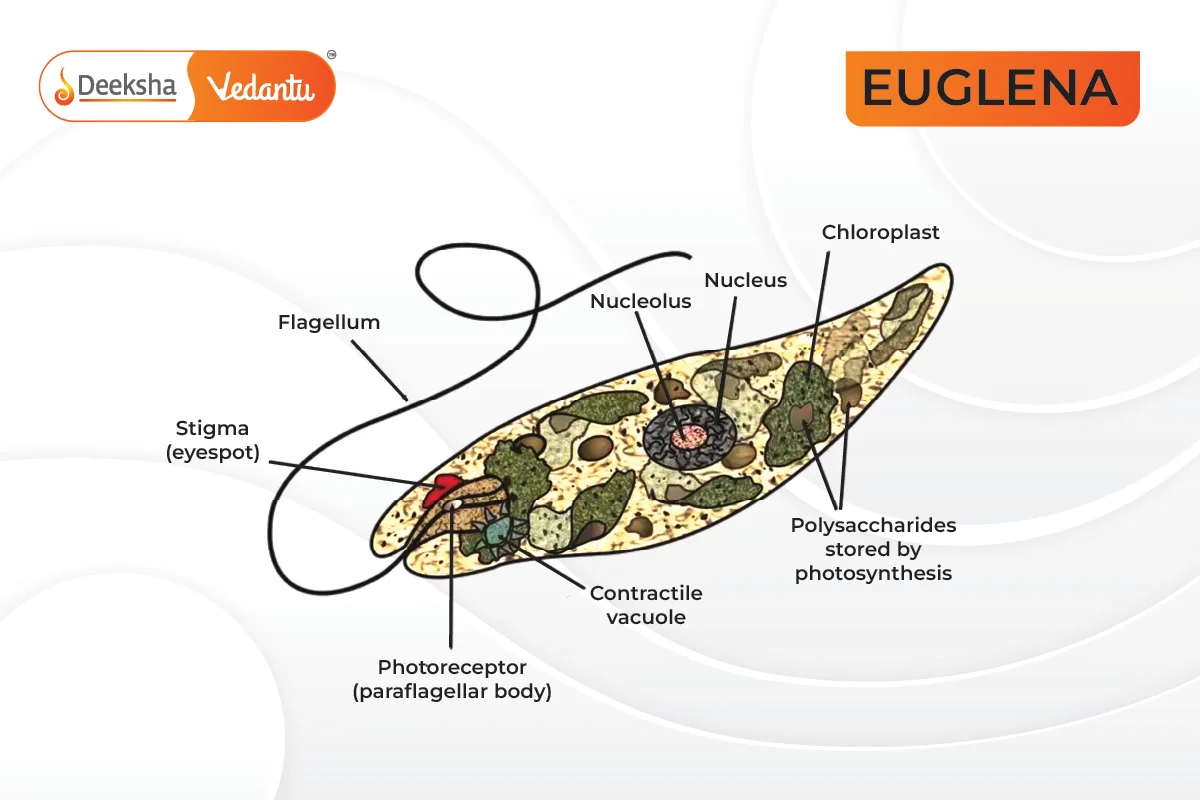
Morphology and Anatomy
- Cell Shape: Elongated, measuring 15-500 micrometers.
- Color: Mostly green due to chlorophyll; some species contain carotenoid pigments, giving them a red color.
- Nucleus: Unicellular with one nucleus.
- Cell Wall: Lacks a cellulose cell wall; instead, it has a flexible outer membrane known as a pellicle.
- Pellicle: Composed of proteinaceous strips and supporting microtubules, providing flexibility and the ability to change shape.
- Plasma Membrane: Thin, enclosing cytoplasm and cell organelles.
- Contractile Vacuole: Removes excess water.
- Reservoir: An inward pocket near the base of the flagella where the contractile vacuole dispels excess water.
- Cell Organelles: Includes mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies.
Nutrition
- Photosynthesis: Contains chloroplasts with chlorophyll, allowing them to perform photosynthesis.
- Heterotrophy: Some species can absorb organic compounds or engulf bacteria and protists.
- Storage: Chloroplasts contain pyrenoids, which synthesize paramylon, a glucose polymer stored as food.
- Euglenophycin: Some species produce an alkaloid toxic to fish.
Locomotion and Phototaxis
- Eyespot (Stigma): Contains photoreceptors for light detection and phototaxis.
- Flagella: One or two flagella, aiding in movement. The long flagellum is used for swimming, while the short one remains within the cell.
Reproduction
- Binary Fission: Asexual reproduction through longitudinal binary fission.
- Lifecycle: Consists of free-swimming and non-motile stages, with protective cyst formation during unfavorable conditions.
FAQs
Euglena is cultivated for commercial production of paramylon and has potential applications in nutrition and biotechnology due to its unique metabolic properties.
The pellicle is a flexible outer membrane composed of proteinaceous strips and microtubules, providing flexibility and shape change.
Yes, Euglena contain chloroplasts with chlorophyll, allowing them to perform photosynthesis.
The eyespot, or stigma, helps Euglena detect light and move towards it (phototaxis).
Euglena reproduce asexually through binary fission, dividing longitudinally.
Euglena are found in freshwater, saltwater, marshes, and moist soil.
Euglena are unicellular microorganisms classified under euglenoids, exhibiting both plant and animal characteristics.



Get Social