Pollution is one of the most critical and pressing environmental issues that our world faces today. It not only deteriorates the quality of natural resources like air, water, and soil but also poses severe threats to the health and wellbeing of living organisms. For Class 10 students, understanding pollution and the steps we can take to control it forms an essential part of building environmental consciousness. This knowledge lays the foundation for taking responsible action to create a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable future.
To begin with, let’s understand what pollution truly means. Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful or toxic substances into the natural environment, causing undesirable changes. These substances, known as pollutants, can be solid, liquid, or gaseous in nature and disrupt the ecosystem’s balance. They affect the climate, destroy habitats, and contribute to widespread health issues. By understanding pollution in depth, students can grasp how everyday actions impact the environment and how preventive measures can make a significant difference.
Explore our full explanation on the Types of Pollution.
Types of Pollution and Their Impact
There are several major types of pollution, each affecting specific components of the environment. Identifying their sources, consequences, and unique characteristics helps us develop tailored control strategies.
![]()
Air Pollution
Air pollution is caused by the release of harmful gases, particulate matter, and chemicals into the atmosphere. Major sources include emissions from vehicles, factories, power plants, construction activities, and the burning of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum.
Effects:
- Causes respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung infections
- Increases the concentration of greenhouse gases, leading to global warming
- Contributes to acid rain which damages buildings, crops, and water bodies
- Reduces visibility and affects wildlife health
Learn more in our guide on Air Pollution Control.
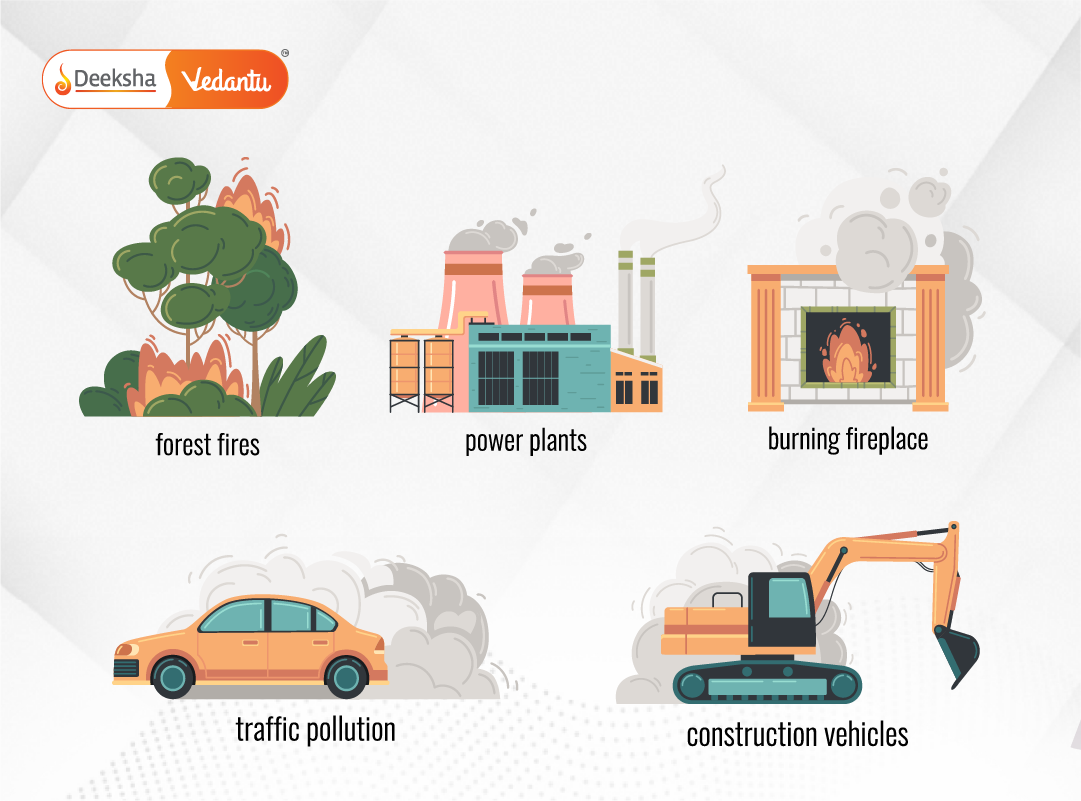
Water Pollution
Water pollution occurs when harmful chemicals, biological waste, or physical contaminants enter water bodies like rivers, lakes, and oceans. It affects drinking water quality and aquatic ecosystems. Sources include industrial discharge, sewage, agricultural runoff (rich in pesticides and fertilizers), and oil spills.
Effects:
- Kills aquatic plants and animals by reducing oxygen levels
- Spreads deadly diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery
- Makes water unfit for human consumption and irrigation
- Disrupts food chains and biodiversity in aquatic habitats
Understand key strategies from our lesson on Water Pollution Control Techniques.
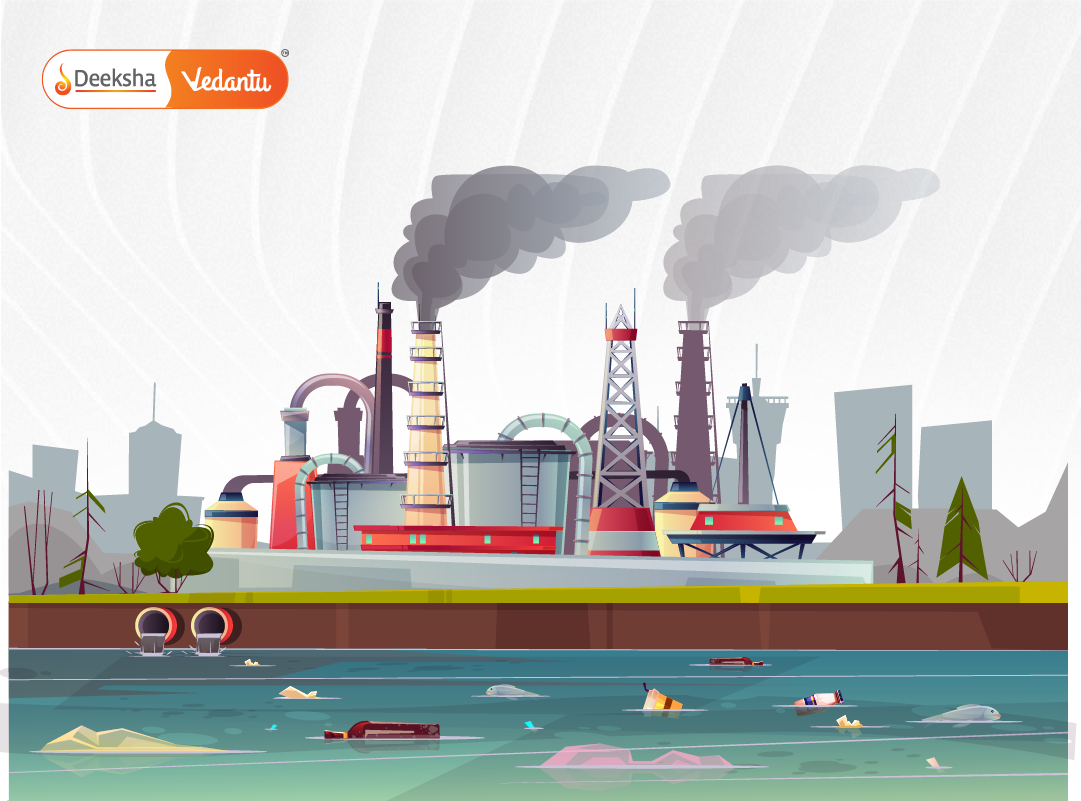

Soil Pollution
Soil pollution happens due to the excessive use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, plastic waste, and industrial chemicals. It reduces the soil’s ability to sustain plant growth, affecting crop yields and food security.
Effects:
- Depletes soil fertility and damages beneficial soil organisms
- Causes toxic substances to enter the food chain
- Leads to groundwater contamination
- Contributes to desertification and land degradation
![]()
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution results from loud, continuous, and unwanted sounds originating from traffic, construction sites, factories, and entertainment sources. It affects both physical and mental health.
Effects:
- Hearing impairment, hypertension, and stress
- Sleep disturbances and poor concentration in students
- Affects communication and behavior in wildlife
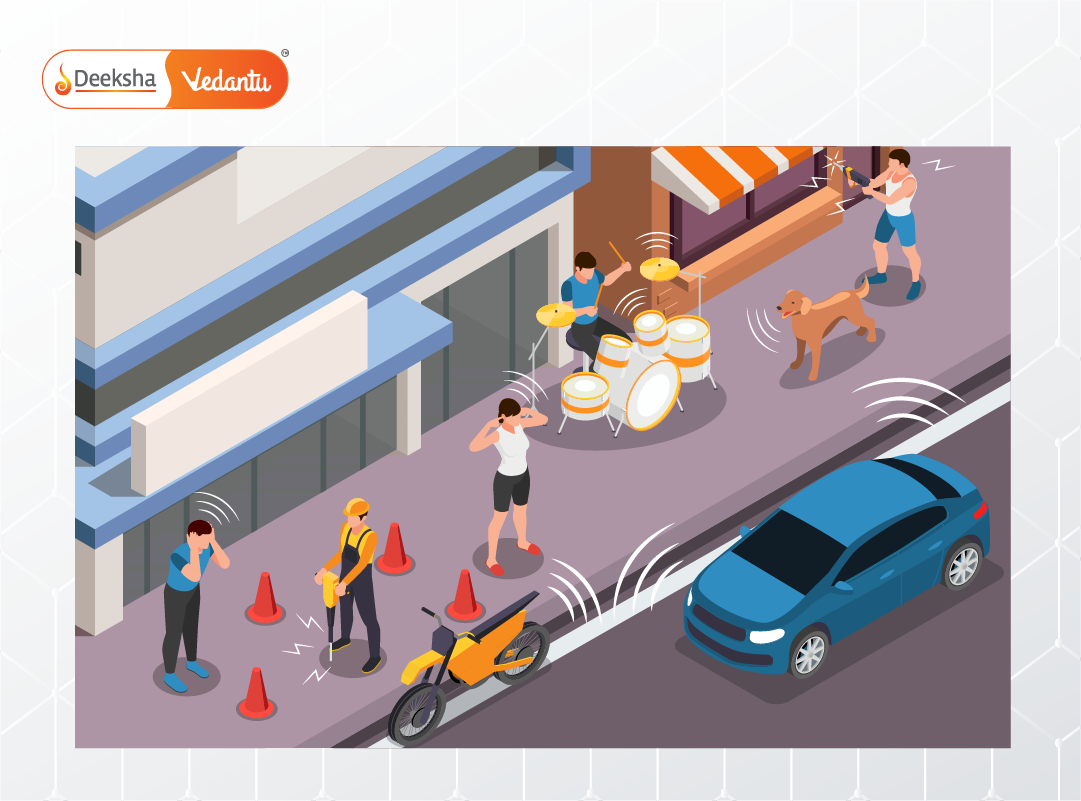

Light and Thermal Pollution
Excessive artificial lighting and uncontrolled heat emissions lead to light and thermal pollution. These types are less visible but significantly disrupt ecosystems and biological rhythms.
Effects:
- Affects nocturnal animal behavior and plant growth
- Wastes energy resources and increases electricity costs
- Alters local weather conditions
Control Measures for Pollution
Understanding pollution is only the beginning. The next important step is implementing effective control measures. Students and communities must be actively involved in practicing and promoting eco-friendly habits.
Air Pollution Prevention Methods
- Encourage the use of bicycles, walking, carpooling, and public transportation
- Shift towards green energy sources like solar and wind power
- Use of pollution-control devices like catalytic converters in vehicles and electrostatic precipitators in industries
- Ban or reduce the use of firecrackers and burning of crop residue
- Increase afforestation efforts and protect urban green zones
Explore our detailed topic on Air Pollution Control for real-world examples.
Water Pollution Control Techniques
- Install water treatment plants for industrial and domestic sewage
- Promote the use of organic fertilizers and sustainable agricultural practices
- Prevent dumping of plastic, oil, or toxic waste into water bodies
- Enforce strict laws against illegal disposal of waste
- Educate communities on the importance of water conservation and pollution prevention
Read more on our page for Water Pollution Control Techniques.
Effective Waste Management
- Separate waste at the source into biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials
- Promote composting, recycling, and reusing items instead of throwing them away
- Ban single-use plastics and switch to sustainable alternatives
- Implement zero-waste programs in schools and local communities
Strategies for Reducing Noise Pollution
- Use silent machinery and sound barriers in industrial areas
- Maintain noise limits in public zones, especially near hospitals and schools
- Reduce volume levels during social events and festivals
- Promote the planting of trees around noisy areas
Global Initiatives and Agreements
- The Paris Agreement focuses on reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change
- Environmental policies by governments worldwide aim at reducing pollution through regulations and incentives
- Promotion of green technologies and sustainable urban development
Impact of Ozone Layer Depletion
The ozone layer in the stratosphere plays a crucial role in shielding life on Earth from the harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun. It absorbs most of the sun’s high-frequency radiation, protecting both ecosystems and human health.
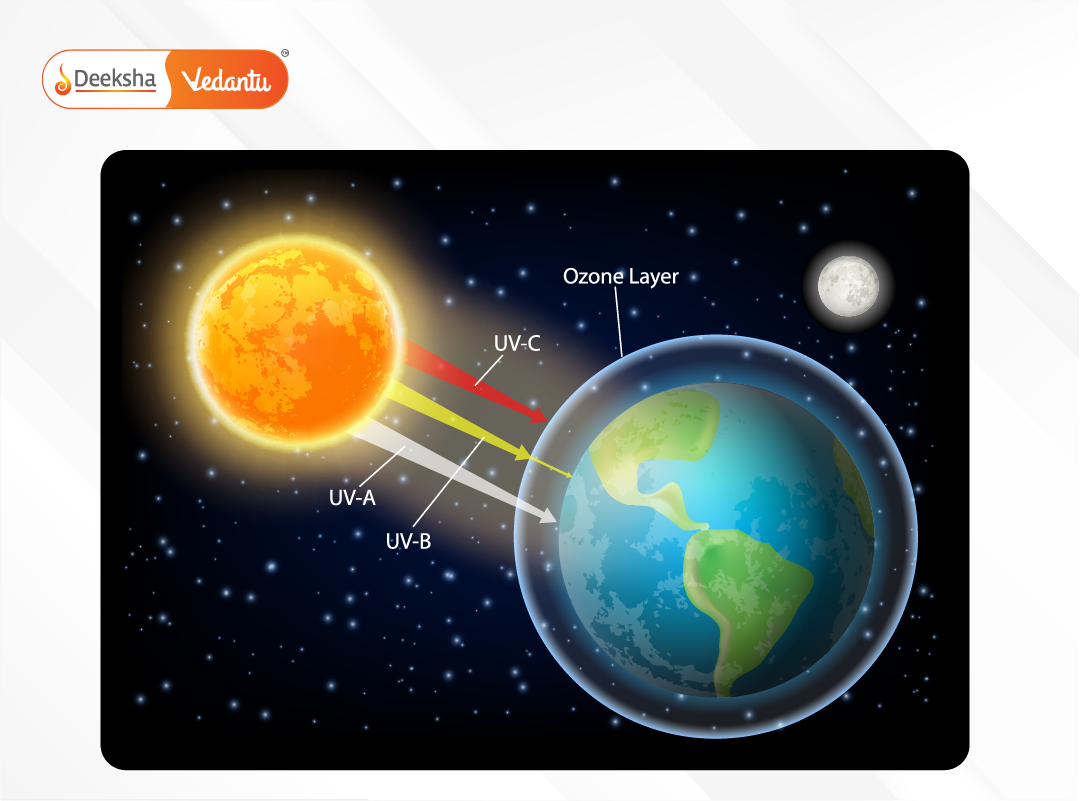
Causes of Depletion:
- Use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in refrigerants and aerosol sprays
- Industrial emissions of halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform
Consequences include:
- Increased cases of skin cancer, eye damage, and immune system disorders
- Adverse effects on marine plankton and aquatic food chains
- Slower growth rates in sensitive crops like wheat and barley
Learn more from our article on Ozone Layer Depletion.
Connection Between Pollution and Global Warming
Pollution and global warming are deeply interconnected. The burning of fossil fuels and industrial emissions release greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) that trap heat in the atmosphere.

Impacts of Global Warming:
- Rise in Earth’s average temperature, causing climate shifts
- Increase in the frequency of floods, droughts, and cyclones
- Loss of biodiversity due to changing habitats
- Melting of polar ice caps leading to rising sea levels
Explore this further in our section on Global Warming.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of pollution?
The primary types of pollution include air, water, soil, noise, light, and thermal pollution. Each affects specific environmental components and requires different control approaches.
2. What are some examples of air pollution control methods?
Effective methods include using public transport, switching to electric vehicles, installing air filters in industries, banning harmful industrial processes, and increasing tree cover in cities.
3. How can we prevent water pollution at home?
Avoid dumping grease, chemicals, and medicine into drains. Use biodegradable cleaning agents and make sure to report any local pollution sources to authorities.
4. What is the role of the ozone layer?
The ozone layer acts as Earth’s sunscreen by filtering out dangerous UV rays. Without it, living beings would be at higher risk of severe health issues, and ecosystems would collapse.
5. How does pollution contribute to global warming?
Air pollution increases greenhouse gas concentrations. These gases trap solar heat in the atmosphere, leading to a gradual rise in global temperatures and changes in weather patterns.
Conclusion
Understanding pollution and its control measures is key to creating a sustainable future. Class 10 students must not only study the types and effects of pollution but also take actionable steps to prevent it. Whether through small actions like reducing plastic use or larger efforts like community cleanups, every initiative matters. By embracing eco-conscious habits, spreading awareness, and supporting global efforts, we can collectively make a positive impact on the planet. Let’s act today to ensure a cleaner, healthier tomorrow for all.







Get Social